 |
PDBsum entry 3i7s

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.4.3.3.7
- 4-hydroxy-tetrahydrodipicolinate synthase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
L-aspartate 4-semialdehyde + pyruvate = (2S,4S)-4-hydroxy-2,3,4,5- tetrahydrodipicolinate + H2O + H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
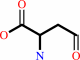 L-aspartate 4-semialdehyde
L-aspartate 4-semialdehyde
|
+
|
pyruvate
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
corresponds exactly
|
=
|
(2S,4S)-4-hydroxy-2,3,4,5- tetrahydrodipicolinate
|
+
|
H2O
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
Biochimie
92:837-845
(2010)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
How essential is the 'essential' active-site lysine in dihydrodipicolinate synthase?
|
|
T.P.Soares da Costa,
A.C.Muscroft-Taylor,
R.C.Dobson,
S.R.Devenish,
G.B.Jameson,
J.A.Gerrard.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Dihydrodipicolinate synthase (DHDPS, E.C. 4.2.1.52), a validated antibiotic
target, catalyses the first committed step in the lysine biosynthetic pathway:
the condensation reaction between (S)-aspartate beta-semialdehyde [(S)-ASA] and
pyruvate via the formation of a Schiff base intermediate between pyruvate and
the absolutely conserved active-site lysine. Escherichia coli DHDPS mutants
K161A and K161R of the active-site lysine were characterised for the first time.
Unexpectedly, the mutant enzymes were still catalytically active, albeit with a
significant decrease in activity. The k(cat) values for DHDPS-K161A and
DHDPS-K161R were 0.06 +/- 0.02 s(-1) and 0.16 +/- 0.06 s(-1) respectively,
compared to 45 +/- 3 s(-1) for the wild-type enzyme. Remarkably, the K(M) values
for pyruvate increased by only 3-fold for DHDPS-K161A and DHDPS-K161R (0.45 +/-
0.04 mM and 0.57 +/- 0.06 mM, compared to 0.15 +/- 0.01 mM for the wild-type
DHDPS), while the K(M) values for (S)-ASA remained the same for DHDPS-K161R
(0.12 +/- 0.01 mM) and increased by only 2-fold for DHDPS-K161A (0.23 +/- 0.02
mM) and the K(i) for lysine was unchanged. The X-ray crystal structures of
DHDPS-K161A and DHDPS-K161R were solved at resolutions of 2.0 and 2.1 A
respectively and showed no changes in their secondary or tertiary structures
when compared to the wild-type structure. The crystal structure of DHDPS-K161A
with pyruvate bound at the active site was solved at a resolution of 2.3 A and
revealed a defined binding pocket for pyruvate that is thus not dependent upon
lysine 161. Taken together with ITC and NMR data, it is concluded that although
lysine 161 is important in the wild-type DHDPS-catalysed reaction, it is not
absolutely essential for catalysis.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

