 |
PDBsum entry 3g8m

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.2.1.2.1
- glycine hydroxymethyltransferase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

Pathway:
|
 |
Folate Coenzymes
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
(6R)-5,10-methylene-5,6,7,8-tetrahydrofolate + glycine + H2O = (6S)- 5,6,7,8-tetrahydrofolate + L-serine
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
(6R)-5,10-methylene-5,6,7,8-tetrahydrofolate
|
+
|
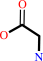 glycine
glycine
|
+
|
H2O
|
=
|
(6S)- 5,6,7,8-tetrahydrofolate
|
+
|
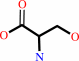 L-serine
L-serine
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Cofactor:
|
 |
Pyridoxal 5'-phosphate
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Pyridoxal 5'-phosphate
Bound ligand (Het Group name =
PLP)
matches with 93.75% similarity
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
Biochemistry
48:12034-12046
(2009)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Role of a conserved active site cation-pi interaction in Escherichia coli serine hydroxymethyltransferase.
|
|
M.Vivoli,
F.Angelucci,
A.Ilari,
V.Morea,
S.Angelaccio,
M.L.di Salvo,
R.Contestabile.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Serine hydroxymethyltransferase is a pyridoxal 5'-phosphate-dependent enzyme
that catalyzes the interconversion of serine and glycine using
tetrahydropteroylglutamate as the one-carbon carrier. In all pyridoxal
phosphate-dependent enzymes, amino acid substrates are bound and released
through a transaldimination process, in which an internal aldimine and an
external aldimine are interconverted via gem-diamine intermediates.
Bioinformatic analyses of serine hydroxymethyltransferase sequences and
structures showed the presence of two highly conserved residues, a tyrosine and
an arginine, engaged in a cation-pi interaction. In Escherichia coli serine
hydroxymethyltranferase, the hydroxyl group of this conserved tyrosine (Tyr55)
is located in a position compatible with a role as hydrogen exchanger in the
transaldimination reaction. Because of the location of Tyr55 at the active site,
the enhancement of its acidic properties caused by the cation-pi interaction
with Arg235, and the hydrogen bonds established by its hydroxyl group, a role of
this residue as acid-base catalyst in the transaldimination process was
envisaged. The role played by this cation-pi interaction in the E. coli serine
hydroxymethyltransferase was investigated by crystallography and site-directed
mutagenesis using Y55F and three R235 mutant forms. The crystal structure of the
Y55F mutant suggests that the presence of Tyr55 is indispensable for a correct
positioning of the cofactor and for the maintenance of the structure of several
loops involved in substrate and cofactor binding. The kinetic properties of all
mutant enzymes are profoundly altered. Substrate binding and rapid kinetic
experiments showed that both Y55 and R235 are required for a correct progress of
the transaldimination reaction.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

