 |
PDBsum entry 3c0p

|
|
|

|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |

|

|

|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
Oxidoreductase
|
PDB id
|
|

|

|
3c0p
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.1.5.99.12
- cytokinin dehydrogenase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
N6-dimethylallyladenine + A + H2O = 3-methyl-2-butenal + adenine + AH2
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
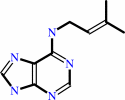 N(6)-dimethylallyladenine
N(6)-dimethylallyladenine
|
+
|
|
+
|
H2O
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 93.33% similarity
|
=
|
3-methyl-2-butenal
|
+
|
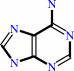 adenine
adenine
|
+
|
AH2
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Cofactor:
|
 |
FAD
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
FAD
Bound ligand (Het Group name =
FAD)
corresponds exactly
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
J Mol Biol
380:886-899
(2008)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Mechanism-based inhibitors of cytokinin oxidase/dehydrogenase attack FAD cofactor.
|
|
D.Kopecný,
M.Sebela,
P.Briozzo,
L.Spíchal,
N.Houba-Hérin,
V.Masek,
N.Joly,
C.Madzak,
P.Anzenbacher,
M.Laloue.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Cytokinin oxidases/dehydrogenases (CKOs) mediate catabolic regulation of
cytokinin levels in plants. Several substrate analogs containing an unsaturated
side chain were studied for their possible inhibitory effect on maize CKO
(ZmCKO1) by use of various bioanalytical methods. Two allenic derivatives,
N(6)-(buta-2,3-dienyl)adenine (HA-8) and N(6)-(penta-2,3-dienyl)adenine (HA-1),
were identified as strong mechanism-based inhibitors of the enzyme. Despite
exhaustive dialysis, the enzyme remained inhibited. Conversely, substrate
analogs with a triple bond in the side chain were much weaker inactivators. The
crystal structures of recombinant ZmCKO1 complexed with HA-1 or HA-8 were solved
to 1.95 A resolution. Together with Raman spectra of the inactivated enzyme, it
was revealed that reactive imine intermediates generated by oxidation of the
allenic inhibitors covalently bind to the flavin adenine dinucleotide (FAD)
cofactor. The binding occurs at the C4a atom of the isoalloxazine ring of FAD,
the planarity of which is consequently disrupted. All the compounds under study
were also analyzed for binding to the Arabidopsis cytokinin receptors AHK3 and
AHK4 in a bacterial receptor assay and for cytokinin activity in the Amaranthus
bioassay. HA-1 and HA-8 were found to be good receptor ligands with a
significant cytokinin activity. Nevertheless, due to their ability to inactivate
CKO in the desired time intervals or developmental stages, they both represent
attractive compounds for physiological studies, as the inhibition mechanism of
HA-1 and HA-8 is mainly FAD dependent.

|

|
|
|

|
| |
Selected figure(s)
|
|

|
| |
 |
 |

|
 |

|
 |
Figure 4.
Fig. 4. Crystal structure of ZmCKO1 inactivated by allenic
cytokinins. (a) Overall surface of the enzyme. β-Strands are
indicated in cyan and α-helices in light blue. FAD cofactor
(yellow), bound HA-1 inhibitor (green) and N-acetyl-glucosamines
(orange) are shown in space-filling CPK representation with
nitrogen atoms in blue and oxygen atoms in red. The five
glycosylated Asn sites are numbered. (b and c) Binding of HA-1
(carbon atoms in green) and HA-8 (carbon atoms in black) in
their 2F[o] − F[c] maps; contoured at 2σ. The new covalent
bond between the C3 atom of the inhibitor side chain and the C4a
atom of FAD is shown in brown. (d) Hydrogen-bonding interactions
of the inhibitor HA-1 at the active site of ZmCKO1. (e) Detail
of the covalent bond between HA-1 inhibitor and FAD cofactor.
|
 |
Figure 6.
Fig. 6. Mechanism of ZmCKO1 inactivation by allenic substrate
analogs. In the first step (reductive half-reaction), the enzyme
reacts with HA-1 or HA-8 and, as a result, the FAD cofactor is
reduced and the corresponding allenic imine intermediate
released. Then the allenic intermediate imine undergoes
hydrolysis to form the corresponding allenic aldehyde and
adenine followed by cofactor reoxidation (route A) or the
strongly electrophilic C3 atom of the allenic imine intermediate
attacks the C4a atom of the reduced cofactor and a covalent
modification of the cofactor occurs (HA–FAD adduct, route B).
|
 |
|
|

|
| |
The above figures are
reprinted
by permission from Elsevier:
J Mol Biol
(2008,
380,
886-899)
copyright 2008.
|
|
| |
Figures were
selected
by an automated process.
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

