 |
PDBsum entry 3ba1

|
|
|

|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |

|

|

|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
Oxidoreductase
|
PDB id
|
|

|

|
3ba1
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.1.1.1.237
- hydroxyphenylpyruvate reductase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
|
1.
|
(2R)-2-hydroxy-3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)propanoate + NADP+ = 3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)pyruvate + NADPH + H+
|
|
2.
|
(2R)-2-hydroxy-3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)propanoate + NAD+ = 3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)pyruvate + NADH + H+
|
|
3.
|
(2R)-3-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)lactate + NAD+ = 3-(3,4- dihydroxyphenyl)pyruvate + NADH + H+
|
|
4.
|
(2R)-3-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)lactate + NADP+ = 3-(3,4- dihydroxyphenyl)pyruvate + NADPH + H+
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
(2R)-2-hydroxy-3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)propanoate
|
+
|
 NADP(+)
NADP(+)
|
=
|
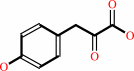 3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)pyruvate
3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)pyruvate
|
+
|
 NADPH
NADPH
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
(2R)-2-hydroxy-3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)propanoate
|
+
|
 NAD(+)
NAD(+)
|
=
|
 3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)pyruvate
3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)pyruvate
|
+
|
 NADH
NADH
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
(2R)-3-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)lactate
|
+
|
 NAD(+)
NAD(+)
|
=
|
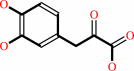 3-(3,4- dihydroxyphenyl)pyruvate
3-(3,4- dihydroxyphenyl)pyruvate
|
+
|
 NADH
NADH
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
(2R)-3-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)lactate
|
+
|
 NADP(+)
NADP(+)
|
=
|
 3-(3,4- dihydroxyphenyl)pyruvate
3-(3,4- dihydroxyphenyl)pyruvate
|
+
|
 NADPH
NADPH
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr
66:593-603
(2010)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Structure and substrate docking of a hydroxy(phenyl)pyruvate reductase from the higher plant Coleus blumei Benth.
|
|
V.Janiak,
M.Petersen,
M.Zentgraf,
G.Klebe,
A.Heine.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Hydroxy(phenyl)pyruvate reductase [H(P)PR] belongs to the family of
D-isomer-specific 2-hydroxyacid dehydrogenases and catalyzes the reduction of
hydroxyphenylpyruvates as well as hydroxypyruvate and pyruvate to the
corresponding lactates. Other non-aromatic substrates are also accepted. NADPH
is the preferred cosubstrate. The crystal structure of the enzyme from Coleus
blumei (Lamiaceae) has been determined at 1.47 A resolution. In addition to the
apoenzyme, the structure of a complex with NADP(+) was determined at a
resolution of 2.2 A. H(P)PR is a dimer with a molecular mass of 34 113 Da per
subunit. The structure is similar to those of other members of the enzyme family
and consists of two domains separated by a deep catalytic cleft. To gain
insights into substrate binding, several compounds were docked into the
cosubstrate complex structure using the program AutoDock. The results show two
possible binding modes with similar docking energy. However, only binding mode A
provides the necessary environment in the active centre for hydride and proton
transfer during reduction, leading to the formation of the (R)-enantiomer of
lactate and/or hydroxyphenyllactate.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

