 |
PDBsum entry 2zr3

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.6.1.1.11
- serine--tRNA ligase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
|
1.
|
tRNA(Ser) + L-serine + ATP = L-seryl-tRNA(Ser) + AMP + diphosphate + H+
|
|
2.
|
tRNA(Sec) + L-serine + ATP = L-seryl-tRNA(Sec) + AMP + diphosphate + H+
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 tRNA(Ser)
tRNA(Ser)
|
+
|
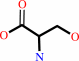 L-serine
L-serine
|
+
|
 ATP
ATP
|
=
|
 L-seryl-tRNA(Ser)
L-seryl-tRNA(Ser)
|
+
|
 AMP
AMP
|
+
|
 diphosphate
diphosphate
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 tRNA(Sec)
tRNA(Sec)
|
+
|
 L-serine
L-serine
|
+
|
 ATP
ATP
|
=
|
 L-seryl-tRNA(Sec)
L-seryl-tRNA(Sec)
|
+
|
 AMP
AMP
|
+
|
 diphosphate
diphosphate
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
Rna Biol
5:169-177
(2008)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Crystallographic and mutational studies of seryl-tRNA synthetase from the archaeon Pyrococcus horikoshii.
|
|
Y.Itoh,
S.Sekine,
C.Kuroishi,
T.Terada,
M.Shirouzu,
S.Kuramitsu,
S.Yokoyama.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Seryl-tRNA synthetase (SerRS) catalyzes the ligation of serine to the 3'-end of
serine tRNA (tRNA(Ser)), which is typical of the type-2 tRNAs characterized by a
long extra arm. The SerRSs are divided into two types, the archaeal/eukaryal and
bacterial types. In this study, we solved the crystal structures of the SerRS
from the archaeon Pyrococcus horikoshii bound with
5'-O-[N-(L-seryl)-sulfamoyl]-adenosine at 2.6 A and with ATP at 2.8 A, as well
as in the apo form at 3.0 A. P. horikoshii SerRS recognizes the seryl and
adenylate moieties in a manner similar to those of the bacterial and
mitochondrial SerRSs from Thermus thermophilus and Bos taurus, respectively, but
different from that of the unusual SerRS from the methanogenic archaeon
Methanosarcina barkeri. P. horikoshii SerRS efficiently aminoacylated not only
P. horikoshii tRNA(Ser) but also bacterial tRNA(Ser)s from T. thermophilus and
Escherichia coli. Models of P. horikoshii SerRS bound with the T. thermophilus
and P. horikoshii tRNA(Ser)s suggested that the helical domain of P. horikoshii
SerRS is involved in the extra arm binding. This region of P. horikoshii SerRS
has additional basic residues as compared with T. thermophilus SerRS, and a Trp
residue specific to the archaeal/eukaryal SerRSs. Mutational analyses revealed
that the basic and Trp residues are important for tRNA aminoacylation. P.
horikoshii SerRS has the archaea-specific insertion, which collaborates with the
core domain to form a basic channel leading to the active site. Two sulfate ions
are bound to the channel, suggesting that the tRNA 3' region might bind to the
channel.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
J.Yuan,
P.O'Donoghue,
A.Ambrogelly,
S.Gundllapalli,
R.Lynn Sherrer,
S.Palioura,
M.Simonović,
and
D.Söll
(2010).
Distinct genetic code expansion strategies for selenocysteine and pyrrolysine are reflected in different aminoacyl-tRNA formation systems.
|
| |
FEBS Lett,
584,
342-349.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.Jaric,
S.Bilokapic,
S.Lesjak,
A.Crnkovic,
N.Ban,
and
I.Weygand-Durasevic
(2009).
Identification of amino acids in the N-terminal domain of atypical methanogenic-type Seryl-tRNA synthetase critical for tRNA recognition.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
284,
30643-30651.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Guo,
Y.E.Chong,
R.Shapiro,
K.Beebe,
X.L.Yang,
and
P.Schimmel
(2009).
Paradox of mistranslation of serine for alanine caused by AlaRS recognition dilemma.
|
| |
Nature,
462,
808-812.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
codes are
shown on the right.
|
 |

