 |
PDBsum entry 2yyi

|
|
|

|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |

|

|

|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
Oxidoreductase
|
PDB id
|
|

|

|
2yyi
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.1.14.14.9
- 4-hydroxyphenylacetate 3-monooxygenase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
4-hydroxyphenylacetate + FADH2 + O2 = 3,4-dihydroxyphenylacetate + FAD + H2O + H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 4-hydroxyphenylacetate
4-hydroxyphenylacetate
|
+
|
FADH2
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
corresponds exactly
|
+
|
 O2
O2
|
=
|
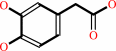 3,4-dihydroxyphenylacetate
3,4-dihydroxyphenylacetate
|
+
|
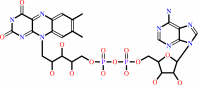 FAD
FAD
|
+
|
H2O
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Cofactor:
|
 |
FAD
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 FAD
FAD
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
J Biol Chem
282:33107-33117
(2007)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Crystal structure of the oxygenase component (HpaB) of the 4-hydroxyphenylacetate 3-monooxygenase from Thermus thermophilus HB8.
|
|
S.H.Kim,
T.Hisano,
K.Takeda,
W.Iwasaki,
A.Ebihara,
K.Miki.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
The 4-hydroxyphenylacetate (4HPA) 3-monooxygenase is involved in the initial
step of the 4HPA degradation pathway and catalyzes 4HPA hydroxylation to
3,4-dihydroxyphenylacetate. This enzyme consists of two components, an oxygenase
(HpaB) and a reductase (HpaC). To understand the structural basis of the
catalytic mechanism of HpaB, crystal structures of HpaB from Thermus
thermophilus HB8 were determined in three states: a ligand-free form, a binary
complex with FAD, and a ternary complex with FAD and 4HPA. Structural analysis
revealed that the binding and dissociation of flavin are accompanied by
conformational changes of the loop between beta5 and beta6 and of the loop
between beta8 and beta9, leading to preformation of part of the
substrate-binding site (Ser-197 and Thr-198). The latter loop further changes
its conformation upon binding of 4HPA and obstructs the active site from the
bulk solvent. Arg-100 is located adjacent to the putative oxygen-binding site
and may be involved in the formation and stabilization of the
C4a-hydroperoxyflavin intermediate.

|

|
|
|

|
| |
Selected figure(s)
|
|

|
| |
 |
 |

|
 |

|
 |
Figure 1.
FIGURE 1. A, crystal structure of HpaB homotetramer (the
unliganded form). Each monomer is shown in a different color. B,
a stereo view of the structure of HpaB monomer (the unliganded
form). The N-terminal domain (Ala-2—Leu-138), the middle
domain (Ala-139—Gly-266), the C-terminal domain
(Asn-267—Tyr-456), and the  -helical tail
(Asn-457—Ala-481) are shown in yellow, cyan, orange, and
magenta, respectively. The secondary structure elements are
labeled. All figures were generated using the PyMOL program. -helical tail
(Asn-457—Ala-481) are shown in yellow, cyan, orange, and
magenta, respectively. The secondary structure elements are
labeled. All figures were generated using the PyMOL program.
|
 |
Figure 7.
FIGURE 7. A proposed catalytic mechanism of HpaB. (i) HpaB
binds reduced FAD (FADH[2]), which is supplied from HpaC. (ii)
FADH[2] reacts with an oxygen molecule and forms the
C4a-hydroperoxyflavin intermediate. (iii) Substrate binds to the
enzyme-C4a-hydroperoxyflavin complex. A hydroxyl group of the
C4a-hydroperoxyflavin intermediate is introduced into the ortho
position on the aromatic ring by electrophilic attack. (iv and
v) The dienone form of the product is rearomatized, and DHPA and
C4a-hydroxyflavin are formed. (vi) DHPA is released from the
enzyme. (vii) Water is eliminated from the C4a-hydroxyflavin.
(viii) Oxidized FAD is released from the enzyme and recycled to
HpaC to be reduced for the next catalytic cycle.
|
 |
|
|

|
| |
The above figures are
reprinted
by permission from the ASBMB:
J Biol Chem
(2007,
282,
33107-33117)
copyright 2007.
|
|
| |
Figures were
selected
by an automated process.
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
B.N.Webb,
J.W.Ballinger,
E.Kim,
S.M.Belchik,
K.S.Lam,
B.Youn,
M.S.Nissen,
L.Xun,
and
C.Kang
(2010).
Characterization of chlorophenol 4-monooxygenase (TftD) and NADH:FAD oxidoreductase (TftC) of Burkholderia cepacia AC1100.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
285,
2014-2027.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Chakraborty,
M.Ortiz-Maldonado,
B.Entsch,
and
D.P.Ballou
(2010).
Studies on the mechanism of p-hydroxyphenylacetate 3-hydroxylase from Pseudomonas aeruginosa: a system composed of a small flavin reductase and a large flavin-dependent oxygenase.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
49,
372-385.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
U.E.Ukaegbu,
A.Kantz,
M.Beaton,
G.T.Gassner,
and
A.C.Rosenzweig
(2010).
Structure and ligand binding properties of the epoxidase component of styrene monooxygenase .
|
| |
Biochemistry,
49,
1678-1688.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Takeo,
M.Murakami,
S.Niihara,
K.Yamamoto,
M.Nishimura,
D.Kato,
and
S.Negoro
(2008).
Mechanism of 4-nitrophenol oxidation in Rhodococcus sp. Strain PN1: characterization of the two-component 4-nitrophenol hydroxylase and regulation of its expression.
|
| |
J Bacteriol,
190,
7367-7374.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
codes are
shown on the right.
|
 |

