 |
PDBsum entry 2x2c

|
|
|

|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |

|

|

|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
Isomerase/immunosuppressant
|
PDB id
|
|

|

|
2x2c
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Isomerase/immunosuppressant
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
Acetyl-cypa:cyclosporine complex
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
Cyclosporin a. Chain: b, f, l, p, r. Synonym: ciclosporin, ciclosporine. Engineered: yes. Peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase a. Chain: k, m, o, q, s. Synonym: ppiase a, rotamase a, cyclophilin a, cyclosporin a-binding protein, cypa. Engineered: yes
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Synthetic: yes. Tolypocladium inflatum. Organism_taxid: 29910. Homo sapiens. Human. Organism_taxid: 9606. Expressed in: escherichia coli. Expression_system_taxid: 562
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
2.41Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.209
|
R-free:
|
0.264
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
M.Lammers,H.Neumann,J.W.Chin,L.C.James
|
|
Key ref:
|
 |
M.Lammers
et al.
(2010).
Acetylation regulates cyclophilin A catalysis, immunosuppression and HIV isomerization.
Nat Chem Biol,
6,
331-337.
PubMed id:
|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
12-Jan-10
|
Release date:
|
23-Mar-10
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
Chains K, M, O, Q, S:
E.C.5.2.1.8
- peptidylprolyl isomerase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
[protein]-peptidylproline (omega=180) = [protein]-peptidylproline (omega=0)
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
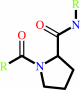 Peptidylproline (omega=180)
Peptidylproline (omega=180)
|
=
|
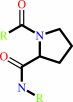 peptidylproline (omega=0)
peptidylproline (omega=0)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
Nat Chem Biol
6:331-337
(2010)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Acetylation regulates cyclophilin A catalysis, immunosuppression and HIV isomerization.
|
|
M.Lammers,
H.Neumann,
J.W.Chin,
L.C.James.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Cyclophilin A (CypA) is a ubiquitous cis-trans prolyl isomerase with key roles
in immunity and viral infection. CypA suppresses T-cell activation through
cyclosporine complexation and is required for effective HIV-1 replication in
host cells. We show that CypA is acetylated in diverse human cell lines and use
a synthetically evolved acetyllysyl-tRNA synthetase/tRNA(CUA) pair to produce
recombinant acetylated CypA in Escherichia coli. We determined atomic-resolution
structures of acetylated CypA and its complexes with cyclosporine and HIV-1
capsid. Acetylation markedly inhibited CypA catalysis of cis to trans
isomerization and stabilized cis rather than trans forms of the HIV-1 capsid.
Furthermore, CypA acetylation antagonized the immunosuppressive effects of
cyclosporine by inhibiting the sequential steps of cyclosporine binding and
calcineurin inhibition. Our results reveal that acetylation regulates key
functions of CypA in immunity and viral infection and provide a general set of
mechanisms by which acetylation modulates interactions to regulate cell function.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|

