 |
PDBsum entry 2x1c

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Transferase
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
The crystal structure of precursor acyl coenzyme a:isopenicillin n acyltransferase from penicillium chrysogenum
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
Acyl-coenzyme. Chain: a, b, c, d. Synonym: isopenicillin-n n-acyltransferase, acyl-coenzyme a\:6- aminopenicillanic-acid-acyltransferase 11 kda subunit, acyl-coenzyme a\:6-aminopenicillanic-acid-acyltransferase 29 kda subunit. Engineered: yes. Mutation: yes
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Penicillium chrysogenum. Organism_taxid: 5076. Strain: as-p-78. Expressed in: escherichia coli. Expression_system_taxid: 562.
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
1.85Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.170
|
R-free:
|
0.193
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
M.Bokhove,H.Yoshida,C.M.H.Hensgens,J.M.Van Der Laan,J.D.Sutherland, B.W.Dijkstra
|
|
Key ref:
|
 |
M.Bokhove
et al.
(2010).
Structures of an isopenicillin N converting Ntn-hydrolase reveal different catalytic roles for the active site residues of precursor and mature enzyme.
Structure,
18,
301-308.
PubMed id:
|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
23-Dec-09
|
Release date:
|
09-Mar-10
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
P15802
(AATA_PENCH) -
Isopenicillin-N N-acyltransferase from Penicillium chrysogenum
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
357 a.a.
355 a.a.*
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|
|
Key: |
 |
PfamA domain |
 |
 |
 |
Secondary structure |
 |
 |
CATH domain |
 |
|
*
PDB and UniProt seqs differ
at 1 residue position (black
cross)
|
|

|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.2.3.1.164
- isopenicillin-N N-acyltransferase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

Pathway:
|
 |
Penicillin Biosynthesis and Metabolism
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
isopenicillin N + phenylacetyl-CoA + H2O = penicillin G + L-2- aminoadipate + CoA + H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
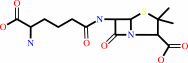 isopenicillin N
isopenicillin N
|
+
|
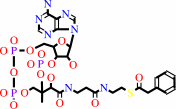 phenylacetyl-CoA
phenylacetyl-CoA
|
+
|
H2O
|
=
|
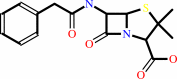 penicillin G
penicillin G
|
+
|
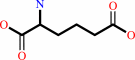 L-2- aminoadipate
L-2- aminoadipate
|
+
|
 CoA
CoA
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
Structure
18:301-308
(2010)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Structures of an isopenicillin N converting Ntn-hydrolase reveal different catalytic roles for the active site residues of precursor and mature enzyme.
|
|
M.Bokhove,
H.Yoshida,
C.M.Hensgens,
J.M.van der Laan,
J.D.Sutherland,
B.W.Dijkstra.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Penicillium chrysogenum Acyl coenzyme A:isopenicillin N acyltransferase (AT)
performs the last step in the biosynthesis of hydrophobic penicillins,
exchanging the hydrophilic side chain of a precursor for various hydrophobic
side chains. Like other N-terminal nucleophile hydrolases AT is produced as an
inactive precursor that matures upon posttranslational cleavage. The structure
of a Cys103Ala precursor mutant shows that maturation is autoproteolytic,
initiated by Cys103 cleaving its preceding peptide bond. The crystal structure
of the mature enzyme shows that after autoproteolysis residues 92-102 fold
outwards, exposing a buried pocket. This pocket is structurally and chemically
flexible and can accommodate substrates of different size and polarity. Modeling
of a substrate-bound state indicates the residues important for catalysis.
Comparison of the proposed autoproteolytic and substrate hydrolysis mechanisms
shows that in both events the same catalytic residues are used, but that they
perform different roles in catalysis.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

