 |
PDBsum entry 2wnh

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.3.1.3.8
- 3-phytase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
1D-myo-inositol hexakisphosphate + H2O = 1D-myo-inositol 1,2,4,5,6- pentakisphosphate + phosphate
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
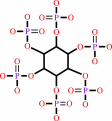 1D-myo-inositol hexakisphosphate
1D-myo-inositol hexakisphosphate
|
+
|
H2O
|
=
|
1D-myo-inositol 1,2,4,5,6- pentakisphosphate
|
+
|
 phosphate
phosphate
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
Febs J
277:1284-1296
(2010)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Crystal structure of Klebsiella sp. ASR1 phytase suggests substrate binding to a preformed active site that meets the requirements of a plant rhizosphere enzyme.
|
|
K.Böhm,
T.Herter,
J.J.Müller,
R.Borriss,
U.Heinemann.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
The extracellular phytase of the plant-associated Klebsiella sp. ASR1 is a
member of the histidine-acid-phosphatase family and acts primarily as a
scavenger of phosphate groups locked in the phytic acid molecule. The Klebsiella
enzyme is distinguished from the Escherichia coli phytase AppA by its sequence
and phytate degradation pathway. The crystal structure of the phytase from
Klebsiella sp. ASR1 has been determined to 1.7 A resolution using
single-wavelength anomalous-diffraction phasing. Despite low sequence
similarity, the overall structure of Klebsiella phytase bears similarity to
other histidine-acid phosphatases, such as E. coli phytase,
glucose-1-phosphatase and human prostatic-acid phosphatase. The polypeptide
chain is organized into an alpha and an alpha/beta domain, and the active site
is located in a positively charged cleft between the domains. Three sulfate ions
bound to the catalytic pocket of an inactive mutant suggest a unique binding
mode for its substrate phytate. Even in the absence of substrate, the Klebsiella
phytase is closer in structure to the E. coli phytase AppA in its
substrate-bound form than to phytate-free AppA. This is taken to suggest a
preformed substrate-binding site in Klebsiella phytase. Differences in habitat
and substrate availability thus gave rise to enzymes with different
substrate-binding modes, specificities and kinetics.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
A.V.Shivange,
U.Schwaneberg,
and
D.Roccatano
(2010).
Conformational dynamics of active site loop in Escherichia coli phytase.
|
| |
Biopolymers,
93,
994.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
|
 |

