 |
PDBsum entry 2vcm

|
|
|

|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |

|

|

|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
Oxidoreductase
|
PDB id
|
|

|

|
2vcm
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.1.21.3.1
- isopenicillin-N synthase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

Pathway:
|
 |
Penicillin N and Deacetoxycephalosporin C Biosynthesis
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
N-[(5S)-5-amino-5-carboxypentanoyl]-L-cysteinyl-D-valine + O2 = isopenicillin N + 2 H2O
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
N-[(5S)-5-amino-5-carboxypentanoyl]-L-cysteinyl-D-valine
|
+
|
 O2
O2
|
=
|
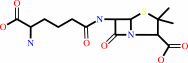 isopenicillin N
isopenicillin N
|
+
|
2
×
H2O
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 48.48% similarity
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
Chembiochem
10:2025-2031
(2009)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Structural studies on the reaction of isopenicillin N synthase with a sterically demanding depsipeptide substrate analogue.
|
|
W.Ge,
I.J.Clifton,
A.R.Howard-Jones,
J.E.Stok,
R.M.Adlington,
J.E.Baldwin,
P.J.Rutledge.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Isopenicillin N synthase (IPNS) is a nonheme iron(II)-dependent oxidase that
catalyses the central step in penicillin biosynthesis, conversion of the
tripeptide delta-L-alpha-aminoadipoyl-L-cysteinyl-D-valine (ACV) to
isopenicillin N (IPN). This report describes mechanistic studies using the
analogue delta-(L-alpha-aminoadipoyl)-(3S-methyl)-L-cysteine
D-alpha-hydroxyisovaleryl ester (A(S)mCOV), designed to intercept the catalytic
cycle at an early stage. A(S)mCOV incorporates two modifications from the
natural substrate: the second and third residues are joined by an ester, so this
analogue lacks the key amide of ACV and cannot form a beta-lactam; and the
cysteinyl residue is substituted at its beta-carbon, bearing a (3S)-methyl
group. It was anticipated that this methyl group will impinge directly on the
site in which the co-substrate dioxygen binds. The novel depsipeptide A(S)mCOV
was prepared in 13 steps and crystallised with IPNS anaerobically. The 1.65 A
structure of the IPNS-Fe(II)-A(S)mCOV complex reveals that the additional
beta-methyl group is not oriented directly into the oxygen binding site, but
does increase steric demand in the active site and increases disorder in the
position of the isovaleryl side chain. Crystals of IPNS-Fe(II)-A(S)mCOV were
incubated with high-pressure oxygen gas, driving substrate turnover to a single
product, an ene-thiol/C-hydroxylated depsipeptide. A mechanism is proposed for
the reaction of A(S)mCOV with IPNS, linking this result to previous
crystallographic studies with related depsipeptides and solution-phase
experiments with cysteine-methylated tripeptides. This result demonstrates that
a (3S)-methyl group at the substrate cysteinyl beta-carbon is not in itself a
block to IPNS activity as previously proposed, and sheds further light on the
steric complexities of IPNS catalysis.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

