 |
PDBsum entry 2vcl

|
|
|

|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |

|

|

|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
Oxidoreductase
|
PDB id
|
|

|

|
2vcl
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.1.3.7.6
- phycoerythrobilin synthase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
(3Z)-phycoerythrobilin + 2 oxidized 2[4Fe-4S]-[ferredoxin] = biliverdin IXalpha + 2 reduced 2[4Fe-4S]-[ferredoxin] + 4 H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
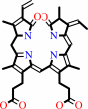 (3Z)-phycoerythrobilin
(3Z)-phycoerythrobilin
|
+
|
2
×
oxidized 2[4Fe-4S]-[ferredoxin]
|
=
|
biliverdin IXalpha
|
+
|
2
×
reduced 2[4Fe-4S]-[ferredoxin]
|
+
|
4
×
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
J Biol Chem
283:27547-27554
(2008)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Phycoerythrobilin Synthase (PebS) of a Marine Virus: CRYSTAL STRUCTURES OF THE BILIVERDIN COMPLEX AND THE SUBSTRATE-FREE FORM.
|
|
T.Dammeyer,
E.Hofmann,
N.Frankenberg-Dinkel.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
The reddish purple open chain tetrapyrrole pigment phycoerythrobilin (PEB;
A(lambdamax) approximately 550 nm) is an essential chromophore of the
light-harvesting phycobiliproteins of most cyanobacteria, red algae, and
cryptomonads. The enzyme phycoerythrobilin synthase (PebS), recently discovered
in a marine virus infecting oceanic cyanobacteria of the genus Prochlorococcus
(cyanophage PSSM-2), is a new member of the ferredoxin-dependent bilin reductase
(FDBR) family. In a formal four-electron reduction, the substrate biliverdin
IXalpha is reduced to yield 3Z-PEB, a reaction that commonly requires the action
of two individual FDBRs. The first reaction catalyzed by PebS is the reduction
of the 15,16-methine bridge of the biliverdin IXalpha tetrapyrrole system. This
reaction is exclusive to PEB biosynthetic enzymes. The second reduction site is
the A-ring 2,3,3(1),3(2)-diene system, the most common target of FDBRs. Here, we
present the first crystal structures of a PEB biosynthetic enzyme. Structures of
the substrate complex were solved at 1.8- and 2.1-A resolution and of the
substrate-free form at 1.55-A resolution. The overall folding revealed an
alpha/beta/alpha-sandwich with similarity to the structure of
phycocyanobilin:ferredoxin oxidoreductase (PcyA). The substrate-binding site is
located between the central beta-sheet and C-terminal alpha-helices. Eight
refined molecules with bound substrate, from two different crystal forms,
revealed a high flexibility of the substrate-binding pocket. The substrate was
found to be either in a planar porphyrin-like conformation or in a helical
conformation and is coordinated by a conserved aspartate/asparagine pair from
the beta-sheet side. From the alpha-helix side, a conserved highly flexible
aspartate/proline pair is involved in substrate binding and presumably catalysis.

|

|
|
|

|
| |
Selected figure(s)
|
|

|
| |
 |
 |

|
 |

|
 |
Figure 1.
FIGURE 1. Biosynthesis of PEB and PCB. PEB biosynthesis
proceeds via two different pathways. PebA and PebB catalyze
consecutive two-electron reductions of BV and 15,16-DHBV to
yield PEB. PebS catalyzes the four-electron reduction of BV to
PEB via the two-electron reduced intermediate 15,16-DHBV. PcyA
catalyzes a four-electron reduction of biliverdin IX  to PCB
via the intermediate 18^1,18^2-DHBV. The electrons for all
reactions come from reduced [2Fe-2S] ferredoxin (Fd[red]). The
carbons of the respective reduction sites are numbered. Fd[ox],
oxidized ferredoxin; P, propionate side chain. to PCB
via the intermediate 18^1,18^2-DHBV. The electrons for all
reactions come from reduced [2Fe-2S] ferredoxin (Fd[red]). The
carbons of the respective reduction sites are numbered. Fd[ox],
oxidized ferredoxin; P, propionate side chain.
|
 |
Figure 3.
FIGURE 3. Stereoview of protein conformations observed in
the crystal structures of PebS. Shown are C-  traces of the
superposed monomers of SePebS without substrate (gray),
SePebS-BV with bound substrate (red; chains A–D), and
wild-type PebS-BV with bound substrate (blue; chains A–D).
Residue numbers are added in regular intervals. traces of the
superposed monomers of SePebS without substrate (gray),
SePebS-BV with bound substrate (red; chains A–D), and
wild-type PebS-BV with bound substrate (blue; chains A–D).
Residue numbers are added in regular intervals.
|
 |
|
|

|
| |
The above figures are
reprinted
by permission from the ASBMB:
J Biol Chem
(2008,
283,
27547-27554)
copyright 2008.
|
|
| |
Figures were
selected
by an automated process.
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
A.W.Busch,
E.J.Reijerse,
W.Lubitz,
E.Hofmann,
and
N.Frankenberg-Dinkel
(2011).
Radical mechanism of cyanophage phycoerythrobilin synthase (PebS).
|
| |
Biochem J,
433,
469-476.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
M.E.Auldridge,
and
K.T.Forest
(2011).
Bacterial phytochromes: more than meets the light.
|
| |
Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol,
46,
67-88.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Kamio,
L.Nguyen,
S.Yaldiz,
and
C.D.Derby
(2010).
How to produce a chemical defense: structural elucidation and anatomical distribution of aplysioviolin and phycoerythrobilin in the sea hare Aplysia californica.
|
| |
Chem Biodivers,
7,
1183-1197.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
Y.Hagiwara,
M.Sugishima,
H.Khawn,
H.Kinoshita,
K.Inomata,
L.Shang,
J.C.Lagarias,
Y.Takahashi,
and
K.Fukuyama
(2010).
Structural insights into vinyl reduction regiospecificity of phycocyanobilin:ferredoxin oxidoreductase (PcyA).
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
285,
1000-1007.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Stoll,
A.Gunn,
M.Brynda,
W.Sughrue,
A.C.Kohler,
A.Ozarowski,
A.J.Fisher,
J.C.Lagarias,
and
R.D.Britt
(2009).
Structure of the biliverdin radical intermediate in phycocyanobilin:ferredoxin oxidoreductase identified by high-field EPR and DFT.
|
| |
J Am Chem Soc,
131,
1986-1995.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
codes are
shown on the right.
|
 |

