
|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|





 (+ 0 more)
284 a.a.
(+ 0 more)
284 a.a.
|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|





 (+ 0 more)
111 a.a.
(+ 0 more)
111 a.a.
|
 |

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Transcription
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
Controlling the storage of nitrogen as arginine: the complex of pii and acetylglutamate kinase from synechococcus elongatus pcc 7942
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
Acetylglutamate kinase. Chain: a, b, c, d, e, f. Synonym: NAG kinase, agk, n-acetyl-l-glutamate 5-phosphotransferase. Engineered: yes. Nitrogen regulatory protein p-ii. Chain: g, h, i, j, k, l. Synonym: pii protein, pii signal transducing protein. Engineered: yes
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Synechococcus elongatus. Organism_taxid: 1140. Strain: pcc 7942. Expressed in: escherichia coli. Expression_system_taxid: 511693.
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
2.75Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.202
|
R-free:
|
0.236
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
J.L.Llacer,C.Marco-Marin,F.Gil-Ortiz,I.Fita,V.Rubio
|
Key ref:

|
 |
J.L.Llácer
et al.
(2007).
The crystal structure of the complex of PII and acetylglutamate kinase reveals how PII controls the storage of nitrogen as arginine.
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
104,
17644-17649.
PubMed id:
DOI:

|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
04-Jul-07
|
Release date:
|
16-Oct-07
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
Chains A, B, C, D, E, F:
E.C.2.7.2.8
- acetylglutamate kinase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

Pathway:
|
 |
Ornithine Biosynthesis
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
N-acetyl-L-glutamate + ATP = N-acetyl-L-glutamyl 5-phosphate + ADP
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
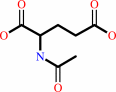 N-acetyl-L-glutamate
N-acetyl-L-glutamate
|
+
|
ATP
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
corresponds exactly
|
=
|
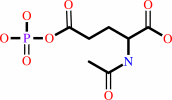 N-acetyl-L-glutamyl 5-phosphate
N-acetyl-L-glutamyl 5-phosphate
|
+
|
 ADP
ADP
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A
104:17644-17649
(2007)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
The crystal structure of the complex of PII and acetylglutamate kinase reveals how PII controls the storage of nitrogen as arginine.
|
|
J.L.Llácer,
A.Contreras,
K.Forchhammer,
C.Marco-Marín,
F.Gil-Ortiz,
R.Maldonado,
I.Fita,
V.Rubio.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Photosynthetic organisms can store nitrogen by synthesizing arginine, and,
therefore, feedback inhibition of arginine synthesis must be relieved in these
organisms when nitrogen is abundant. This relief is accomplished by the binding
of the PII signal transduction protein to acetylglutamate kinase (NAGK), the
controlling enzyme of arginine synthesis. Here, we describe the crystal
structure of the complex between NAGK and PII of Synechococcus elongatus, at
2.75-A resolution. We prove the physiological relevance of the observed
interactions by site-directed mutagenesis and functional studies. The complex
consists of two polar PII trimers sandwiching one ring-like hexameric NAGK (a
trimer of dimers) with the threefold axes of these molecules aligned. The
binding of PII favors a narrow ring conformation of the NAGK hexamer that is
associated with arginine sites having low affinity for this inhibitor. Each PII
subunit contacts one NAGK subunit only. The contacts map in the inner
circumference of the NAGK ring and involve two surfaces of the PII subunit. One
surface is on the PII body and interacts with the C-domain of the NAGK subunit,
helping widen the arginine site found on the other side of this domain. The
other surface is at the distal region of a protruding large loop (T-loop) that
presents a novel compact shape. This loop is inserted in the interdomain crevice
of the NAGK subunit, contacting mainly the N-domain, and playing key roles in
anchoring PII on NAGK, in activating NAGK, and in complex formation regulation
by MgATP, ADP, 2-oxoglutarate, and by phosphorylation of serine-49.

|

|
|
|

|
| |
Selected figure(s)
|
|

|
| |
 |
 |

|
 |

|
 |
Figure 1.
Fig. 1. P[II]–NAGK complex. NAGK, P[II], and NAG are
shown as surface, ribbons, and spheres, respectively. NAGK
dimers and P[II] subunits are colored independently. Views are
along the threefold axis (A) or the twofold axis (B).
|
 |
Figure 2.
Fig. 2. P[II] subunit–NAGK subunit contacts. P[II], NAGK,
and NAG are shown as strings, ribbons, and spheres,
respectively. The contacting parts of the T-loop, B-loop, and
 1– 1–
 1
connection, including some interacting side chains (in sticks),
are blue, red, and green, respectively. The surfaces provided by
these elements form meshworks of the same colors. The NAGK
central 1
connection, including some interacting side chains (in sticks),
are blue, red, and green, respectively. The surfaces provided by
these elements form meshworks of the same colors. The NAGK
central  -sheet is green, and
other -sheet is green, and
other  -strands and the -strands and the  -helices
are brownish and grayish for N- and C-domains, respectively.
Some NAGK elements and P[II] residues are labeled. (Inset)
Structure of bound NAG, encased within its electron density omit
map contoured at 2.5 -helices
are brownish and grayish for N- and C-domains, respectively.
Some NAGK elements and P[II] residues are labeled. (Inset)
Structure of bound NAG, encased within its electron density omit
map contoured at 2.5  . .
|
 |
|
|
| |
Figures were
selected
by an automated process.
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
M.Radchenko,
and
M.Merrick
(2011).
The role of effector molecules in signal transduction by PII proteins.
|
| |
Biochem Soc Trans,
39,
189-194.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.B.Feria Bourrellier,
B.Valot,
A.Guillot,
F.Ambard-Bretteville,
J.Vidal,
and
M.Hodges
(2010).
Chloroplast acetyl-CoA carboxylase activity is 2-oxoglutarate-regulated by interaction of PII with the biotin carboxyl carrier subunit.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
107,
502-507.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.Bandyopadhyay,
A.Arora,
S.Jain,
A.Laskar,
C.Mandal,
V.A.Ivanisenko,
E.S.Fomin,
S.S.Pintus,
N.A.Kolchanov,
S.Maiti,
and
S.Ramachandran
(2010).
Expression and molecular characterization of the Mycobacterium tuberculosis PII protein.
|
| |
J Biochem,
147,
279-289.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.Espinosa,
M.A.Castells,
K.B.Laichoubi,
K.Forchhammer,
and
A.Contreras
(2010).
Effects of spontaneous mutations in PipX functions and regulatory complexes on the cyanobacterium Synechococcus elongatus strain PCC 7942.
|
| |
Microbiology,
156,
1517-1526.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.L.Llácer,
J.Espinosa,
M.A.Castells,
A.Contreras,
K.Forchhammer,
and
V.Rubio
(2010).
Structural basis for the regulation of NtcA-dependent transcription by proteins PipX and PII.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
107,
15397-15402.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
N.D.Shetty,
M.C.Reddy,
S.K.Palaninathan,
J.L.Owen,
and
J.C.Sacchettini
(2010).
Crystal structures of the apo and ATP bound Mycobacterium tuberculosis nitrogen regulatory PII protein.
|
| |
Protein Sci,
19,
1513-1524.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
O.Fokina,
V.R.Chellamuthu,
K.Forchhammer,
and
K.Zeth
(2010).
Mechanism of 2-oxoglutarate signaling by the Synechococcus elongatus PII signal transduction protein.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
107,
19760-19765.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
J.Espinosa,
M.A.Castells,
K.B.Laichoubi,
and
A.Contreras
(2009).
Mutations at pipX suppress lethality of PII-deficient mutants of Synechococcus elongatus PCC 7942.
|
| |
J Bacteriol,
191,
4863-4869.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.Paz-Yepes,
E.Flores,
and
A.Herrero
(2009).
Expression and mutational analysis of the glnB genomic region in the heterocyst-forming Cyanobacterium Anabaena sp. strain PCC 7120.
|
| |
J Bacteriol,
191,
2353-2361.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
L.F.Huergo,
M.Merrick,
R.A.Monteiro,
L.S.Chubatsu,
M.B.Steffens,
F.O.Pedrosa,
and
E.M.Souza
(2009).
In vitro interactions between the PII proteins and the nitrogenase regulatory enzymes dinitrogenase reductase ADP-ribosyltransferase (DraT) and dinitrogenase reductase-activating glycohydrolase (DraG) in Azospirillum brasilense.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
284,
6674-6682.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
B.Bagautdinov,
Y.Matsuura,
S.Bagautdinova,
N.Kunishima,
and
K.Yutani
(2008).
Structure of putative CutA1 from Homo sapiens determined at 2.05 A resolution.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun,
64,
351-357.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
J.L.Llácer,
I.Fita,
and
V.Rubio
(2008).
Arginine and nitrogen storage.
|
| |
Curr Opin Struct Biol,
18,
673-681.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.L.Fernández-Murga,
and
V.Rubio
(2008).
Basis of arginine sensitivity of microbial N-acetyl-L-glutamate kinases: mutagenesis and protein engineering study with the Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Escherichia coli enzymes.
|
| |
J Bacteriol,
190,
3018-3025.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
codes are
shown on the right.
|
 |

