 |
PDBsum entry 2qx9

|
|
|

|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |

|

|

|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
Oxidoreductase
|
PDB id
|
|

|

|
2qx9
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Oxidoreductase
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
Crystal structure of quinone reductase ii
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
Ribosyldihydronicotinamide dehydrogenase [quinone]. Chain: a, b. Synonym: nrh dehydrogenase [quinone] 2, quinone reductase 2, qr2, nrh:quinone oxidoreductase 2. Engineered: yes
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Homo sapiens. Human. Gene: nqo2, nmor2. Expressed in: escherichia coli.
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
2.31Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.213
|
R-free:
|
0.286
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
B.Calamini,B.D.Santarsiero,J.A.Boutin,A.D.Mesecar
|
|
Key ref:
|
 |
B.Calamini
et al.
(2008).
Kinetic, thermodynamic and X-ray structural insights into the interaction of melatonin and analogues with quinone reductase 2.
Biochem J,
413,
81-91.
PubMed id:
|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
10-Aug-07
|
Release date:
|
02-Sep-08
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
P16083
(NQO2_HUMAN) -
Ribosyldihydronicotinamide dehydrogenase [quinone] from Homo sapiens
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
231 a.a.
230 a.a.*
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|
|
Key: |
 |
PfamA domain |
 |
 |
 |
Secondary structure |
 |
 |
CATH domain |
 |
|
*
PDB and UniProt seqs differ
at 1 residue position (black
cross)
|
|

|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.1.10.5.1
- ribosyldihydronicotinamide dehydrogenase (quinone).
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
1-(beta-D-ribofuranosyl)-1,4-dihydronicotinamide + a quinone + H+ = beta-nicotinamide D-riboside + a quinol
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
1-(beta-D-ribofuranosyl)-1,4-dihydronicotinamide
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 44.00% similarity
|
+
|
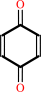 quinone
quinone
|
+
|
H(+)
|
=
|
beta-nicotinamide D-riboside
|
+
|
quinol
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Cofactor:
|
 |
FAD; Zn(2+)
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
FAD
Bound ligand (Het Group name =
FAD)
corresponds exactly
|
Zn(2+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
Biochem J
413:81-91
(2008)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Kinetic, thermodynamic and X-ray structural insights into the interaction of melatonin and analogues with quinone reductase 2.
|
|
B.Calamini,
B.D.Santarsiero,
J.A.Boutin,
A.D.Mesecar.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Melatonin exerts its biological effects through at least two transmembrane
G-protein-coupled receptors, MT1 and MT2, and a lower-affinity cytosolic binding
site, designated MT3. MT3 has recently been identified as QR2 (quinone reductase
2) (EC 1.10.99.2) which is of significance since it links the antioxidant
effects of melatonin to a mechanism of action. Initially, QR2 was believed to
function analogously to QR1 in protecting cells from highly reactive quinones.
However, recent studies indicate that QR2 may actually transform certain quinone
substrates into more highly reactive compounds capable of causing cellular
damage. Therefore it is hypothesized that inhibition of QR2 in certain cases may
lead to protection of cells against these highly reactive species. Since
melatonin is known to inhibit QR2 activity, but its binding site and mode of
inhibition are not known, we determined the mechanism of inhibition of QR2 by
melatonin and a series of melatonin and 5-hydroxytryptamine (serotonin)
analogues, and we determined the X-ray structures of melatonin and
2-iodomelatonin in complex with QR2 to between 1.5 and 1.8 A (1 A=0.1 nm)
resolution. Finally, the thermodynamic binding constants for melatonin and
2-iodomelatonin were determined by ITC (isothermal titration calorimetry). The
kinetic results indicate that melatonin is a competitive inhibitor against
N-methyldihydronicotinamide (K(i)=7.2 microM) and uncompetitive against
menadione (K(i)=92 microM), and the X-ray structures shows that melatonin binds
in multiple orientations within the active sites of the QR2 dimer as opposed to
an allosteric site. These results provide new insights into the binding
mechanisms of melatonin and analogues to QR2.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
V.Leclerc,
M.Ettaoussi,
M.Rami,
A.Farce,
J.A.Boutin,
P.Delagrange,
D.H.Caignard,
P.Renard,
P.Berthelot,
and
S.Yous
(2011).
Design and synthesis of naphthalenic derivatives as new ligands at the melatonin binding site MT3.
|
| |
Eur J Med Chem,
46,
1622-1629.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
G.F.Oxenkrug,
S.O.Bachurin,
I.V.Prakhie,
and
N.S.Zefirov
(2010).
Quinone reductase 2 and antidepressant effect of melatonin derivatives.
|
| |
Ann N Y Acad Sci,
1199,
121-124.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.H.Yang,
T.P.Kondratyuk,
L.E.Marler,
X.Qiu,
Y.Choi,
H.Cao,
R.Yu,
M.Sturdy,
S.Pegan,
Y.Liu,
L.Q.Wang,
A.D.Mesecar,
R.B.Van Breemen,
J.M.Pezzuto,
H.H.Fong,
Y.G.Chen,
and
H.J.Zhang
(2010).
Isolation and evaluation of kaempferol glycosides from the fern Neocheiropteris palmatopedata.
|
| |
Phytochemistry,
71,
641-647.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
R.J.Falconer,
A.Penkova,
I.Jelesarov,
and
B.M.Collins
(2010).
Survey of the year 2008: applications of isothermal titration calorimetry.
|
| |
J Mol Recognit,
23,
395-413.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
T.C.Hsieh,
and
J.M.Wu
(2010).
Resveratrol: Biological and pharmaceutical properties as anticancer molecule.
|
| |
Biofactors,
36,
360-369.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.Maiti,
P.V.Reddy,
M.Sturdy,
L.Marler,
S.D.Pegan,
A.D.Mesecar,
J.M.Pezzuto,
and
M.Cushman
(2009).
Synthesis of casimiroin and optimization of its quinone reductase 2 and aromatase inhibitory activities.
|
| |
J Med Chem,
52,
1873-1884.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
J.A.Winger,
O.Hantschel,
G.Superti-Furga,
and
J.Kuriyan
(2009).
The structure of the leukemia drug imatinib bound to human quinone reductase 2 (NQO2).
|
| |
BMC Struct Biol,
9,
7.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
J.A.Boutin,
E.Marcheteau,
P.Hennig,
N.Moulharat,
S.Berger,
P.Delagrange,
J.P.Bouchet,
and
G.Ferry
(2008).
MT3/QR2 melatonin binding site does not use melatonin as a substrate or a co-substrate.
|
| |
J Pineal Res,
45,
524-531.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
Y.Fu,
L.Buryanovskyy,
and
Z.Zhang
(2008).
Quinone reductase 2 is a catechol quinone reductase.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
283,
23829-23835.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
codes are
shown on the right.
|
 |

