 |
PDBsum entry 2off

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Transferase
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
The crystal structure of glycogen phosphorylase b in complex with a potent allosteric inhibitor
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
Glycogen phosphorylase, muscle form. Chain: a. Synonym: myophosphorylase. Ec: 2.4.1.1
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Oryctolagus cuniculus. Rabbit. Organism_taxid: 9986. Tissue: muscle
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
2.20Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.185
|
R-free:
|
0.213
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
C.Tiraidis,K.-M.Alexacou,S.E.Zographos,D.D.Leonidas,T.Gimisis, N.G.Oikonomakos
|
Key ref:

|
 |
C.Tiraidis
et al.
(2007).
FR258900, a potential anti-hyperglycemic drug, binds at the allosteric site of glycogen phosphorylase.
Protein Sci,
16,
1773-1782.
PubMed id:
DOI:

|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
03-Jan-07
|
Release date:
|
07-Aug-07
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
P00489
(PYGM_RABIT) -
Glycogen phosphorylase, muscle form from Oryctolagus cuniculus
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
843 a.a.
810 a.a.*
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|
|
Key: |
 |
PfamA domain |
 |
 |
 |
Secondary structure |
 |
 |
CATH domain |
 |
|
*
PDB and UniProt seqs differ
at 1 residue position (black
cross)
|
|

|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.2.4.1.1
- glycogen phosphorylase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

Pathway:
|
 |
Glycogen
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
[(1->4)-alpha-D-glucosyl](n) + phosphate = [(1->4)-alpha-D-glucosyl](n-1) + alpha-D-glucose 1-phosphate
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
[(1->4)-alpha-D-glucosyl](n)
|
+
|
 phosphate
phosphate
|
=
|
[(1->4)-alpha-D-glucosyl](n-1)
|
+
|
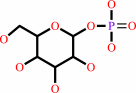 alpha-D-glucose 1-phosphate
alpha-D-glucose 1-phosphate
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Protein Sci
16:1773-1782
(2007)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
FR258900, a potential anti-hyperglycemic drug, binds at the allosteric site of glycogen phosphorylase.
|
|
C.Tiraidis,
K.M.Alexacou,
S.E.Zographos,
D.D.Leonidas,
T.Gimisis,
N.G.Oikonomakos.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
FR258900 has been discovered as a novel inhibitor of human liver glycogen
phosphorylase a and proved to suppress hepatic glycogen breakdown and reduce
plasma glucose concentrations in diabetic mice models. To elucidate the
mechanism of inhibition, we have determined the crystal structure of the
cocrystallized rabbit muscle glycogen phosphorylase b-FR258900 complex and
refined it to 2.2 A resolution. The structure demonstrates that the inhibitor
binds at the allosteric activator site, where the physiological activator AMP
binds. The contacts from FR258900 to glycogen phosphorylase are dominated by
nonpolar van der Waals interactions with Gln71, Gln72, Phe196, and Val45' (from
the symmetry-related subunit), and also by ionic interactions from the
carboxylate groups to the three arginine residues (Arg242, Arg309, and Arg310)
that form the allosteric phosphate-recognition subsite. The binding of FR258900
to the protein promotes conformational changes that stabilize an inactive
T-state quaternary conformation of the enzyme. The ligand-binding mode is
different from those of the potent phenoxy-phthalate and acyl urea inhibitors,
previously described, illustrating the broad specificity of the allosteric site.

|

|
|
|

|
| |
Selected figure(s)
|
|

|
| |
 |
 |

|
 |

|
 |
Figure 3.
Figure 3. A schematic diagram of the T-state rmGPb dimeric molecule,
|
 |
Figure 7.
Figure 7. Comparison of the position of the inhibitor FR258900 as
|
 |
|
|

|
| |
The above figures are
reprinted
by permission from the Protein Society:
Protein Sci
(2007,
16,
1773-1782)
copyright 2007.
|
|
| |
Figures were
selected
by the author.
|
|

|
| |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|

|
| |
Isolated from the cultured broth of a fungal strain No. 13835 compound FR258900) proved effective in lowering plasma glucose levels in animal models of diabetes. The X-ray crystallographic study of RMGPb in complex with FR258900 showed that the compound binds at the allosteric site, at the subunit-subunit interface of the dimer with a high affinity (Ki = 0.46 mikroM).
N.G. Oikonomakos
|
|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
K.Cheng,
J.Liu,
H.Sun,
and
J.Xie
(2010).
Synthesis of oleanolic acid dimers as inhibitors of glycogen phosphorylase.
|
| |
Chem Biodivers,
7,
690-697.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
|
 |

