 |
PDBsum entry 2oat

|
|
|

|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |

|

|

|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
Aminotransferase
|
PDB id
|
|

|

|
2oat
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.2.6.1.13
- ornithine aminotransferase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
a 2-oxocarboxylate + L-ornithine = L-glutamate 5-semialdehyde + an L-alpha-amino acid
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
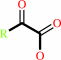 2-oxocarboxylate
2-oxocarboxylate
|
+
|
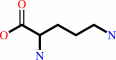 L-ornithine
L-ornithine
|
=
|
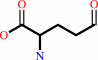 L-glutamate 5-semialdehyde
L-glutamate 5-semialdehyde
|
+
|
L-alpha-amino acid
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Cofactor:
|
 |
Pyridoxal 5'-phosphate
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Pyridoxal 5'-phosphate
Bound ligand (Het Group name =
PFM)
matches with 57.69% similarity
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
J Mol Biol
285:297-309
(1999)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Crystal structure of human ornithine aminotransferase complexed with the highly specific and potent inhibitor 5-fluoromethylornithine.
|
|
P.Storici,
G.Capitani,
R.Müller,
T.Schirmer,
J.N.Jansonius.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Ornithine aminotransferase (l-ornithine:2-oxoacid delta-aminotransferase; EC
2.6.1.13), a pyridoxal-5'-phosphate-dependent mitochondrial enzyme controls the
l-ornithine level in tissues by catalyzing the transfer of the delta-amino group
of l-ornithine to 2-oxoglutarate, producing l-glutamate- gamma-semialdehyde and
l-glutamate. (2S, 5S)-5-Fluoromethylornithine is the only inhibitor exclusively
specific for ornithine aminotransferase known to date. Both in vitro and in
vivo, it blocks the enzyme by a suicide reaction leading to a covalent adduct
with the cofactor. The crystal structure of the enzyme-inhibitor complex was
solved at a resolution of 1.95 A. No significant conformational changes compared
with the native enzyme structure were observed. The structure reveals the atomic
details of the cofactor-inhibitor adduct and its interactions with the active
site of the enzyme. The main residues responsible for specific binding of the
inhibitor are Arg180, which forms a strong salt bridge with the
alpha-carboxylate and Tyr55, which is involved in a short hydrogen bond with the
alpha-amino group. The experimental observation that in the racemic mixture,
(2S, 5S)-5-fluoromethylornithine is exclusively responsible for the enzyme
inhibition can be explained on the basis of the active site topology. Model
building studies strongly suggest that the natural substrate l-ornithine, in its
external aldimine adduct with the enzyme, makes use of the same recognition site
as the inhibitor. It is proposed that the neutralization of the active site
Arg413 by a salt bridge with Glu235 also plays an important role in productive
binding of both 5-fluoromethylornithine and l-ornithine. Arg180 and Arg413 are
believed to be instrumental in recognition of l-glutamate, by binding its gamma
and alpha-carboxylate groups, respectively. This requires a different side-chain
conformation of Glu235. Lys292 is the only obvious candidate for catalyzing the
rate-limiting proton transfer steps in the transamination reaction.

|

|
|
|

|
| |
Selected figure(s)
|
|

|
| |
 |
 |

|
 |

|
 |
Figure 2.
Figure 2. Structural formulas of (a) ornithine (Orn)
and (b) 5-fluoromethylornithine (6-fluoro-2,5-diamino-
hexanoic acid, 5FMOrn).
|
 |
Figure 3.
Figure 3. Schematic drawing of the reactants and the product of the inhibition reaction (Bolkenius et al., 1990).
5FMOrn reacts with the cofactor-K292 internal aldimine and, via a multistep reaction (see the text for more detail), a
stable adduct with PLP is formed. This is an unsaturated ketone with an absorption maximum at 458 nm. The sys-
tematic name of this molecule is 2-ammonio-7-(2-methyl-3-oxido-5-((phosphonoxy)-methyl)-4-pyridoxyl-5-oxo-6-hep-
tenoate. For simplicity, we refer to it as FMP.
|
 |
|
|

|
| |
The above figures are
reprinted
by permission from Elsevier:
J Mol Biol
(1999,
285,
297-309)
copyright 1999.
|
|
| |
Figures were
selected
by an automated process.
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
B.K.Cho,
H.Y.Park,
J.H.Seo,
J.Kim,
T.J.Kang,
B.S.Lee,
and
B.G.Kim
(2008).
Redesigning the substrate specificity of omega-aminotransferase for the kinetic resolution of aliphatic chiral amines.
|
| |
Biotechnol Bioeng,
99,
275-284.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.J.Tanner
(2008).
Structural biology of proline catabolism.
|
| |
Amino Acids,
35,
719-730.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.Stránská,
D.Kopecný,
M.Tylichová,
J.Snégaroff,
and
M.Sebela
(2008).
Ornithine delta-aminotransferase: An enzyme implicated in salt tolerance in higher plants.
|
| |
Plant Signal Behav,
3,
929-935.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
V.Rajaram,
P.Ratna Prasuna,
H.S.Savithri,
and
M.R.Murthy
(2008).
Structure of biosynthetic N-acetylornithine aminotransferase from Salmonella typhimurium: studies on substrate specificity and inhibitor binding.
|
| |
Proteins,
70,
429-441.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
V.Rajaram,
K.Prasad,
P.Ratna Prasuna,
N.Ramachandra,
S.R.Bharath,
H.S.Savithri,
and
M.R.Murthy
(2006).
Cloning, purification, crystallization and preliminary X-ray crystallographic analysis of the biosynthetic N-acetylornithine aminotransferases from Salmonella typhimurium and Escherichia coli.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun,
62,
980-983.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
K.Hirotsu,
M.Goto,
A.Okamoto,
and
I.Miyahara
(2005).
Dual substrate recognition of aminotransferases.
|
| |
Chem Rec,
5,
160-172.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Markova,
C.Peneff,
M.J.Hewlins,
T.Schirmer,
and
R.A.John
(2005).
Determinants of substrate specificity in omega-aminotransferases.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
280,
36409-36416.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
A.C.Eliot,
and
J.F.Kirsch
(2004).
Pyridoxal phosphate enzymes: mechanistic, structural, and evolutionary considerations.
|
| |
Annu Rev Biochem,
73,
383-415.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
C.G.Cheong,
J.C.Escalante-Semerena,
and
I.Rayment
(2002).
Structural studies of the L-threonine-O-3-phosphate decarboxylase (CobD) enzyme from Salmonella enterica: the apo, substrate, and product-aldimine complexes.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
41,
9079-9089.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
B.J.Berger
(2000).
Antimalarial activities of aminooxy compounds.
|
| |
Antimicrob Agents Chemother,
44,
2540-2542.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
P.Storici,
G.Capitani,
D.De Biase,
M.Moser,
R.A.John,
J.N.Jansonius,
and
T.Schirmer
(1999).
Crystal structure of GABA-aminotransferase, a target for antiepileptic drug therapy.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
38,
8628-8634.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
codes are
shown on the right.
|
 |

