 |
PDBsum entry 2nsh

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.5.4.99.18
- 5-(carboxyamino)imidazole ribonucleotide mutase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
5-carboxyamino-1-(5-phospho-D-ribosyl)imidazole + H+ = 5-amino-1- (5-phospho-D-ribosyl)imidazole-4-carboxylate
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
5-carboxyamino-1-(5-phospho-D-ribosyl)imidazole
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 76.00% similarity
|
+
|
H(+)
|
=
|
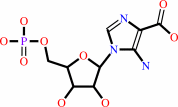 5-amino-1- (5-phospho-D-ribosyl)imidazole-4-carboxylate
5-amino-1- (5-phospho-D-ribosyl)imidazole-4-carboxylate
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Biochemistry
46:2842-2855
(2007)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
N5-CAIR mutase: role of a CO2 binding site and substrate movement in catalysis.
|
|
A.A.Hoskins,
M.Morar,
T.J.Kappock,
I.I.Mathews,
J.B.Zaugg,
T.E.Barder,
P.Peng,
A.Okamoto,
S.E.Ealick,
J.Stubbe.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
N5-Carboxyaminoimidazole ribonucleotide mutase (N5-CAIR mutase or PurE) from
Escherichia coli catalyzes the reversible interconversion of N5-CAIR to
carboxyaminoimidazole ribonucleotide (CAIR) with direct CO2 transfer.
Site-directed mutagenesis, a pH-rate profile, DFT calculations, and X-ray
crystallography together provide new insight into the mechanism of this unusual
transformation. These studies suggest that a conserved, protonated histidine
(His45) plays an essential role in catalysis. The importance of proton transfers
is supported by DFT calculations on CAIR and N5-CAIR analogues in which the
ribose 5'-phosphate is replaced with a methyl group. The calculations suggest
that the nonaromatic tautomer of CAIR (isoCAIR) is only 3.1 kcal/mol higher in
energy than its aromatic counterpart, implicating this species as a potential
intermediate in the PurE-catalyzed reaction. A structure of wild-type PurE
cocrystallized with 4-nitroaminoimidazole ribonucleotide (NO2-AIR, a CAIR
analogue) and structures of H45N and H45Q PurEs soaked with CAIR have been
determined and provide the first insight into the binding of an intact PurE
substrate. A comparison of 19 available structures of PurE and PurE mutants in
apo and nucleotide-bound forms reveals a common, buried carboxylate or CO2
binding site for CAIR and N5-CAIR in a hydrophobic pocket in which the
carboxylate or CO2 interacts with backbone amides. This work has led to a
mechanistic proposal in which the carboxylate orients the substrate for proton
transfer from His45 to N5-CAIR to form an enzyme-bound aminoimidazole
ribonucleotide (AIR) and CO2 intermediate. Subsequent movement of the
aminoimidazole moiety of AIR reorients it for addition of CO2 at C4 to generate
isoCAIR. His45 is now in a position to remove a C4 proton to produce CAIR.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
S.M.Firestine,
W.Wu,
H.Youn,
and
V.J.Davisson
(2009).
Interrogating the mechanism of a tight binding inhibitor of AIR carboxylase.
|
| |
Bioorg Med Chem,
17,
794-803.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
G.S.Brandt,
N.Nemeria,
S.Chakraborty,
M.J.McLeish,
A.Yep,
G.L.Kenyon,
G.A.Petsko,
F.Jordan,
and
D.Ringe
(2008).
Probing the active center of benzaldehyde lyase with substitutions and the pseudosubstrate analogue benzoylphosphonic acid methyl ester.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
47,
7734-7743.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
Y.Zhang,
M.Morar,
and
S.E.Ealick
(2008).
Structural biology of the purine biosynthetic pathway.
|
| |
Cell Mol Life Sci,
65,
3699-3724.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.Schaefer,
H.Jiang,
A.E.Ransome,
and
T.J.Kappock
(2007).
Multiple active site histidine protonation states in Acetobacter aceti N5-carboxyaminoimidazole ribonucleotide mutase detected by REDOR NMR.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
46,
9507-9512.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
code is
shown on the right.
|
 |

