 |
PDBsum entry 2myt

|
|
|

|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |

|

|

|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
Oxidoreductase
|
PDB id
|
|

|

|
2myt
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 2:
|
 |
E.C.1.20.4.1
- arsenate reductase (glutathione/glutaredoxin).
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
[glutaredoxin]-dithiol + arsenate + glutathione + H+ = glutathionyl-S- S-[glutaredoxin] + arsenite + H2O
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
[glutaredoxin]-dithiol
|
+
|
 arsenate
arsenate
|
+
|
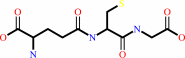 glutathione
glutathione
|
+
|
H(+)
|
=
|
glutathionyl-S- S-[glutaredoxin]
|
+
|
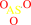 arsenite
arsenite
|
+
|
H2O
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Cofactor:
|
 |
Mo cation
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 3:
|
 |
E.C.3.1.3.48
- protein-tyrosine-phosphatase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
O-phospho-L-tyrosyl-[protein] + H2O = L-tyrosyl-[protein] + phosphate
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
O-phospho-L-tyrosyl-[protein]
|
+
|
H2O
|
=
|
L-tyrosyl-[protein]
|
+
|
 phosphate
phosphate
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Note, where more than one E.C. class is given (as above), each may
correspond to a different protein domain or, in the case of polyprotein
precursors, to a different mature protein.
|
|
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
J Biol Chem
290:22262-22273
(2015)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
A Hybrid Mechanism for the Synechocystis Arsenate Reductase Revealed by Structural Snapshots during Arsenate Reduction.
|
|
C.Hu,
C.Yu,
Y.Liu,
X.Hou,
X.Liu,
Y.Hu,
C.Jin.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Evolution of enzymes plays a crucial role in obtaining new biological functions
for all life forms. Arsenate reductases (ArsC) are several families of arsenic
detoxification enzymes that reduce arsenate to arsenite, which can subsequently
be extruded from cells by specific transporters. Among these, the Synechocystis
ArsC (SynArsC) is structurally homologous to the well characterized thioredoxin
(Trx)-coupled ArsC family but requires the glutaredoxin (Grx) system for its
reactivation, therefore classified as a unique Trx/Grx-hybrid family. The
detailed catalytic mechanism of SynArsC is unclear and how the
"hybrid" mechanism evolved remains enigmatic. Herein, we report the
molecular mechanism of SynArsC by biochemical and structural studies. Our work
demonstrates that arsenate reduction is carried out via an intramolecular
thiol-disulfide cascade similar to the Trx-coupled family, whereas the enzyme
reactivation step is diverted to the coupling of the glutathione-Grx pathway due
to the local structural difference. The current results support the hypothesis
that SynArsC is likely a molecular fossil representing an intermediate stage
during the evolution of the Trx-coupled ArsC family from the low molecular
weight protein phosphotyrosine phosphatase (LMW-PTPase) family.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

