 |
PDBsum entry 2mda

|
|
|

|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |

|

|

|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
Oxidoreductase
|
PDB id
|
|

|

|
2mda
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.1.14.16.2
- tyrosine 3-monooxygenase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

Pathway:
|
 |
Dopa Biosynthesis
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
(6R)-L-erythro-5,6,7,8-tetrahydrobiopterin + L-tyrosine + O2 = (4aS,6R)- 4a-hydroxy-L-erythro-5,6,7,8-tetrahydrobiopterin + L-dopa
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
(6R)-L-erythro-5,6,7,8-tetrahydrobiopterin
|
+
|
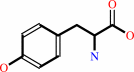 L-tyrosine
L-tyrosine
|
+
|
 O2
O2
|
=
|
(4aS,6R)- 4a-hydroxy-L-erythro-5,6,7,8-tetrahydrobiopterin
|
+
|
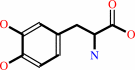 L-dopa
L-dopa
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Cofactor:
|
 |
Fe cation
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
J Mol Biol
426:1483-1497
(2014)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
The solution structure of the regulatory domain of tyrosine hydroxylase.
|
|
S.Zhang,
T.Huang,
U.Ilangovan,
A.P.Hinck,
P.F.Fitzpatrick.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Tyrosine hydroxylase (TyrH) catalyzes the hydroxylation of tyrosine to form
3,4-dihydroxyphenylalanine in the biosynthesis of the catecholamine
neurotransmitters. The activity of the enzyme is regulated by phosphorylation of
serine residues in a regulatory domain and by binding of catecholamines to the
active site. Available structures of TyrH lack the regulatory domain, limiting
the understanding of the effect of regulation on structure. We report the use of
NMR spectroscopy to analyze the solution structure of the isolated regulatory
domain of rat TyrH. The protein is composed of a largely unstructured N-terminal
region (residues 1-71) and a well-folded C-terminal portion (residues 72-159).
The structure of a truncated version of the regulatory domain containing
residues 65-159 has been determined and establishes that it is an ACT domain.
The isolated domain is a homodimer in solution, with the structure of each
monomer very similar to that of the core of the regulatory domain of
phenylalanine hydroxylase. Two TyrH regulatory domain monomers form an ACT
domain dimer composed of a sheet of eight strands with four α-helices on one
side of the sheet. Backbone dynamic analyses were carried out to characterize
the conformational flexibility of TyrH65-159. The results provide molecular
details critical for understanding the regulatory mechanism of TyrH.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

