 |
PDBsum entry 2jgi

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.3.1.1.7
- acetylcholinesterase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
acetylcholine + H2O = choline + acetate + H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
acetylcholine
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 41.18% similarity
|
+
|
H2O
|
=
|
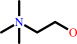 choline
choline
|
+
|
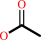 acetate
acetate
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
Biochemistry
46:4815-4825
(2007)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Crystal structures of acetylcholinesterase in complex with organophosphorus compounds suggest that the acyl pocket modulates the aging reaction by precluding the formation of the trigonal bipyramidal transition state.
|
|
A.Hörnberg,
A.K.Tunemalm,
F.Ekström.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Organophosphorus compounds (OPs), such as nerve agents and a group of
insecticides, irreversibly inhibit the enzyme acetylcholinesterase (AChE) by a
rapid phosphorylation of the catalytic Ser203 residue. The formed AChE-OP
conjugate subsequently undergoes an elimination reaction, termed aging, that
results in an enzyme completely resistant to oxime-mediated reactivation by
medical antidotes. In this study, we present crystal structures of the non-aged
and aged complexes between Mus musculus AChE (mAChE) and the nerve agents sarin,
VX, and diisopropyl fluorophosphate (DFP) and the OP-based insecticides
methamidophos (MeP) and fenamiphos (FeP). Non-aged conjugates of MeP, sarin, and
FeP and aged conjugates of MeP, sarin, and VX are very similar to the
noninhibited apo conformation of AChE. A minor structural change in the side
chain of His447 is observed in the non-aged conjugate of VX. In contrast, an
extensive rearrangement of the acyl loop region (residues 287-299) is observed
in the non-aged structure of DFP and in the aged structures of DFP and FeP. In
the case of FeP, the relatively large substituents of the phosphorus atom are
reorganized during aging, providing a structural support of an aging reaction
that proceeds through a nucleophilic attack on the phosphorus atom. The FeP
aging rate constant is 14 times lower than the corresponding constant for the
structurally related OP insecticide MeP, suggesting that tight steric
constraints of the acyl pocket loop preclude the formation of a trigonal
bipyramidal intermediate.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
K.Musilek,
O.Holas,
J.Misik,
M.Pohanka,
L.Novotny,
V.Dohnal,
V.Opletalova,
and
K.Kuca
(2010).
Monooxime-monocarbamoyl Bispyridinium Xylene-Linked Reactivators of Acetylcholinesterase-Synthesis, In vitro and Toxicity Evaluation, and Docking Studies.
|
| |
ChemMedChem,
5,
247-254.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
F.Ekström,
A.Hörnberg,
E.Artursson,
L.G.Hammarström,
G.Schneider,
and
Y.P.Pang
(2009).
Structure of HI-6*sarin-acetylcholinesterase determined by X-ray crystallography and molecular dynamics simulation: reactivator mechanism and design.
|
| |
PLoS One,
4,
e5957.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
J.Liu,
Y.Zhang,
and
C.G.Zhan
(2009).
Reaction pathway and free-energy barrier for reactivation of dimethylphosphoryl-inhibited human acetylcholinesterase.
|
| |
J Phys Chem B,
113,
16226-16236.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
T.M.Epstein,
U.Samanta,
S.D.Kirby,
D.M.Cerasoli,
and
B.J.Bahnson
(2009).
Crystal structures of brain group-VIII phospholipase A2 in nonaged complexes with the organophosphorus nerve agents soman and sarin.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
48,
3425-3435.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
U.Samanta,
S.D.Kirby,
P.Srinivasan,
D.M.Cerasoli,
and
B.J.Bahnson
(2009).
Crystal structures of human group-VIIA phospholipase A2 inhibited by organophosphorus nerve agents exhibit non-aged complexes.
|
| |
Biochem Pharmacol,
78,
420-429.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
Y.P.Pang,
F.Ekström,
G.A.Polsinelli,
Y.Gao,
S.Rana,
D.H.Hua,
B.Andersson,
P.O.Andersson,
L.Peng,
S.K.Singh,
R.K.Mishra,
K.Y.Zhu,
A.M.Fallon,
D.W.Ragsdale,
and
S.Brimijoin
(2009).
Selective and irreversible inhibitors of mosquito acetylcholinesterases for controlling malaria and other mosquito-borne diseases.
|
| |
PLoS One,
4,
e6851.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
Y.Pan,
J.L.Muzyka,
and
C.G.Zhan
(2009).
Model of human butyrylcholinesterase tetramer by homology modeling and dynamics simulation.
|
| |
J Phys Chem B,
113,
6543-6552.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
P.Masson,
M.T.Froment,
E.Gillon,
F.Nachon,
O.Lockridge,
and
L.M.Schopfer
(2008).
Kinetic analysis of effector modulation of butyrylcholinesterase-catalysed hydrolysis of acetanilides and homologous esters.
|
| |
FEBS J,
275,
2617-2631.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
codes are
shown on the right.
|
 |

