 |
PDBsum entry 2ib9

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.2.3.1.9
- acetyl-CoA C-acetyltransferase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

Pathway:
|
 |
Mevalonate Biosynthesis
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
2 acetyl-CoA = acetoacetyl-CoA + CoA
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 2
×
acetyl-CoA
2
×
acetyl-CoA
|
=
|
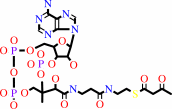 acetoacetyl-CoA
acetoacetyl-CoA
|
+
|
 CoA
CoA
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
Biochemistry
46:4305-4321
(2007)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Crystallographic and kinetic studies of human mitochondrial acetoacetyl-CoA thiolase: the importance of potassium and chloride ions for its structure and function.
|
|
A.M.Haapalainen,
G.Meriläinen,
P.L.Pirilä,
N.Kondo,
T.Fukao,
R.K.Wierenga.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Thiolases are CoA-dependent enzymes which catalyze the formation of a
carbon-carbon bond in a Claisen condensation step and its reverse reaction via a
thiolytic degradation mechanism. Mitochondrial acetoacetyl-coenzyme A (CoA)
thiolase (T2) is important in the pathways for the synthesis and degradation of
ketone bodies as well as for the degradation of 2-methylacetoacetyl-CoA. Human
T2 deficiency has been identified in more than 60 patients. A unique property of
T2 is its activation by potassium ions. High-resolution human T2 crystal
structures are reported for the apo form and the CoA complex, with and without a
bound potassium ion. The potassium ion is bound near the CoA binding site and
the catalytic site. Binding of the potassium ion at this low-affinity binding
site causes the rigidification of a CoA binding loop and an active site loop.
Unexpectedly, a high-affinity binding site for a chloride ion has also been
identified. The chloride ion is copurified, and its binding site is at the dimer
interface, near two catalytic loops. A unique property of T2 is its ability to
use 2-methyl-branched acetoacetyl-CoA as a substrate, whereas the other
structurally characterized thiolases cannot utilize the 2-methylated compounds.
The kinetic measurements show that T2 can degrade acetoacetyl-CoA and
2-methylacetoacetyl-CoA with similar catalytic efficiencies. For both
substrates, the turnover numbers increase approximately 3-fold when the
potassium ion concentration is increased from 0 to 40 mM KCl. The structural
analysis of the active site of T2 indicates that the Phe325-Pro326 dipeptide
near the catalytic cavity is responsible for the exclusive 2-methyl-branched
substrate specificity.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
J.H.Dyer,
A.Maina,
I.D.Gomez,
M.Cadet,
S.Oeljeklaus,
and
A.C.Schiedel
(2009).
Cloning, expression and purification of an acetoacetyl CoA thiolase from sunflower cotyledon.
|
| |
Int J Biol Sci,
5,
736-744.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
G.Meriläinen,
W.Schmitz,
R.K.Wierenga,
and
P.Kursula
(2008).
The sulfur atoms of the substrate CoA and the catalytic cysteine are required for a productive mode of substrate binding in bacterial biosynthetic thiolase, a thioester-dependent enzyme.
|
| |
FEBS J,
275,
6136-6148.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
J.J.Reddick,
and
J.K.Williams
(2008).
The mmgA gene from Bacillus subtilis encodes a degradative acetoacetyl-CoA thiolase.
|
| |
Biotechnol Lett,
30,
1045-1050.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
K.U.Wendt,
M.S.Weiss,
P.Cramer,
and
D.W.Heinz
(2008).
Structures and diseases.
|
| |
Nat Struct Mol Biol,
15,
117-120.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
codes are
shown on the right.
|
 |

