 |
PDBsum entry 2hs3

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.6.3.5.3
- phosphoribosylformylglycinamidine synthase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

Pathway:
|
 |
Purine Biosynthesis (early stages)
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
N2-formyl-N1-(5-phospho-beta-D-ribosyl)glycinamide + L-glutamine + ATP + H2O = 2-formamido-N1-(5-O-phospho-beta-D-ribosyl)acetamidine + L-glutamate + ADP + phosphate + H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
N(2)-formyl-N(1)-(5-phospho-beta-D-ribosyl)glycinamide
|
+
|
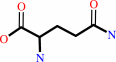 L-glutamine
L-glutamine
|
+
|
 ATP
ATP
|
+
|
H2O
|
=
|
2-formamido-N(1)-(5-O-phospho-beta-D-ribosyl)acetamidine
|
+
|
L-glutamate
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 62.07% similarity
|
+
|
 ADP
ADP
|
+
|
 phosphate
phosphate
|
+
|
H(+)
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
corresponds exactly
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Biochemistry
45:14880-14895
(2006)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Complexed structures of formylglycinamide ribonucleotide amidotransferase from Thermotoga maritima describe a novel ATP binding protein superfamily.
|
|
M.Morar,
R.Anand,
A.A.Hoskins,
J.Stubbe,
S.E.Ealick.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Formylglycinamide ribonucleotide amidotransferase (FGAR-AT) catalyzes the
ATP-dependent synthesis of formylglycinamidine ribonucleotide (FGAM) from
formylglycinamide ribonucleotide (FGAR) and glutamine in the fourth step of the
purine biosynthetic pathway. FGAR-AT is encoded by the purL gene. Two types of
PurL have been detected. The first type, found in eukaryotes and Gram-negative
bacteria, consists of a single 140 kDa polypeptide chain and is designated large
PurL (lgPurL). The second type, small PurL (smPurL), is found in archaea and
Gram-positive bacteria and consists of an 80 kDa polypeptide chain. SmPurL
requires two additional gene products, PurQ and PurS, for activity. PurL is a
member of a protein superfamily that contains a novel ATP-binding domain.
Structures of several members of this superfamily are available in the
unliganded form. We determined five different structures of FGAR-AT from
Thermotoga maritima in the presence of substrates, a substrate analogue, and a
product. These complexes have allowed a detailed description of the novel
ATP-binding motif. The availability of a ternary complex enabled mapping of the
active site, thus identifying potential residues involved in catalysis. The
complexes show a conformational change in the active site compared to the
unliganded structure. Surprising discoveries, an ATP molecule in an auxiliary
site of the protein and the conformational changes associated with its binding,
provoke speculation about the regulatory role of the auxiliary site in formation
of the PurLSQ complex as well as the evolutionary relationship of PurLs from
different organisms.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
M.Welin,
J.G.Grossmann,
S.Flodin,
T.Nyman,
P.Stenmark,
L.Trésaugues,
T.Kotenyova,
I.Johansson,
P.Nordlund,
and
L.Lehtiö
(2010).
Structural studies of tri-functional human GART.
|
| |
Nucleic Acids Res,
38,
7308-7319.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
E.Matsumoto,
S.I.Sekine,
R.Akasaka,
Y.Otta,
K.Katsura,
M.Inoue,
T.Kaminishi,
T.Terada,
M.Shirouzu,
and
S.Yokoyama
(2008).
Structure of an N-terminally truncated selenophosphate synthetase from Aquifex aeolicus.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun,
64,
453-458.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
E.S.Rangarajan,
A.Asinas,
A.Proteau,
C.Munger,
J.Baardsnes,
P.Iannuzzi,
A.Matte,
and
M.Cygler
(2008).
Structure of [NiFe] hydrogenase maturation protein HypE from Escherichia coli and its interaction with HypF.
|
| |
J Bacteriol,
190,
1447-1458.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Morar,
A.A.Hoskins,
J.Stubbe,
and
S.E.Ealick
(2008).
Formylglycinamide ribonucleotide amidotransferase from Thermotoga maritima: structural insights into complex formation.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
47,
7816-7830.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
Y.Zhang,
M.Morar,
and
S.E.Ealick
(2008).
Structural biology of the purine biosynthetic pathway.
|
| |
Cell Mol Life Sci,
65,
3699-3724.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
Y.Zhang,
R.H.White,
and
S.E.Ealick
(2008).
Crystal structure and function of 5-formaminoimidazole-4-carboxamide ribonucleotide synthetase from Methanocaldococcus jannaschii.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
47,
205-217.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Mouilleron,
and
B.Golinelli-Pimpaneau
(2007).
Conformational changes in ammonia-channeling glutamine amidotransferases.
|
| |
Curr Opin Struct Biol,
17,
653-664.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
Y.O.You,
and
W.A.van der Donk
(2007).
Mechanistic investigations of the dehydration reaction of lacticin 481 synthetase using site-directed mutagenesis.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
46,
5991-6000.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
codes are
shown on the right.
|
 |

