 |
PDBsum entry 2hmf

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.2.7.2.4
- aspartate kinase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

Pathway:
|
 |
Lysine biosynthesis (early stages)
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
L-aspartate + ATP = 4-phospho-L-aspartate + ADP
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
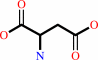 L-aspartate
L-aspartate
|
+
|
ATP
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
corresponds exactly
|
=
|
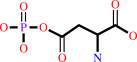 4-phospho-L-aspartate
4-phospho-L-aspartate
|
+
|
ADP
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
corresponds exactly
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Acta Crystallograph Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun
62:962-966
(2006)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
The initial step in the archaeal aspartate biosynthetic pathway catalyzed by a monofunctional aspartokinase.
|
|
C.R.Faehnle,
X.Liu,
A.Pavlovsky,
R.E.Viola.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
The activation of the beta-carboxyl group of aspartate catalyzed by
aspartokinase is the commitment step to amino-acid biosynthesis in the aspartate
pathway. The first structure of a microbial aspartokinase, that from
Methanococcus jannaschii, has been determined in the presence of the amino-acid
substrate L-aspartic acid and the nucleotide product MgADP. The enzyme assembles
into a dimer of dimers, with the interfaces mediated by both the N- and
C-terminal domains. The active-site functional groups responsible for substrate
binding and specificity have been identified and roles have been proposed for
putative catalytic functional groups.

|

|
|
|

|
| |
Selected figure(s)
|
|

|
| |
 |
 |

|
 |

|
 |
Figure 3.
Figure 3 An F[o] - F[c] OMIT map showing the fit of the
substrate (L-aspartate) and product (MgADP) to the electron
density.
|
 |
Figure 4.
Figure 4 Expansion of the mjAK structure showing the
substrate-binding sites. (a) The amino-acid binding site, with
each interaction <3.4 Å annotated. The  -carboxyl
group of L-aspartate (L-ASP) forms an ion pair with Arg207 and a
hydrogen bond with the backbone amide of Gly206 and the side
chain of Thr46. The -carboxyl
group of L-aspartate (L-ASP) forms an ion pair with Arg207 and a
hydrogen bond with the backbone amide of Gly206 and the side
chain of Thr46. The  -amino
group of L-aspartate interacts electrostatically with the
carboxyl group of Glu130. The -amino
group of L-aspartate interacts electrostatically with the
carboxyl group of Glu130. The  -carboxyl
group, the phosphoryl acceptor, forms hydrogen bonds with the
backbone amide of Ser210 and the side chain of Ser40. (b) The
nucleotide-binding site. The divalent cation, Mg^2+, forms a
bridge between the -carboxyl
group, the phosphoryl acceptor, forms hydrogen bonds with the
backbone amide of Ser210 and the side chain of Ser40. (b) The
nucleotide-binding site. The divalent cation, Mg^2+, forms a
bridge between the  -
and -
and  -phosphate
groups of ADP. The ribose moiety is bound by interactions with
the side chains of Asp231, Asp239 and Arg241, while the adenine
ring is positioned through hydrophobic interactions with Val267
as well as a hydrogen bond to the hydroxyl group of Tyr236. -phosphate
groups of ADP. The ribose moiety is bound by interactions with
the side chains of Asp231, Asp239 and Arg241, while the adenine
ring is positioned through hydrophobic interactions with Val267
as well as a hydrogen bond to the hydroxyl group of Tyr236.
|
 |
|
|

|
| |
The above figures are
reprinted
by permission from the IUCr:
Acta Crystallograph Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun
(2006,
62,
962-966)
copyright 2006.
|
|
| |
Figures were
selected
by the author.
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

