 |
PDBsum entry 2g0a

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Hydrolase
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
X-ray structure of mouse pyrimidine 5'-nucleotidase type 1 with lead(ii) bound in active site
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
Cytosolic 5'-nucleotidase iii. Chain: a, b. Synonym: cn-iii, pyrimidine 5'- nucleotidase 1, p5'n-1, p5n-1, pn-i, lupin. Engineered: yes
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Mus musculus. House mouse. Organism_taxid: 10090. Gene: nt5c3. Expressed in: escherichia coli. Expression_system_taxid: 562.
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
2.35Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.153
|
R-free:
|
0.229
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
E.Bitto,C.A.Bingman,G.E.Wesenberg,G.N.Phillips Jr.,Center For Eukaryotic Structural Genomics (Cesg)
|
Key ref:

|
 |
E.Bitto
et al.
(2006).
Structure of pyrimidine 5'-nucleotidase type 1. Insight into mechanism of action and inhibition during lead poisoning.
J Biol Chem,
281,
20521-20529.
PubMed id:
DOI:

|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
11-Feb-06
|
Release date:
|
04-Apr-06
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
Q9D020
(5NT3A_MOUSE) -
Cytosolic 5'-nucleotidase 3A from Mus musculus
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
331 a.a.
291 a.a.*
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|
|
Key: |
 |
PfamA domain |
 |
 |
 |
Secondary structure |
 |
 |
CATH domain |
 |
|
*
PDB and UniProt seqs differ
at 5 residue positions (black
crosses)
|
|

|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 1:
|
 |
E.C.3.1.3.5
- 5'-nucleotidase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
a ribonucleoside 5'-phosphate + H2O = a ribonucleoside + phosphate
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
ribonucleoside 5'-phosphate
|
+
|
H2O
|
=
|
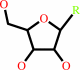 ribonucleoside
ribonucleoside
|
+
|
 phosphate
phosphate
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 2:
|
 |
E.C.3.1.3.91
- 7-methylguanosine nucleotidase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
|
1.
|
N7-methyl-GMP + H2O = N7-methylguanosine + phosphate
|
|
2.
|
CMP + H2O = cytidine + phosphate
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
N(7)-methyl-GMP
|
+
|
H2O
|
=
|
N(7)-methylguanosine
|
+
|
 phosphate
phosphate
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
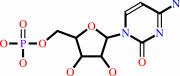 CMP
CMP
|
+
|
H2O
|
=
|
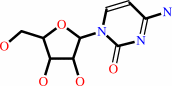 cytidine
cytidine
|
+
|
 phosphate
phosphate
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Note, where more than one E.C. class is given (as above), each may
correspond to a different protein domain or, in the case of polyprotein
precursors, to a different mature protein.
|
|
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
J Biol Chem
281:20521-20529
(2006)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Structure of pyrimidine 5'-nucleotidase type 1. Insight into mechanism of action and inhibition during lead poisoning.
|
|
E.Bitto,
C.A.Bingman,
G.E.Wesenberg,
J.G.McCoy,
G.N.Phillips.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Eukaryotic pyrimidine 5'-nucleotidase type 1 (P5N-1) catalyzes dephosphorylation
of pyrimidine 5'-mononucleotides. Deficiency of P5N-1 activity in red blood
cells results in nonspherocytic hemolytic anemia. The enzyme deficiency is
either familial or can be acquired through lead poisoning. We present the
crystal structure of mouse P5N-1 refined to 2.35 A resolution. The mouse P5N-1
has a 92% sequence identity to its human counterpart. The structure revealed
that P5N-1 adopts a fold similar to enzymes of the haloacid dehydrogenase
superfamily. The active site of this enzyme is structurally highly similar to
those of phosphoserine phosphatases. We propose a catalytic mechanism for P5N-1
that is also similar to that of phosphoserine phosphatases and provide
experimental evidence for the mechanism in the form of structures of several
reaction cycle states, including: 1) P5N-1 with bound Mg(II) at 2.25 A, 2)
phosphoenzyme intermediate analog at 2.30 A, 3) product-transition complex
analog at 2.35 A, and 4) product complex at 2.1A resolution with phosphate bound
in the active site. Furthermore the structure of Pb(II)-inhibited P5N-1 (at 2.35
A) revealed that Pb(II) binds within the active site in a way that compromises
function of the cationic cavity, which is required for the recognition and
binding of the phosphate group of nucleotides.

|

|
|
|

|
| |
Selected figure(s)
|
|

|
| |
 |
 |

|
 |

|
 |
Figure 2.
FIGURE 2. Comparison of mP5N-1 and its closest structural
homolog. A, a stereo representation of structural superposition
of mP5N-1 (red; Protein Data Bank code 2bdu) and hPSP (cyan;
Protein Data Bank code 1l8o). Every 10th C[  ]carbon of mP5N-1 is
highlighted by a red sphere, and some are labeled by residue
numbers for better orientation. B, structural superposition of
the active sites of mP5N-1 (red) and hPSP (cyan; Protein Data
Bank code 1nnl). ]carbon of mP5N-1 is
highlighted by a red sphere, and some are labeled by residue
numbers for better orientation. B, structural superposition of
the active sites of mP5N-1 (red) and hPSP (cyan; Protein Data
Bank code 1nnl).
|
 |
Figure 3.
FIGURE 3. The reaction scheme of mP5N-1. A, mP5N-1 has two
enzymatic activities: nucleotidase activity (steps 1 and 2a) and
phosphotransferase activity (steps 1 and 2b). B, the proposed
catalytic mechanism for nucleotidase activity of mP5N-1. "R"
represents ribonucleoside. Individual states of the reaction
mechanism include apoenzyme (I), active enzyme (II), the
substrate complex (III), the substrate-transition complex (IV),
the phosphoenzyme intermediate (V), the product-transition
complex (VI), and the product complex (VII).
|
 |
|
|

|
| |
The above figures are
reprinted
by permission from the ASBMB:
J Biol Chem
(2006,
281,
20521-20529)
copyright 2006.
|
|
| |
Figures were
selected
by an automated process.
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
K.Walldén,
and
P.Nordlund
(2011).
Structural Basis for the Allosteric Regulation and Substrate Recognition of Human Cytosolic 5'-Nucleotidase II.
|
| |
J Mol Biol,
408,
684-696.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
M.D.Zimmerman,
M.Proudfoot,
A.Yakunin,
and
W.Minor
(2008).
Structural insight into the mechanism of substrate specificity and catalytic activity of an HD-domain phosphohydrolase: the 5'-deoxyribonucleotidase YfbR from Escherichia coli.
|
| |
J Mol Biol,
378,
215-226.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
C.W.Chung
(2007).
The use of biophysical methods increases success in obtaining liganded crystal structures.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr,
63,
62-71.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
G.N.Phillips,
B.G.Fox,
J.L.Markley,
B.F.Volkman,
E.Bae,
E.Bitto,
C.A.Bingman,
R.O.Frederick,
J.G.McCoy,
B.L.Lytle,
B.S.Pierce,
J.Song,
and
S.N.Twigger
(2007).
Structures of proteins of biomedical interest from the Center for Eukaryotic Structural Genomics.
|
| |
J Struct Funct Genomics,
8,
73-84.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
codes are
shown on the right.
|
 |

