 |
PDBsum entry 2fzc

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Transferase
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
The structure of wild-type e. Coli aspartate transcarbamoylase in complex with novel t state inhibitors at 2.10 resolution
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
Aspartate carbamoyltransferase catalytic chain. Chain: a, c. Synonym: aspartate transcarbamylase, atcase. Engineered: yes. Aspartate carbamoyltransferase regulatory chain. Chain: b, d. Engineered: yes
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Escherichia coli. Organism_taxid: 562. Gene: pyrb. Expressed in: escherichia coli. Expression_system_taxid: 562. Gene: pyri.
|
|
Biol. unit:
|
 |
 Dodecamer (from PDB file)
Dodecamer (from PDB file)
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
2.10Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.196
|
R-free:
|
0.250
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
S.Heng,K.A.Stieglitz,J.Eldo,J.Xia,J.P.Cardia,E.R.Kantrowitz
|
Key ref:

|
 |
S.Heng
et al.
(2006).
T-state inhibitors of E. coli aspartate transcarbamoylase that prevent the allosteric transition.
Biochemistry,
45,
10062-10071.
PubMed id:
DOI:
|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
09-Feb-06
|
Release date:
|
29-Aug-06
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
Chains A, C:
E.C.2.1.3.2
- aspartate carbamoyltransferase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

Pathway:
|
 |
Pyrimidine Biosynthesis
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
carbamoyl phosphate + L-aspartate = N-carbamoyl-L-aspartate + phosphate + H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
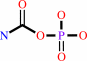 carbamoyl phosphate
carbamoyl phosphate
|
+
|
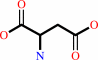 L-aspartate
L-aspartate
|
=
|
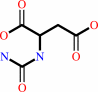 N-carbamoyl-L-aspartate
N-carbamoyl-L-aspartate
|
+
|
 phosphate
phosphate
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Biochemistry
45:10062-10071
(2006)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
T-state inhibitors of E. coli aspartate transcarbamoylase that prevent the allosteric transition.
|
|
S.Heng,
K.A.Stieglitz,
J.Eldo,
J.Xia,
J.P.Cardia,
E.R.Kantrowitz.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Escherichia coli aspartate transcarbamoylase (ATCase) catalyzes the committed
step in pyrimidine nucleotide biosynthesis, the reaction between carbamoyl
phosphate (CP) and l-aspartate to form N-carbamoyl-l-aspartate and inorganic
phosphate. The enzyme exhibits homotropic cooperativity and is allosterically
regulated. Upon binding l-aspartate in the presence of a saturating
concentration of CP, the enzyme is converted from the low-activity low-affinity
T state to the high-activity high-affinity R state. The potent inhibitor
N-phosphonacetyl-l-aspartate (PALA), which combines the binding features of Asp
and CP into one molecule, has been shown to induce the allosteric transition to
the R state. In the presence of only CP, the enzyme is the T structure with the
active site primed for the binding of aspartate. In a structure of the enzyme-CP
complex (T(CP)), two CP molecules were observed in the active site approximately
7A apart, one with high occupancy and one with low occupancy. The high occupancy
site corresponds to the position for CP observed in the structure of the enzyme
with CP and the aspartate analogue succinate bound. The position of the second
CP is in a unique site and does not overlap with the aspartate binding site. As
a means to generate a new class of inhibitors for ATCase, the domain-open T
state of the enzyme was targeted. We designed, synthesized, and characterized
three inhibitors that were composed of two phosphonacetamide groups linked
together. These two phosphonacetamide groups mimic the positions of the two CP
molecules in the T(CP) structure. X-ray crystal structures of ATCase-inhibitor
complexes revealed that each of these inhibitors bind to the T state of the
enzyme and occupy the active site area. As opposed to the binding of Asp in the
presence of CP or PALA, these inhibitors are unable to initiate the global T to
R conformational change. Although the best of these T-state inhibitors only has
a K(i) value in the micromolar range, the structural information with respect to
their mode of binding provides important information for the design of second
generation inhibitors that will have even higher affinity for the active site of
the T state of the enzyme.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
J.Eldo,
S.Heng,
and
E.R.Kantrowitz
(2007).
Design, synthesis, and bioactivity of novel inhibitors of E. coli aspartate transcarbamoylase.
|
| |
Bioorg Med Chem Lett,
17,
2086-2090.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
|
 |
|

