 |
PDBsum entry 2fmz

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Lyase
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
Carbonic anhydrase activators. Activation of isoforms i, ii, iv, va, vii and xiv with l- and d- phenylalanine, structure with d- phenylalanine.
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
Carbonic anhydrase 2. Chain: a. Synonym: carbonic anhydrase ii, carbonate dehydratase ii, ca-ii, carbonic anhydrasE C. Ec: 4.2.1.1
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Homo sapiens. Human. Organism_taxid: 9606
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
1.60Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.218
|
R-free:
|
0.237
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
C.Temperini,A.Scozzafava,D.Vullo,C.T.Supuran
|
|
Key ref:
|
 |
C.Temperini
et al.
(2006).
Carbonic anhydrase activators. Activation of isoforms I, II, IV, VA, VII, and XIV with L- and D-phenylalanine and crystallographic analysis of their adducts with isozyme II: stereospecific recognition within the active site of an enzyme and its consequences for the drug design.
J Med Chem,
49,
3019-3027.
PubMed id:
DOI:
|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
10-Jan-06
|
Release date:
|
23-May-06
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
P00918
(CAH2_HUMAN) -
Carbonic anhydrase 2 from Homo sapiens
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
260 a.a.
257 a.a.
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|
|
Key: |
 |
PfamA domain |
 |
 |
 |
Secondary structure |
 |
 |
CATH domain |
 |
|

|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 2:
|
 |
E.C.4.2.1.1
- carbonic anhydrase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
hydrogencarbonate + H+ = CO2 + H2O
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 hydrogencarbonate
hydrogencarbonate
|
+
|
H(+)
|
=
|
 CO2
CO2
|
+
|
H2O
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Cofactor:
|
 |
Zn(2+)
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 3:
|
 |
E.C.4.2.1.69
- cyanamide hydratase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
urea = cyanamide + H2O
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
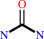 urea
urea
|
=
|
 cyanamide
cyanamide
|
+
|
H2O
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Note, where more than one E.C. class is given (as above), each may
correspond to a different protein domain or, in the case of polyprotein
precursors, to a different mature protein.
|
|
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
J Med Chem
49:3019-3027
(2006)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Carbonic anhydrase activators. Activation of isoforms I, II, IV, VA, VII, and XIV with L- and D-phenylalanine and crystallographic analysis of their adducts with isozyme II: stereospecific recognition within the active site of an enzyme and its consequences for the drug design.
|
|
C.Temperini,
A.Scozzafava,
D.Vullo,
C.T.Supuran.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Activation of six human brain carbonic anhydrases (hCAs, EC 4.2.1.1), hCA I, II,
IV, VA, VII, and XIV, with l-/d-phenylalanine was investigated kinetically and
by X-ray crystallography. l-Phe was a potent activator of isozymes I, II, and
XIV (K(A)s of 13-240 nM), a weaker activator of hCA VA and VII (K(A)s of
9.8-10.9 microM), and a quite inefficient hCA IV activator (K(A) of 52 microM).
d-Phe showed good hCA II activatory properties (K(A) of 35 nM), being a moderate
hCA VA, VII, and XIV (K(A)s of 4.6-9.7 microM) and a weak hCA I and IV activator
(K(A)s of 63-86 microM). X-ray crystallography of the hCA II-l-Phe/d-Phe adducts
showed the activators to be anchored at the entrance of the active site,
participating in numerous bonds and hydrophobic interactions with amino acid
residues His64, Thr200, Trp5, and Pro201. This is the first study showing
different binding modes of stereoisomeric activators within the hCA II active
site, with consequences for overall proton transfer processes (rate-determining
for the catalytic cycle). It also points out differences of activation
efficiency between various isozymes with structurally related activators,
exploitable for designing alternative proton transfer pathways. CA activators
may lead to the design of pharmacologically useful derivatives for the
enhancement of synaptic efficacy, which may represent a conceptually new
approach for the treatment of Alzheimer's disease, aging, and other conditions
in which spatial learning and memory therapy must be enhanced. As the blood and
brain concentrations of l-Phe are quite variable (30-73 microM), activity of
some brain CAs may strongly be influenced by the level of activator(s) present
in such tissues.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
K.Dave,
A.Scozzafava,
D.Vullo,
C.T.Supuran,
and
M.A.Ilies
(2011).
Pyridinium derivatives of histamine are potent activators of cytosolic carbonic anhydrase isoforms I, II and VII.
|
| |
Org Biomol Chem,
9,
2790-2800.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
K.Dave,
M.A.Ilies,
A.Scozzafava,
C.Temperini,
D.Vullo,
and
C.T.Supuran
(2011).
An inhibitor-like binding mode of a carbonic anhydrase activator within the active site of isoform II.
|
| |
Bioorg Med Chem Lett,
21,
2764-2768.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
B.Kanbar,
and
E.Ozdemir
(2010).
Thermal stability of carbonic anhydrase immobilized within polyurethane foam.
|
| |
Biotechnol Prog,
26,
1474-1480.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
C.T.Supuran
(2008).
Carbonic anhydrases: novel therapeutic applications for inhibitors and activators.
|
| |
Nat Rev Drug Discov,
7,
168-181.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.Yang,
S.Singh,
and
J.Shen
(2008).
13C saturation transfer effect of carbon dioxide-bicarbonate exchange catalyzed by carbonic anhydrase in vivo.
|
| |
Magn Reson Med,
59,
492-498.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
V.M.Krishnamurthy,
G.K.Kaufman,
A.R.Urbach,
I.Gitlin,
K.L.Gudiksen,
D.B.Weibel,
and
G.M.Whitesides
(2008).
Carbonic anhydrase as a model for biophysical and physical-organic studies of proteins and protein-ligand binding.
|
| |
Chem Rev,
108,
946.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
D.Bhatt,
S.Z.Fisher,
C.Tu,
R.McKenna,
and
D.N.Silverman
(2007).
Location of binding sites in small molecule rescue of human carbonic anhydrase II.
|
| |
Biophys J,
92,
562-570.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
I.Nishimori,
S.Onishi,
D.Vullo,
A.Innocenti,
A.Scozzafava,
and
C.T.Supuran
(2007).
Carbonic anhydrase activators: the first activation study of the human secretory isoform VI with amino acids and amines.
|
| |
Bioorg Med Chem,
15,
5351-5357.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
codes are
shown on the right.
|
 |

