 |
PDBsum entry 2fa3

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.2.3.3.10
- hydroxymethylglutaryl-CoA synthase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

Pathway:
|
 |
Mevalonate Biosynthesis
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
acetoacetyl-CoA + acetyl-CoA + H2O = (3S)-3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA + CoA + H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
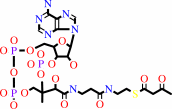 acetoacetyl-CoA
acetoacetyl-CoA
|
+
|
acetyl-CoA
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
corresponds exactly
|
+
|
H2O
|
=
|
(3S)-3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA
|
+
|
 CoA
CoA
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A
103:11491-11496
(2006)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Structural basis for the design of potent and species-specific inhibitors of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl CoA synthases.
|
|
F.Pojer,
J.L.Ferrer,
S.B.Richard,
D.A.Nagegowda,
M.L.Chye,
T.J.Bach,
J.P.Noel.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
3-Hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl CoA synthase (HMGS) catalyzes the first committed
step in the mevalonate metabolic pathway for isoprenoid biosynthesis and serves
as an alternative target for cholesterol-lowering and antibiotic drugs. We have
determined a previously undescribed crystal structure of a eukaryotic HMGS bound
covalently to a potent and specific inhibitor F-244
[(E,E)-11-[3-(hydroxymethyl)-4-oxo-2-oxytanyl]-3,5,7-trimethyl-2,4-undecadienenoic
acid]. Given the accessibility of synthetic analogs of the F-244 natural
product, this inhibited eukaryotic HMGS structure serves as a necessary starting
point for structure-based methods that may improve the potency and
species-specific selectivity of the next generation of F-244 analogs designed to
target particular eukaryotic and prokaryotic HMGS.

|

|
|
|

|
| |
Selected figure(s)
|
|

|
| |
 |
 |

|
 |

|
 |
Figure 3.
Fig. 3. Overview of HMGS in complex with F-244. (A)
Electrostatic surface of HMGS covalently bound to ring-opened
F-244. Color-coding is identical to Fig. 2A. The inhibitor F-244
does not occupy the same part of the pantothenate-binding tunnel
as the CoA tail shown in Fig. 2A. (B) Stereoview of the HMGS
active site for the ring-opened F-244 covalent complex.
Color-coding and map calculations are identical to Fig. 2B. The
first eight carbons of the acyl tail of F-244 are well ordered;
however, the position of the remaining six carbons display much
weaker electron density as the tail protrudes out of the active
site entrance. (C) Close-up view of the HMGS active site for the
ring-opened F-244 covalent complex. The SIGMAA-weighted 2F[o] -
F[c] electron density map is shown in blue, contoured at 1  . A
H-bond between Glu-83 and the 2-hydroxymethyl moiety of
ring-opened F-244 is shown as rendered green cylinders. . A
H-bond between Glu-83 and the 2-hydroxymethyl moiety of
ring-opened F-244 is shown as rendered green cylinders.
|
 |
Figure 4.
Fig. 4. Close-up view of F-244 covalently modifying the
BjHMGS1 active site and a posited reaction mechanism based on
the F-244 complex. (A) Secondary structure is shown as ribbons
colored as in Fig. 1. Side chains and F-244 are depicted as
half-colored bonds with red for oxygen, blue for nitrogen, and
gold and gray for carbons on F-244 and HMGS side chains,
respectively. The oxygen atoms of the ring-opened form of F-244
form H-bonds (green dashes) with Glu-83, His-247, and Asn-326
through a water molecule (red sphere) and backbone amides of
Ser-359 and Cys-117. (B) Schematic representation of F-244
tethered to Cys-117 highlighting all intermolecular
interactions. H-bonds are depicted as green dashes. Orange half
circles depict van der Waals contacts with dashed curves
specifying residues sitting behind the plane formed by F-244.
(C) Putative reaction mechanism of HMGS. The proposed role of
Glu-83 in the last hydrolytic step necessary for release of
HMG-CoA is shown in a yellow box. The residues implicated in
formation of the oxyanion hole are depicted in green, and
H-bonds are shown as dashed bonds.
|
 |
|
|
| |
Figures were
selected
by an automated process.
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
A.F.Kluge,
and
R.C.Petter
(2010).
Acylating drugs: redesigning natural covalent inhibitors.
|
| |
Curr Opin Chem Biol,
14,
421-427.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
|
 |

