 |
PDBsum entry 2f8c

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Transferase
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
Crystal structure of fpps in complex with zoledronate
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
Farnesyl diphosphate synthase. Chain: f. Fragment: residues 6-353. Synonym: fpp synthetase. Fps. Farnesyl pyrophosphate synthetase. Engineered: yes. Other_details: includes: dimethylallyltranstransferase. Geranyltranstransferase
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Homo sapiens. Human. Organism_taxid: 9606. Gene: fdps, fps, kiaa1293. Expressed in: escherichia coli. Expression_system_taxid: 562.
|
|
Biol. unit:
|
 |
 Dimer (from PDB file)
Dimer (from PDB file)
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
2.20Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.222
|
R-free:
|
0.268
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
J.-M.Rondeau,F.Bitsch,E.Bourgier,M.Geiser,R.Hemmig,M.Kroemer, S.Lehmann,P.Ramage,S.Rieffel,A.Strauss,J.R.Green,W.Jahnke
|
|
Key ref:
|
 |
J.M.Rondeau
et al.
(2006).
Structural basis for the exceptional in vivo efficacy of bisphosphonate drugs.
Chemmedchem,
1,
267-273.
PubMed id:
|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
02-Dec-05
|
Release date:
|
28-Feb-06
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
P14324
(FPPS_HUMAN) -
Farnesyl pyrophosphate synthase from Homo sapiens
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
419 a.a.
343 a.a.
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|
|
Key: |
 |
PfamA domain |
 |
 |
 |
Secondary structure |
 |
 |
CATH domain |
 |
|

|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 1:
|
 |
E.C.2.5.1.1
- dimethylallyltranstransferase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

Pathway:
|
 |
Terpenoid biosynthesis
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
isopentenyl diphosphate + dimethylallyl diphosphate = (2E)- geranyl diphosphate + diphosphate
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
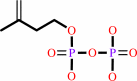 isopentenyl diphosphate
isopentenyl diphosphate
|
+
|
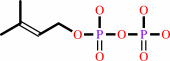 dimethylallyl diphosphate
dimethylallyl diphosphate
|
=
|
(2E)- geranyl diphosphate
|
+
|
diphosphate
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 55.56% similarity
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 2:
|
 |
E.C.2.5.1.10
- (2E,6E)-farnesyl diphosphate synthase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

Pathway:
|
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
isopentenyl diphosphate + (2E)-geranyl diphosphate = (2E,6E)-farnesyl diphosphate + diphosphate
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 isopentenyl diphosphate
isopentenyl diphosphate
|
+
|
(2E)-geranyl diphosphate
|
=
|
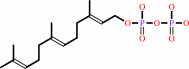 (2E,6E)-farnesyl diphosphate
(2E,6E)-farnesyl diphosphate
|
+
|
diphosphate
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 55.56% similarity
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Note, where more than one E.C. class is given (as above), each may
correspond to a different protein domain or, in the case of polyprotein
precursors, to a different mature protein.
|
|
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
Chemmedchem
1:267-273
(2006)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Structural basis for the exceptional in vivo efficacy of bisphosphonate drugs.
|
|
J.M.Rondeau,
F.Bitsch,
E.Bourgier,
M.Geiser,
R.Hemmig,
M.Kroemer,
S.Lehmann,
P.Ramage,
S.Rieffel,
A.Strauss,
J.R.Green,
W.Jahnke.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
To understand the structural basis for bisphosphonate therapy of bone diseases,
we solved the crystal structures of human farnesyl pyrophosphate synthase (FPPS)
in its unliganded state, in complex with the nitrogen-containing bisphosphonate
(N-BP) drugs zoledronate, pamidronate, alendronate, and ibandronate, and in the
ternary complex with zoledronate and the substrate isopentenyl pyrophosphate
(IPP). By revealing three structural snapshots of the enzyme catalytic cycle,
each associated with a distinct conformational state, and details about the
interactions with N-BPs, these structures provide a novel understanding of the
mechanism of FPPS catalysis and inhibition. In particular, the accumulating
substrate, IPP, was found to bind to and stabilize the FPPS-N-BP complexes
rather than to compete with and displace the N-BP inhibitor. Stabilization of
the FPPS-N-BP complex through IPP binding is supported by differential scanning
calorimetry analyses of a set of representative N-BPs. Among other factors such
as high binding affinity for bone mineral, this particular mode of FPPS
inhibition contributes to the exceptional in vivo efficacy of N-BP drugs.
Moreover, our data form the basis for structure-guided design of optimized N-BPs
with improved pharmacological properties.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
F.Fanord,
K.Fairbairn,
H.Kim,
A.Garces,
V.Bhethanabotla,
and
V.K.Gupta
(2011).
Bisphosphonate-modified gold nanoparticles: a useful vehicle to study the treatment of osteonecrosis of the femoral head.
|
| |
Nanotechnology,
22,
035102.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.D.Artz,
A.K.Wernimont,
J.E.Dunford,
M.Schapira,
A.Dong,
Y.Zhao,
J.Lew,
R.G.Russell,
F.H.Ebetino,
U.Oppermann,
and
R.Hui
(2011).
Molecular characterization of a novel geranylgeranyl pyrophosphate synthase from Plasmodium parasites.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
286,
3315-3322.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
J.Räikkönen,
M.Taskinen,
J.E.Dunford,
H.Mönkkönen,
S.Auriola,
and
J.Mönkkönen
(2011).
Correlation between time-dependent inhibition of human farnesyl pyrophosphate synthase and blockade of mevalonate pathway by nitrogen-containing bisphosphonates in cultured cells.
|
| |
Biochem Biophys Res Commun,
407,
663-667.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
C.H.Huang,
S.B.Gabelli,
E.Oldfield,
and
L.M.Amzel
(2010).
Binding of nitrogen-containing bisphosphonates (N-BPs) to the Trypanosoma cruzi farnesyl diphosphate synthase homodimer.
|
| |
Proteins,
78,
888-899.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
E.Matczak-Jon,
T.Kowalik-Jankowska,
K.Slepokura,
P.Kafarski,
and
A.Rajewska
(2010).
Specificity of the zinc(II), magnesium(II) and calcium(II) complexation by (pyridin-2-yl)aminomethane-1,1-diphosphonic acids and related 1,3-(thiazol-2-yl) and 1,3-(benzothiazol-2-yl) derivatives.
|
| |
Dalton Trans,
39,
1207-1221.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
F.Y.Lin,
C.I.Liu,
Y.L.Liu,
Y.Zhang,
K.Wang,
W.Y.Jeng,
T.P.Ko,
R.Cao,
A.H.Wang,
and
E.Oldfield
(2010).
Mechanism of action and inhibition of dehydrosqualene synthase.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
107,
21337-21342.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
J.Gao,
X.Chu,
Y.Qiu,
L.Wu,
Y.Qiao,
J.Wu,
and
D.Li
(2010).
Discovery of potent inhibitor for farnesyl pyrophosphate synthase in the mevalonate pathway.
|
| |
Chem Commun (Camb),
46,
5340-5342.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
T.H.Chang,
F.L.Hsieh,
T.P.Ko,
K.H.Teng,
P.H.Liang,
and
A.H.Wang
(2010).
Structure of a heterotetrameric geranyl pyrophosphate synthase from mint (Mentha piperita) reveals intersubunit regulation.
|
| |
Plant Cell,
22,
454-467.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
W.Jahnke,
and
C.Henry
(2010).
An in vitro assay to measure targeted drug delivery to bone mineral.
|
| |
ChemMedChem,
5,
770-776.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
W.Jahnke,
J.M.Rondeau,
S.Cotesta,
A.Marzinzik,
X.Pellé,
M.Geiser,
A.Strauss,
M.Götte,
F.Bitsch,
R.Hemmig,
C.Henry,
S.Lehmann,
J.F.Glickman,
T.P.Roddy,
S.J.Stout,
and
J.R.Green
(2010).
Allosteric non-bisphosphonate FPPS inhibitors identified by fragment-based discovery.
|
| |
Nat Chem Biol,
6,
660-666.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
I.Podgorski
(2009).
Future of anticathepsin K drugs: dual therapy for skeletal disease and atherosclerosis?
|
| |
Future Med Chem,
1,
21-34.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
N.Bivi,
M.Romanello,
R.Harrison,
I.Clarke,
D.C.Hoyle,
L.Moro,
F.Ortolani,
A.Bonetti,
F.Quadrifoglio,
G.Tell,
and
D.Delneri
(2009).
Identification of secondary targets of N-containing bisphosphonates in mammalian cells via parallel competition analysis of the barcoded yeast deletion collection.
|
| |
Genome Biol,
10,
R93.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
Y.Zhang,
R.Cao,
F.Yin,
M.P.Hudock,
R.T.Guo,
K.Krysiak,
S.Mukherjee,
Y.G.Gao,
H.Robinson,
Y.Song,
J.H.No,
K.Bergan,
A.Leon,
L.Cass,
A.Goddard,
T.K.Chang,
F.Y.Lin,
E.Van Beek,
S.Papapoulos,
A.H.Wang,
T.Kubo,
M.Ochi,
D.Mukkamala,
and
E.Oldfield
(2009).
Lipophilic bisphosphonates as dual farnesyl/geranylgeranyl diphosphate synthase inhibitors: an X-ray and NMR investigation.
|
| |
J Am Chem Soc,
131,
5153-5162.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
C.K-M Chen,
M.P.Hudock,
Y.Zhang,
R.T.Guo,
R.Cao,
J.H.No,
P.H.Liang,
T.P.Ko,
T.H.Chang,
S.C.Chang,
Y.Song,
J.Axelson,
A.Kumar,
A.H.Wang,
and
E.Oldfield
(2008).
Inhibition of geranylgeranyl diphosphate synthase by bisphosphonates: a crystallographic and computational investigation.
|
| |
J Med Chem,
51,
5594-5607.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
J.D.Artz,
J.E.Dunford,
M.J.Arrowood,
A.Dong,
M.Chruszcz,
K.L.Kavanagh,
W.Minor,
R.G.Russell,
F.H.Ebetino,
U.Oppermann,
and
R.Hui
(2008).
Targeting a uniquely nonspecific prenyl synthase with bisphosphonates to combat cryptosporidiosis.
|
| |
Chem Biol,
15,
1296-1306.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
R.G.Russell,
N.B.Watts,
F.H.Ebetino,
and
M.J.Rogers
(2008).
Mechanisms of action of bisphosphonates: similarities and differences and their potential influence on clinical efficacy.
|
| |
Osteoporos Int,
19,
733-759.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
C.T.Morita,
C.Jin,
G.Sarikonda,
and
H.Wang
(2007).
Nonpeptide antigens, presentation mechanisms, and immunological memory of human Vgamma2Vdelta2 T cells: discriminating friend from foe through the recognition of prenyl pyrophosphate antigens.
|
| |
Immunol Rev,
215,
59-76.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
H.Mönkkönen,
P.D.Ottewell,
J.Kuokkanen,
J.Mönkkönen,
S.Auriola,
and
I.Holen
(2007).
Zoledronic acid-induced IPP/ApppI production in vivo.
|
| |
Life Sci,
81,
1066-1070.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
H.M.Weiss,
B.Wirz,
A.Schweitzer,
R.Amstutz,
M.I.Rodriguez Perez,
H.Andres,
Y.Metz,
J.Gardiner,
and
D.Seebach
(2007).
ADME investigations of unnatural peptides: distribution of a 14C-labeled beta 3-octaarginine in rats.
|
| |
Chem Biodivers,
4,
1413-1437.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.F.Glickman,
and
A.Schmid
(2007).
Farnesyl pyrophosphate synthase: real-time kinetics and inhibition by nitrogen-containing bisphosphonates in a scintillation assay.
|
| |
Assay Drug Dev Technol,
5,
205-214.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
R.T.Guo,
R.Cao,
P.H.Liang,
T.P.Ko,
T.H.Chang,
M.P.Hudock,
W.Y.Jeng,
C.K.Chen,
Y.Zhang,
Y.Song,
C.J.Kuo,
F.Yin,
E.Oldfield,
and
A.H.Wang
(2007).
Bisphosphonates target multiple sites in both cis- and trans-prenyltransferases.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
104,
10022-10027.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
K.L.Kavanagh,
K.Guo,
J.E.Dunford,
X.Wu,
S.Knapp,
F.H.Ebetino,
M.J.Rogers,
R.G.Russell,
and
U.Oppermann
(2006).
The molecular mechanism of nitrogen-containing bisphosphonates as antiosteoporosis drugs.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
103,
7829-7834.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
codes are
shown on the right.
|
 |

