 |
PDBsum entry 2f2d

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Isomerase
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
Solution structure of the fk506-binding domain of human fkbp38
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
38 kda fk-506 binding protein homolog, fkbp38. Chain: a. Fragment: fk506-binding domain, residues 35-153. Synonym: fkbpr38, fk506-binding protein 8. Engineered: yes
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Homo sapiens. Human. Organism_taxid: 9606. Gene: fkbp8, fkbp38. Expressed in: escherichia coli bl21(de3). Expression_system_taxid: 469008.
|
|
NMR struc:
|
 |
20 models
|
 |
|
Authors:
|
 |
M.Maestre-Martinez,F.Edlich,F.Jarczowski,M.Weiwad,G.Fischer,C.Luecke
|
|
Key ref:
|
 |
M.Maestre-Martínez
et al.
(2006).
Solution structure of the FK506-binding domain of human FKBP38.
J Biomol Nmr,
34,
197-202.
PubMed id:
|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
16-Nov-05
|
Release date:
|
02-May-06
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
Q14318
(FKBP8_HUMAN) -
Peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase FKBP8 from Homo sapiens
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
412 a.a.
121 a.a.*
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|
|
Key: |
 |
PfamA domain |
 |
 |
 |
Secondary structure |
 |
 |
CATH domain |
 |
|
*
PDB and UniProt seqs differ
at 2 residue positions (black
crosses)
|
|

|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.5.2.1.8
- peptidylprolyl isomerase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
[protein]-peptidylproline (omega=180) = [protein]-peptidylproline (omega=0)
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
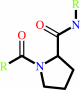 Peptidylproline (omega=180)
Peptidylproline (omega=180)
|
=
|
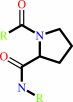 peptidylproline (omega=0)
peptidylproline (omega=0)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
J Biomol Nmr
34:197-202
(2006)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Solution structure of the FK506-binding domain of human FKBP38.
|
|
M.Maestre-Martínez,
F.Edlich,
F.Jarczowski,
M.Weiwad,
G.Fischer,
C.Lücke.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
M.Maestre-Martínez,
K.Haupt,
F.Edlich,
P.Neumann,
C.Parthier,
M.T.Stubbs,
G.Fischer,
and
C.Lücke
(2011).
A charge-sensitive loop in the FKBP38 catalytic domain modulates Bcl-2 binding.
|
| |
J Mol Recognit,
24,
23-34.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Maestre-Martínez,
K.Haupt,
F.Edlich,
G.Jahreis,
F.Jarczowski,
F.Erdmann,
G.Fischer,
and
C.Lücke
(2010).
New structural aspects of FKBP38 activation.
|
| |
Biol Chem,
391,
1157-1167.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.E.Ong,
M.Schenone,
A.A.Margolin,
X.Li,
K.Do,
M.K.Doud,
D.R.Mani,
L.Kuai,
X.Wang,
J.L.Wood,
N.J.Tolliday,
A.N.Koehler,
L.A.Marcaurelle,
T.R.Golub,
R.J.Gould,
S.L.Schreiber,
and
S.A.Carr
(2009).
Identifying the proteins to which small-molecule probes and drugs bind in cells.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
106,
4617-4622.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
C.Stordeur,
R.Dallüge,
O.Birkenmeier,
H.Wienk,
R.Rudolph,
C.Lange,
and
C.Lücke
(2008).
The NMR solution structure of the artificial protein M7 matches the computationally designed model.
|
| |
Proteins,
72,
1104-1107.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
D.Ma,
X.Bai,
S.Guo,
and
Y.Jiang
(2008).
The switch I region of Rheb is critical for its interaction with FKBP38.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
283,
25963-25970.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.A.Somarelli,
S.Y.Lee,
J.Skolnick,
and
R.J.Herrera
(2008).
Structure-based classification of 45 FK506-binding proteins.
|
| |
Proteins,
72,
197-208.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
F.Edlich,
M.Maestre-Martínez,
F.Jarczowski,
M.Weiwad,
M.C.Moutty,
M.Malesević,
G.Jahreis,
G.Fischer,
and
C.Lücke
(2007).
A novel calmodulin-Ca2+ target recognition activates the Bcl-2 regulator FKBP38.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
282,
36496-36504.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Geisler,
and
A.Bailly
(2007).
Tête-à-tête: the function of FKBPs in plant development.
|
| |
Trends Plant Sci,
12,
465-473.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.Bailly,
V.Sovero,
and
M.Geisler
(2006).
The Twisted Dwarf's ABC: How Immunophilins Regulate Auxin Transport.
|
| |
Plant Signal Behav,
1,
277-280.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
code is
shown on the right.
|
 |

