 |
PDBsum entry 2ex0
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Transferase
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
Crystal structure of multifunctional sialyltransferase from pasteurella multocida
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
A2,3-sialyltransferase, a2,6-sialyltransferase. Chain: a, b. Engineered: yes. Other_details: the protein has four enzymatic activities
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Pasteurella multocida. Organism_taxid: 747. Strain: pm70. Gene: pm0188. Expressed in: escherichia coli bl21(de3). Expression_system_taxid: 469008.
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
1.65Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.193
|
R-free:
|
0.218
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
L.Ni,M.Sun,X.Chen,A.J.Fisher
|
Key ref:

|
 |
L.Ni
et al.
(2006).
Cytidine 5'-monophosphate (CMP)-induced structural changes in a multifunctional sialyltransferase from Pasteurella multocida.
Biochemistry,
45,
2139-2148.
PubMed id:
DOI:
|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
07-Nov-05
|
Release date:
|
28-Feb-06
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
Q15KI8
(Q15KI8_PASMD) -
Alpha-2,3/2,6-sialyltransferase/sialidase from Pasteurella multocida
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
412 a.a.
392 a.a.*
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|
|
Key: |
 |
 |
Secondary structure |
 |
 |
CATH domain |
 |
|
*
PDB and UniProt seqs differ
at 1 residue position (black
cross)
|
|

|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.2.4.99.6
- Transferred entry: 2.4.3.6.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
CMP-N-acetyl-beta-neuraminate + beta-D-galactosyl-(1->4)-N-acetyl-beta-D- glucosaminyl-R = CMP + N-acetyl-alpha-neuraminyl-(2->3)-beta-D- galactosyl-(1->4)-N-acetyl-beta-D-glucosaminyl-R
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
CMP-N-acetyl-beta-neuraminate
|
+
|
beta-D-galactosyl-(1->4)-N-acetyl-beta-D- glucosaminyl-R
|
=
|
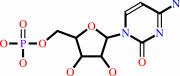 CMP
CMP
|
+
|
N-acetyl-alpha-neuraminyl-(2->3)-beta-D- galactosyl-(1->4)-N-acetyl-beta-D-glucosaminyl-R
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Biochemistry
45:2139-2148
(2006)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Cytidine 5'-monophosphate (CMP)-induced structural changes in a multifunctional sialyltransferase from Pasteurella multocida.
|
|
L.Ni,
M.Sun,
H.Yu,
H.Chokhawala,
X.Chen,
A.J.Fisher.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Sialyltransferases catalyze reactions that transfer a sialic acid from
CMP-sialic acid to an acceptor (a structure terminated with galactose,
N-acetylgalactosamine, or sialic acid). They are key enzymes that catalyze the
synthesis of sialic acid-containing oligosaccharides, polysaccharides, and
glycoconjugates that play pivotal roles in many critical physiological and
pathological processes. The structures of a truncated multifunctional
Pasteurella multocida sialyltransferase (Delta24PmST1), in the absence and
presence of CMP, have been determined by X-ray crystallography at 1.65 and 2.0 A
resolutions, respectively. The Delta24PmST1 exists as a monomer in solution and
in crystals. Different from the reported crystal structure of a bifunctional
sialyltransferase CstII that has only one Rossmann domain, the overall structure
of the Delta24PmST1 consists of two separate Rossmann nucleotide-binding
domains. The Delta24PmST1 structure, thus, represents the first
sialyltransferase structure that belongs to the glycosyltransferase-B (GT-B)
structural group. Unlike all other known GT-B structures, however, there is no
C-terminal extension that interacts with the N-terminal domain in the
Delta24PmST1 structure. The CMP binding site is located in the deep cleft
between the two Rossmann domains. Nevertheless, the CMP only forms interactions
with residues in the C-terminal domain. The binding of CMP to the protein causes
a large closure movement of the N-terminal Rossmann domain toward the C-terminal
nucleotide-binding domain. Ser 143 of the N-terminal domain moves up to
hydrogen-bond to Tyr 388 of the C-terminal domain. Both Ser 143 and Tyr 388 form
hydrogen bonds to a water molecule, which in turn hydrogen-bonds to the terminal
phosphate oxygen of CMP. These interactions may trigger the closure between the
two domains. Additionally, a short helix near the active site seen in the apo
structure becomes disordered upon binding to CMP. This helix may swing down upon
binding to donor CMP-sialic acid to form the binding pocket for an acceptor.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
D.C.Watson,
S.Leclerc,
W.W.Wakarchuk,
and
N.M.Young
(2011).
Enzymatic synthesis and properties of glycoconjugates with legionaminic acid as a replacement for neuraminic acid.
|
| |
Glycobiology,
21,
99.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
G.Sugiarto,
K.Lau,
H.Yu,
S.Vuong,
V.Thon,
Y.Li,
S.Huang,
and
X.Chen
(2011).
Cloning and characterization of a viral {alpha}2-3-sialyltransferase (vST3Gal-I) for the synthesis of sialyl Lewisx.
|
| |
Glycobiology,
21,
387-396.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Audry,
C.Jeanneau,
A.Imberty,
A.Harduin-Lepers,
P.Delannoy,
and
C.Breton
(2011).
Current trends in the structure-activity relationships of sialyltransferases.
|
| |
Glycobiology,
21,
716-726.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.L.Lovering,
L.Y.Lin,
E.W.Sewell,
T.Spreter,
E.D.Brown,
and
N.C.Strynadka
(2010).
Structure of the bacterial teichoic acid polymerase TagF provides insights into membrane association and catalysis.
|
| |
Nat Struct Mol Biol,
17,
582-589.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
X.Chen,
and
A.Varki
(2010).
Advances in the biology and chemistry of sialic acids.
|
| |
ACS Chem Biol,
5,
163-176.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Liu,
L.Meng,
K.W.Moremen,
and
J.H.Prestegard
(2009).
Nuclear magnetic resonance structural characterization of substrates bound to the alpha-2,6-sialyltransferase, ST6Gal-I.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
48,
11211-11219.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.Buschiazzo,
and
P.M.Alzari
(2008).
Structural insights into sialic acid enzymology.
|
| |
Curr Opin Chem Biol,
12,
565-572.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
L.L.Lairson,
B.Henrissat,
G.J.Davies,
and
S.G.Withers
(2008).
Glycosyltransferases: structures, functions, and mechanisms.
|
| |
Annu Rev Biochem,
77,
521-555.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
F.Freiberger,
H.Claus,
A.Günzel,
I.Oltmann-Norden,
J.Vionnet,
M.Mühlenhoff,
U.Vogel,
W.F.Vann,
R.Gerardy-Schahn,
and
K.Stummeyer
(2007).
Biochemical characterization of a Neisseria meningitidis polysialyltransferase reveals novel functional motifs in bacterial sialyltransferases.
|
| |
Mol Microbiol,
65,
1258-1275.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
H.Tsukamoto,
Y.Takakura,
and
T.Yamamoto
(2007).
Purification, cloning, and expression of an alpha/beta-galactoside alpha-2,3-sialyltransferase from a luminous marine bacterium, Photobacterium phosphoreum.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
282,
29794-29802.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
H.Y.Sun,
S.W.Lin,
T.P.Ko,
J.F.Pan,
C.L.Liu,
C.N.Lin,
A.H.Wang,
and
C.H.Lin
(2007).
Structure and mechanism of Helicobacter pylori fucosyltransferase. A basis for lipopolysaccharide variation and inhibitor design.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
282,
9973-9982.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
N.Okino,
Y.Kakuta,
H.Kajiwara,
M.Ichikawa,
Y.Takakura,
M.Ito,
and
T.Yamamoto
(2007).
Purification, crystallization and preliminary crystallographic characterization of the alpha 2,6-sialyltransferase from Photobacterium sp. JT-ISH-224.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun,
63,
662-664.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Liu,
A.Venot,
L.Meng,
F.Tian,
K.W.Moremen,
G.J.Boons,
and
J.H.Prestegard
(2007).
Spin-labeled analogs of CMP-NeuAc as NMR probes of the alpha-2,6-sialyltransferase ST6Gal I.
|
| |
Chem Biol,
14,
409-418.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
codes are
shown on the right.
|
 |

