 |
PDBsum entry 2e9c

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Transferase
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
E. Coli undecaprenyl pyrophosphate synthase in complex with bph-675
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
Undecaprenyl pyrophosphate synthetase. Chain: a, b. Synonym: upp synthetase, di-trans,poly-cis-decaprenylcistransferase, undecaprenyl diphosphate synthase, uds. Engineered: yes
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Escherichia coli. Organism_taxid: 562. Expressed in: escherichia coli. Expression_system_taxid: 469008.
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
2.05Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.209
|
R-free:
|
0.248
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
R.T.Guo,T.P.Ko,R.Cao,P.H.Liang,E.Oldfield,A.H.J.Wang
|
Key ref:

|
 |
R.T.Guo
et al.
(2007).
Bisphosphonates target multiple sites in both cis- and trans-prenyltransferases.
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
104,
10022-10027.
PubMed id:
DOI:

|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
24-Jan-07
|
Release date:
|
12-Jun-07
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
P60472
(UPPS_ECOLI) -
Ditrans,polycis-undecaprenyl-diphosphate synthase ((2E,6E)-farnesyl-diphosphate specific) from Escherichia coli (strain K12)
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
253 a.a.
208 a.a.
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|
|
Key: |
 |
 |
Secondary structure |
 |
 |
CATH domain |
 |
|

|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.2.5.1.31
- ditrans,polycis-undecaprenyl-diphosphate synthase [(2E,6E)-farnesyl-
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

Pathway:
|
 |
Polyprenol biosynthesis
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
8 isopentenyl diphosphate + (2E,6E)-farnesyl diphosphate = di-trans,octa- cis-undecaprenyl diphosphate + 8 diphosphate
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
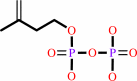 8
×
isopentenyl diphosphate
8
×
isopentenyl diphosphate
|
+
|
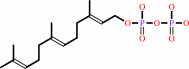 (2E,6E)-farnesyl diphosphate
(2E,6E)-farnesyl diphosphate
|
=
|
 di-trans,octa- cis-undecaprenyl diphosphate
di-trans,octa- cis-undecaprenyl diphosphate
|
+
|
 8
×
diphosphate
8
×
diphosphate
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A
104:10022-10027
(2007)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Bisphosphonates target multiple sites in both cis- and trans-prenyltransferases.
|
|
R.T.Guo,
R.Cao,
P.H.Liang,
T.P.Ko,
T.H.Chang,
M.P.Hudock,
W.Y.Jeng,
C.K.Chen,
Y.Zhang,
Y.Song,
C.J.Kuo,
F.Yin,
E.Oldfield,
A.H.Wang.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Bisphosphonate drugs (e.g., Fosamax and Zometa) are thought to act primarily by
inhibiting farnesyl diphosphate synthase (FPPS), resulting in decreased
prenylation of small GTPases. Here, we show that some bisphosphonates can also
inhibit geranylgeranyl diphosphate synthase (GGPPS), as well as undecaprenyl
diphosphate synthase (UPPS), a cis-prenyltransferase of interest as a target for
antibacterial therapy. Our results on GGPPS (10 structures) show that there are
three bisphosphonate-binding sites, consisting of FPP or isopentenyl diphosphate
substrate-binding sites together with a GGPP product- or inhibitor-binding site.
In UPPS, there are a total of four binding sites (in five structures). These
results are of general interest because they provide the first structures of
GGPPS- and UPPS-inhibitor complexes, potentially important drug targets, in
addition to revealing a remarkably broad spectrum of binding modes not seen in
FPPS inhibition.

|

|
|
|

|
| |
Selected figure(s)
|
|

|
| |
 |
 |

|
 |

|
 |
Figure 2.
Fig. 2. Bisphosphonates and GGPPS structures. (A)
Structures of bisphosphonates investigated as GGPPS inhibitors.
(B) GGPPS structure containing zoledronate (PDB ID code 2E91)
showing dimer structure. (C) Stereoview of minodronate bound to
GGPPS (PDB ID code 2E92). (D) Stereoview of zoledronate/GGPPS
(PDB ID code 2E91) superimposed on zoledronate/IPP/FPPS
structure (PDB ID code 2F8C).
|
 |
Figure 3.
Fig. 3. Structures of hydrophobic bisphosphonates bound to
GGPPS. (A) Stereoview of BPH-675 (PDB ID code 2E95). (B)
Electron density (green contoured at 1  , red at 3 , red at 3  ) for
the two BPH-629 conformers (PDB ID code 2E93). (C) Structure of
BPH-629 bound to GGPPS (monomer A model is shown). ) for
the two BPH-629 conformers (PDB ID code 2E93). (C) Structure of
BPH-629 bound to GGPPS (monomer A model is shown).
|
 |
|
|
| |
Figures were
selected
by an automated process.
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
J.D.Artz,
A.K.Wernimont,
J.E.Dunford,
M.Schapira,
A.Dong,
Y.Zhao,
J.Lew,
R.G.Russell,
F.H.Ebetino,
U.Oppermann,
and
R.Hui
(2011).
Molecular characterization of a novel geranylgeranyl pyrophosphate synthase from Plasmodium parasites.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
286,
3315-3322.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
F.Y.Lin,
C.I.Liu,
Y.L.Liu,
Y.Zhang,
K.Wang,
W.Y.Jeng,
T.P.Ko,
R.Cao,
A.H.Wang,
and
E.Oldfield
(2010).
Mechanism of action and inhibition of dehydrosqualene synthase.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
107,
21337-21342.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
H.J.Choi,
J.Y.Choi,
S.W.Cho,
D.Kang,
K.O.Han,
S.W.Kim,
S.Y.Kim,
Y.S.Chung,
and
C.S.Shin
(2010).
Genetic polymorphism of geranylgeranyl diphosphate synthase (GGSP1) predicts bone density response to bisphosphonate therapy in Korean women.
|
| |
Yonsei Med J,
51,
231-238.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.Green,
and
A.Lipton
(2010).
Anticancer properties of zoledronic acid.
|
| |
Cancer Invest,
28,
944-957.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.H.Lee,
S.Raboune,
J.M.Walker,
and
H.B.Bradshaw
(2010).
Distribution of endogenous farnesyl pyrophosphate and four species of lysophosphatidic Acid in rodent brain.
|
| |
Int J Mol Sci,
11,
3965-3976.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
T.H.Chang,
F.L.Hsieh,
T.P.Ko,
K.H.Teng,
P.H.Liang,
and
A.H.Wang
(2010).
Structure of a heterotetrameric geranyl pyrophosphate synthase from mint (Mentha piperita) reveals intersubunit regulation.
|
| |
Plant Cell,
22,
454-467.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
W.Wang,
K.Wang,
Y.L.Liu,
J.H.No,
J.Li,
M.J.Nilges,
and
E.Oldfield
(2010).
Bioorganometallic mechanism of action, and inhibition, of IspH.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
107,
4522-4527.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
Y.Zhang,
R.Cao,
F.Yin,
F.Y.Lin,
H.Wang,
K.Krysiak,
J.H.No,
D.Mukkamala,
K.Houlihan,
J.Li,
C.T.Morita,
and
E.Oldfield
(2010).
Lipophilic pyridinium bisphosphonates: potent gammadelta T cell stimulators.
|
| |
Angew Chem Int Ed Engl,
49,
1136-1138.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
R.M.Garza,
P.N.Tran,
and
R.Y.Hampton
(2009).
Geranylgeranyl pyrophosphate is a potent regulator of HRD-dependent 3-Hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA reductase degradation in yeast.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
284,
35368-35380.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
T.Nishiguchi,
T.Akiyoshi,
S.Anami,
T.Nakabayashi,
K.Matsuyama,
and
S.Matzno
(2009).
Synergistic action of statins and nitrogen-containing bisphosphonates in the development of rhabdomyolysis in L6 rat skeletal myoblasts.
|
| |
J Pharm Pharmacol,
61,
781-788.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
Y.Zhang,
R.Cao,
F.Yin,
M.P.Hudock,
R.T.Guo,
K.Krysiak,
S.Mukherjee,
Y.G.Gao,
H.Robinson,
Y.Song,
J.H.No,
K.Bergan,
A.Leon,
L.Cass,
A.Goddard,
T.K.Chang,
F.Y.Lin,
E.Van Beek,
S.Papapoulos,
A.H.Wang,
T.Kubo,
M.Ochi,
D.Mukkamala,
and
E.Oldfield
(2009).
Lipophilic bisphosphonates as dual farnesyl/geranylgeranyl diphosphate synthase inhibitors: an X-ray and NMR investigation.
|
| |
J Am Chem Soc,
131,
5153-5162.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
C.I.Liu,
G.Y.Liu,
Y.Song,
F.Yin,
M.E.Hensler,
W.Y.Jeng,
V.Nizet,
A.H.Wang,
and
E.Oldfield
(2008).
A cholesterol biosynthesis inhibitor blocks Staphylococcus aureus virulence.
|
| |
Science,
319,
1391-1394.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
C.J.Kuo,
R.T.Guo,
I.L.Lu,
H.G.Liu,
S.Y.Wu,
T.P.Ko,
A.H.Wang,
and
P.H.Liang
(2008).
Structure-based inhibitors exhibit differential activities against Helicobacter pylori and Escherichia coli undecaprenyl pyrophosphate synthases.
|
| |
J Biomed Biotechnol,
2008,
841312.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
C.K-M Chen,
M.P.Hudock,
Y.Zhang,
R.T.Guo,
R.Cao,
J.H.No,
P.H.Liang,
T.P.Ko,
T.H.Chang,
S.C.Chang,
Y.Song,
J.Axelson,
A.Kumar,
A.H.Wang,
and
E.Oldfield
(2008).
Inhibition of geranylgeranyl diphosphate synthase by bisphosphonates: a crystallographic and computational investigation.
|
| |
J Med Chem,
51,
5594-5607.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
D.Mukkamala,
J.H.No,
L.M.Cass,
T.K.Chang,
and
E.Oldfield
(2008).
Bisphosphonate inhibition of a Plasmodium farnesyl diphosphate synthase and a general method for predicting cell-based activity from enzyme data.
|
| |
J Med Chem,
51,
7827-7833.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.D.Artz,
J.E.Dunford,
M.J.Arrowood,
A.Dong,
M.Chruszcz,
K.L.Kavanagh,
W.Minor,
R.G.Russell,
F.H.Ebetino,
U.Oppermann,
and
R.Hui
(2008).
Targeting a uniquely nonspecific prenyl synthase with bisphosphonates to combat cryptosporidiosis.
|
| |
Chem Biol,
15,
1296-1306.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
J.Weigelt,
L.D.McBroom-Cerajewski,
M.Schapira,
Y.Zhao,
C.H.Arrowsmith,
and
C.H.Arrowmsmith
(2008).
Structural genomics and drug discovery: all in the family.
|
| |
Curr Opin Chem Biol,
12,
32-39.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Noike,
T.Katagiri,
T.Nakayama,
T.Koyama,
T.Nishino,
and
H.Hemmi
(2008).
The product chain length determination mechanism of type II geranylgeranyl diphosphate synthase requires subunit interaction.
|
| |
FEBS J,
275,
3921-3933.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
R.Cao,
C.K.Chen,
R.T.Guo,
A.H.Wang,
and
E.Oldfield
(2008).
Structures of a potent phenylalkyl bisphosphonate inhibitor bound to farnesyl and geranylgeranyl diphosphate synthases.
|
| |
Proteins,
73,
431-439.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
R.Docampo,
and
S.N.Moreno
(2008).
The acidocalcisome as a target for chemotherapeutic agents in protozoan parasites.
|
| |
Curr Pharm Des,
14,
882-888.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.H.Szajnman,
G.E.García Liñares,
Z.H.Li,
C.Jiang,
M.Galizzi,
E.J.Bontempi,
M.Ferella,
S.N.Moreno,
R.Docampo,
and
J.B.Rodriguez
(2008).
Synthesis and biological evaluation of 2-alkylaminoethyl-1,1-bisphosphonic acids against Trypanosoma cruzi and Toxoplasma gondii targeting farnesyl diphosphate synthase.
|
| |
Bioorg Med Chem,
16,
3283-3290.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
codes are
shown on the right.
|
 |

