 |
PDBsum entry 2dyn

|
|
|

|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |

|

|

|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
Signal transduction
|
PDB id
|
|

|

|
2dyn
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.3.6.5.5
- dynamin GTPase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
GTP + H2O = GDP + phosphate + H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 GTP
GTP
|
+
|
H2O
|
=
|
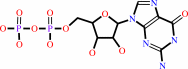 GDP
GDP
|
+
|
 phosphate
phosphate
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
Nat Struct Biol
1:782-788
(1994)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Crystal structure of the pleckstrin homology domain from dynamin.
|
|
D.Timm,
K.Salim,
I.Gout,
L.Guruprasad,
M.Waterfield,
T.Blundell.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
The pleckstrin homology (PH) domain is a conserved module present in many signal
transducing and cytoskeletal proteins. Here we report the 2.8 A crystal
structure of the PH domain from dynamin. This domain consists of seven
beta-strands forming two roughly orthogonal antiparallel beta-sheets terminating
with an amphipathic alpha-helix. The structure also reveals a non-covalent
dimeric association of the PH domain and a hydrophobic pocket surrounded by a
charged rim. The dynamin PH domain structure is discussed in relation to its
potential role in mediating interactions between proteins.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
Q.Xu,
A.Bateman,
R.D.Finn,
P.Abdubek,
T.Astakhova,
H.L.Axelrod,
C.Bakolitsa,
D.Carlton,
C.Chen,
H.J.Chiu,
M.Chiu,
T.Clayton,
D.Das,
M.C.Deller,
L.Duan,
K.Ellrott,
D.Ernst,
C.L.Farr,
J.Feuerhelm,
J.C.Grant,
A.Grzechnik,
G.W.Han,
L.Jaroszewski,
K.K.Jin,
H.E.Klock,
M.W.Knuth,
P.Kozbial,
S.S.Krishna,
A.Kumar,
D.Marciano,
D.McMullan,
M.D.Miller,
A.T.Morse,
E.Nigoghossian,
A.Nopakun,
L.Okach,
C.Puckett,
R.Reyes,
C.L.Rife,
N.Sefcovic,
H.J.Tien,
C.B.Trame,
H.van den Bedem,
D.Weekes,
T.Wooten,
K.O.Hodgson,
J.Wooley,
M.A.Elsliger,
A.M.Deacon,
A.Godzik,
S.A.Lesley,
and
I.A.Wilson
(2010).
Bacterial pleckstrin homology domains: a prokaryotic origin for the PH domain.
|
| |
J Mol Biol,
396,
31-46.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
Y.H.Huang,
and
K.Sauer
(2010).
Lipid signaling in T-cell development and function.
|
| |
Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol,
2,
a002428.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
L.R.Odell,
N.Chau,
A.Mariana,
M.E.Graham,
P.J.Robinson,
and
A.McCluskey
(2009).
Azido and diazarinyl analogues of bis-tyrphostin as asymmetrical inhibitors of dynamin GTPase.
|
| |
ChemMedChem,
4,
1182-1188.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.A.Mears,
P.Ray,
and
J.E.Hinshaw
(2007).
A corkscrew model for dynamin constriction.
|
| |
Structure,
15,
1190-1202.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.Chugh,
A.Chatterjee,
A.Kumar,
R.K.Mishra,
R.Mittal,
and
R.V.Hosur
(2006).
Structural characterization of the large soluble oligomers of the GTPase effector domain of dynamin.
|
| |
FEBS J,
273,
388-397.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
G.E.Cozier,
D.Bouyoucef,
and
P.J.Cullen
(2003).
Engineering the phosphoinositide-binding profile of a class I pleckstrin homology domain.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
278,
39489-39496.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
F.M.Brodsky,
C.Y.Chen,
C.Knuehl,
M.C.Towler,
and
D.E.Wakeham
(2001).
Biological basket weaving: formation and function of clathrin-coated vesicles.
|
| |
Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol,
17,
517-568.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
P.Zhang,
and
J.E.Hinshaw
(2001).
Three-dimensional reconstruction of dynamin in the constricted state.
|
| |
Nat Cell Biol,
3,
922-926.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
D.E.Wakeham,
J.A.Ybe,
F.M.Brodsky,
and
P.K.Hwang
(2000).
Molecular structures of proteins involved in vesicle coat formation.
|
| |
Traffic,
1,
393-398.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
D.J.Owen,
and
J.P.Luzio
(2000).
Structural insights into clathrin-mediated endocytosis.
|
| |
Curr Opin Cell Biol,
12,
467-474.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.E.Hinshaw
(2000).
Dynamin and its role in membrane fission.
|
| |
Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol,
16,
483-519.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.H.Hurley,
and
S.Misra
(2000).
Signaling and subcellular targeting by membrane-binding domains.
|
| |
Annu Rev Biophys Biomol Struct,
29,
49-79.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Ogasawara,
S.C.Kim,
R.Adamik,
A.Togawa,
V.J.Ferrans,
K.Takeda,
M.Kirby,
J.Moss,
and
M.Vaughan
(2000).
Similarities in function and gene structure of cytohesin-4 and cytohesin-1, guanine nucleotide-exchange proteins for ADP-ribosylation factors.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
275,
3221-3230.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.D.Ma,
and
C.S.Abrams
(1999).
Pleckstrin induces cytoskeletal reorganization via a Rac-dependent pathway.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
274,
28730-28735.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.E.Hinshaw
(1999).
Dynamin spirals.
|
| |
Curr Opin Struct Biol,
9,
260-267.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
L.Yao,
P.Janmey,
L.G.Frigeri,
W.Han,
J.Fujita,
Y.Kawakami,
J.R.Apgar,
and
T.Kawakami
(1999).
Pleckstrin homology domains interact with filamentous actin.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
274,
19752-19761.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
Y.Vallis,
P.Wigge,
B.Marks,
P.R.Evans,
and
H.T.McMahon
(1999).
Importance of the pleckstrin homology domain of dynamin in clathrin-mediated endocytosis.
|
| |
Curr Biol,
9,
257-260.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
D.E.Klein,
A.Lee,
D.W.Frank,
M.S.Marks,
and
M.A.Lemmon
(1998).
The pleckstrin homology domains of dynamin isoforms require oligomerization for high affinity phosphoinositide binding.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
273,
27725-27733.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.A.Pitcher,
N.J.Freedman,
and
R.J.Lefkowitz
(1998).
G protein-coupled receptor kinases.
|
| |
Annu Rev Biochem,
67,
653-692.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.M.Kavran,
D.E.Klein,
A.Lee,
M.Falasca,
S.J.Isakoff,
E.Y.Skolnik,
and
M.A.Lemmon
(1998).
Specificity and promiscuity in phosphoinositide binding by pleckstrin homology domains.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
273,
30497-30508.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.J.Bottomley,
K.Salim,
and
G.Panayotou
(1998).
Phospholipid-binding protein domains.
|
| |
Biochim Biophys Acta,
1436,
165-183.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.J.Rebecchi,
and
S.Scarlata
(1998).
Pleckstrin homology domains: a common fold with diverse functions.
|
| |
Annu Rev Biophys Biomol Struct,
27,
503-528.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.D.Ma,
L.F.Brass,
and
C.S.Abrams
(1997).
Pleckstrin associates with plasma membranes and induces the formation of membrane projections: requirements for phosphorylation and the NH2-terminal PH domain.
|
| |
J Cell Biol,
136,
1071-1079.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
C.R.Artalejo,
M.A.Lemmon,
J.Schlessinger,
and
H.C.Palfrey
(1997).
Specific role for the PH domain of dynamin-1 in the regulation of rapid endocytosis in adrenal chromaffin cells.
|
| |
EMBO J,
16,
1565-1574.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
L.E.Rameh,
A.Arvidsson,
K.L.Carraway,
A.D.Couvillon,
G.Rathbun,
A.Crompton,
B.VanRenterghem,
M.P.Czech,
K.S.Ravichandran,
S.J.Burakoff,
D.S.Wang,
C.S.Chen,
and
L.C.Cantley
(1997).
A comparative analysis of the phosphoinositide binding specificity of pleckstrin homology domains.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
272,
22059-22066.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
P.M.Okamoto,
J.S.Herskovits,
and
R.B.Vallee
(1997).
Role of the basic, proline-rich region of dynamin in Src homology 3 domain binding and endocytosis.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
272,
11629-11635.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
R.M.Scaife,
and
R.L.Margolis
(1997).
The role of the PH domain and SH3 binding domains in dynamin function.
|
| |
Cell Signal,
9,
395-401.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
W.D.Singer,
H.A.Brown,
and
P.C.Sternweis
(1997).
Regulation of eukaryotic phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C and phospholipase D.
|
| |
Annu Rev Biochem,
66,
475-509.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
C.S.Abrams,
W.Zhao,
and
L.F.Brass
(1996).
A site of interaction between pleckstrin's PH domains and G beta gamma.
|
| |
Biochim Biophys Acta,
1314,
233-238.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.A.Pitcher,
Z.L.Fredericks,
W.C.Stone,
R.T.Premont,
R.H.Stoffel,
W.J.Koch,
and
R.J.Lefkowitz
(1996).
Phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate (PIP2)-enhanced G protein-coupled receptor kinase (GRK) activity. Location, structure, and regulation of the PIP2 binding site distinguishes the GRK subfamilies.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
271,
24907-24913.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.Font de Mora,
C.Guerrero,
D.Mahadevan,
J.J.Coque,
J.M.Rojas,
L.M.Esteban,
M.Rebecchi,
and
E.Santos
(1996).
Isolated Sos1 PH domain exhibits germinal vesicle breakdown-inducing activity in Xenopus oocytes.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
271,
18272-18276.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.W.Lomasney,
H.F.Cheng,
L.P.Wang,
Y.Kuan,
S.Liu,
S.W.Fesik,
and
K.King
(1996).
Phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate binding to the pleckstrin homology domain of phospholipase C-delta1 enhances enzyme activity.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
271,
25316-25326.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
K.Salim,
M.J.Bottomley,
E.Querfurth,
M.J.Zvelebil,
I.Gout,
R.Scaife,
R.L.Margolis,
R.Gigg,
C.I.Smith,
P.C.Driscoll,
M.D.Waterfield,
and
G.Panayotou
(1996).
Distinct specificity in the recognition of phosphoinositides by the pleckstrin homology domains of dynamin and Bruton's tyrosine kinase.
|
| |
EMBO J,
15,
6241-6250.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.J.McClure,
and
P.J.Robinson
(1996).
Dynamin, endocytosis and intracellular signalling (review).
|
| |
Mol Membr Biol,
13,
189-215.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
Y.Kawakami,
L.Yao,
W.Han,
and
T.Kawakami
(1996).
Tec family protein-tyrosine kinases and pleckstrin homology domains in mast cells.
|
| |
Immunol Lett,
54,
113-117.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
Y.Zheng,
D.Zangrilli,
R.A.Cerione,
and
A.Eva
(1996).
The pleckstrin homology domain mediates transformation by oncogenic dbl through specific intracellular targeting.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
271,
19017-19020.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
C.A.Orengo,
M.B.Swindells,
A.D.Michie,
M.J.Zvelebil,
P.C.Driscoll,
M.D.Waterfield,
and
J.M.Thornton
(1995).
Structural similarity between the pleckstrin homology domain and verotoxin: the problem of measuring and evaluating structural similarity.
|
| |
Protein Sci,
4,
1977-1983.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
C.S.Abrams,
H.Wu,
W.Zhao,
E.Belmonte,
D.White,
and
L.F.Brass
(1995).
Pleckstrin inhibits phosphoinositide hydrolysis initiated by G-protein-coupled and growth factor receptors. A role for pleckstrin's PH domains.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
270,
14485-14492.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
C.S.Abrams,
W.Zhao,
E.Belmonte,
and
L.F.Brass
(1995).
Protein kinase C regulates pleckstrin by phosphorylation of sites adjacent to the N-terminal pleckstrin homology domain.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
270,
23317-23321.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
D.Fushman,
S.Cahill,
M.A.Lemmon,
J.Schlessinger,
and
D.Cowburn
(1995).
Solution structure of pleckstrin homology domain of dynamin by heteronuclear NMR spectroscopy.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
92,
816-820.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.A.Pitcher,
K.Touhara,
E.S.Payne,
and
R.J.Lefkowitz
(1995).
Pleckstrin homology domain-mediated membrane association and activation of the beta-adrenergic receptor kinase requires coordinate interaction with G beta gamma subunits and lipid.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
270,
11707-11710.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
K.Touhara,
W.J.Koch,
B.E.Hawes,
and
R.J.Lefkowitz
(1995).
Mutational analysis of the pleckstrin homology domain of the beta-adrenergic receptor kinase. Differential effects on G beta gamma and phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate binding.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
270,
17000-17005.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
L.M.Luttrell,
B.E.Hawes,
K.Touhara,
T.van Biesen,
W.J.Koch,
and
R.J.Lefkowitz
(1995).
Effect of cellular expression of pleckstrin homology domains on Gi-coupled receptor signaling.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
270,
12984-12989.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.A.Lemmon,
K.M.Ferguson,
R.O'Brien,
P.B.Sigler,
and
J.Schlessinger
(1995).
Specific and high-affinity binding of inositol phosphates to an isolated pleckstrin homology domain.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
92,
10472-10476.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Hyvönen,
M.J.Macias,
M.Nilges,
H.Oschkinat,
M.Saraste,
and
M.Wilmanns
(1995).
Structure of the binding site for inositol phosphates in a PH domain.
|
| |
EMBO J,
14,
4676-4685.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Saraste,
and
M.Hyvönen
(1995).
Pleckstrin homology domains: a fact file.
|
| |
Curr Opin Struct Biol,
5,
403-408.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
P.Zhang,
S.Talluri,
H.Deng,
D.Branton,
and
G.Wagner
(1995).
Solution structure of the pleckstrin homology domain of Drosophila beta-spectrin.
|
| |
Structure,
3,
1185-1195.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
codes are
shown on the right.
|
 |

