 |
PDBsum entry 2dhe

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.3.8.1.5
- haloalkane dehalogenase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
1-haloalkane + H2O = a halide anion + a primary alcohol + H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
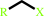 1-haloalkane
1-haloalkane
|
+
|
H2O
|
=
|
halide anion
|
+
|
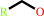 primary alcohol
primary alcohol
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
Nature
363:693-698
(1993)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Crystallographic analysis of the catalytic mechanism of haloalkane dehalogenase.
|
|
K.H.Verschueren,
F.Seljée,
H.J.Rozeboom,
K.H.Kalk,
B.W.Dijkstra.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Crystal structures of haloalkane dehalogenase were determined in the presence of
the substrate 1,2-dichloroethane. At pH 5 and 4 degrees C, substrate is bound in
the active site without being converted; warming to room temperature causes the
substrate's carbon-chlorine bond to be broken, producing a chloride ion with
concomitant alkylation of the active-site residue Asp124. At pH 6 and room
temperature the alkylated enzyme is hydrolysed by a water molecule activated by
the His289-Asp260 pair in the active site. These results show that catalysis by
the dehalogenase proceeds by a two-step mechanism involving an ester
intermediate covalently bound at Asp124.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
R.Shi,
L.McDonald,
Q.Cui,
A.Matte,
M.Cygler,
and
I.Ekiel
(2011).
Structural and mechanistic insight into covalent substrate binding by Escherichia coli dihydroxyacetone kinase.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
108,
1302-1307.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
T.Kurihara
(2011).
A mechanistic analysis of enzymatic degradation of organohalogen compounds.
|
| |
Biosci Biotechnol Biochem,
75,
189-198.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.Lesarri,
A.Vega-Toribio,
R.D.Suenram,
D.J.Brugh,
and
J.U.Grabow
(2010).
The conformational landscape of the volatile anesthetic sevoflurane.
|
| |
Phys Chem Chem Phys,
12,
9624-9631.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
B.Michielsen,
J.J.Dom,
B.J.van der Veken,
S.Hesse,
Z.Xue,
M.A.Suhm,
and
W.A.Herrebout
(2010).
The complexes of halothane with benzene: the temperature dependent direction of the complexation shift of the aliphatic C-H stretching.
|
| |
Phys Chem Chem Phys,
12,
14034-14044.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
D.J.Sukovich,
J.L.Seffernick,
J.E.Richman,
J.A.Gralnick,
and
L.P.Wackett
(2010).
Widespread head-to-head hydrocarbon biosynthesis in bacteria and role of OleA.
|
| |
Appl Environ Microbiol,
76,
3850-3862.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
D.O'Hagan,
and
J.W.Schmidberger
(2010).
Enzymes that catalyse SN2 reaction mechanisms.
|
| |
Nat Prod Rep,
27,
900-918.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
G.Wang,
R.Li,
S.Li,
and
J.Jiang
(2010).
A novel hydrolytic dehalogenase for the chlorinated aromatic compound chlorothalonil.
|
| |
J Bacteriol,
192,
2737-2745.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
L.Simón,
F.M.Muñiz,
A.F.de Arriba,
V.Alcázar,
C.Raposo,
and
J.R.Morán
(2010).
Synthesis of a chiral artificial receptor with catalytic activity in Michael additions and its chiral resolution by a new methodology.
|
| |
Org Biomol Chem,
8,
1763-1768.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
P.Domínguez de María,
R.W.van Gemert,
A.J.Straathof,
and
U.Hanefeld
(2010).
Biosynthesis of ethers: unusual or common natural events?
|
| |
Nat Prod Rep,
27,
370-392.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
R.A.Steiner,
H.J.Janssen,
P.Roversi,
A.J.Oakley,
and
S.Fetzner
(2010).
Structural basis for cofactor-independent dioxygenation of N-heteroaromatic compounds at the alpha/beta-hydrolase fold.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
107,
657-662.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
B.A.Robertson,
G.K.Schroeder,
Z.Jin,
K.A.Johnson,
and
C.P.Whitman
(2009).
Pre-steady-state kinetic analysis of cis-3-chloroacrylic acid dehalogenase: analysis and implications.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
48,
11737-11744.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
D.Makuc,
M.Lenarcic,
G.W.Bates,
P.A.Gale,
and
J.Plavec
(2009).
Anion-induced conformational changes in 2,7-disubstituted indole-based receptors.
|
| |
Org Biomol Chem,
7,
3505-3511.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
K.Jitsumori,
R.Omi,
T.Kurihara,
A.Kurata,
H.Mihara,
I.Miyahara,
K.Hirotsu,
and
N.Esaki
(2009).
X-Ray crystallographic and mutational studies of fluoroacetate dehalogenase from Burkholderia sp. strain FA1.
|
| |
J Bacteriol,
191,
2630-2637.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Pavlova,
M.Klvana,
Z.Prokop,
R.Chaloupkova,
P.Banas,
M.Otyepka,
R.C.Wade,
M.Tsuda,
Y.Nagata,
and
J.Damborsky
(2009).
Redesigning dehalogenase access tunnels as a strategy for degrading an anthropogenic substrate.
|
| |
Nat Chem Biol,
5,
727-733.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Sunbul,
and
J.Yin
(2009).
Site specific protein labeling by enzymatic posttranslational modification.
|
| |
Org Biomol Chem,
7,
3361-3371.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
T.Kamachi,
T.Nakayama,
O.Shitamichi,
K.Jitsumori,
T.Kurihara,
N.Esaki,
and
K.Yoshizawa
(2009).
The catalytic mechanism of fluoroacetate dehalogenase: a computational exploration of biological dehalogenation.
|
| |
Chemistry,
15,
7394-7403.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
C.Caltagirone,
P.A.Gale,
J.R.Hiscock,
S.J.Brooks,
M.B.Hursthouse,
and
M.E.Light
(2008).
1,3-Diindolylureas: high affinity dihydrogen phosphate receptors.
|
| |
Chem Commun (Camb),
(),
3007-3009.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
E.Yaffe,
D.Fishelovitch,
H.J.Wolfson,
D.Halperin,
and
R.Nussinov
(2008).
MolAxis: efficient and accurate identification of channels in macromolecules.
|
| |
Proteins,
73,
72-86.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Otyepka,
P.Banás,
A.Magistrato,
P.Carloni,
and
J.Damborský
(2008).
Second step of hydrolytic dehalogenation in haloalkane dehalogenase investigated by QM/MM methods.
|
| |
Proteins,
70,
707-717.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
P.A.Gale
(2008).
Synthetic indole, carbazole, biindole and indolocarbazole-based receptors: applications in anion complexation and sensing.
|
| |
Chem Commun (Camb),
(),
4525-4540.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
U.I.Kim,
J.M.Suk,
V.R.Naidu,
and
K.S.Jeong
(2008).
Folding and anion-binding properties of fluorescent oligoindole foldamers.
|
| |
Chemistry,
14,
11406-11414.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
E.J.Bertaccini,
J.R.Trudell,
and
N.P.Franks
(2007).
The common chemical motifs within anesthetic binding sites.
|
| |
Anesth Analg,
104,
318-324.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Ito,
Z.Prokop,
M.Klvana,
Y.Otsubo,
M.Tsuda,
J.Damborský,
and
Y.Nagata
(2007).
Degradation of beta-hexachlorocyclohexane by haloalkane dehalogenase LinB from gamma-hexachlorocyclohexane-utilizing bacterium Sphingobium sp. MI1205.
|
| |
Arch Microbiol,
188,
313-325.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
R.Omi,
K.Jitsumori,
T.Yamauchi,
S.Ichiyama,
T.Kurihara,
N.Esaki,
N.Kamiya,
K.Hirotsu,
and
I.Miyahara
(2007).
Expression, purification and preliminary X-ray characterization of DL-2-haloacid dehalogenase from Methylobacterium sp. CPA1.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun,
63,
586-589.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
X.Liu,
B.L.Hanson,
P.Langan,
and
R.E.Viola
(2007).
The effect of deuteration on protein structure: a high-resolution comparison of hydrogenous and perdeuterated haloalkane dehalogenase.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr,
63,
1000-1008.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
Y.Sato,
R.Natsume,
M.Tsuda,
J.Damborsky,
Y.Nagata,
and
T.Senda
(2007).
Crystallization and preliminary crystallographic analysis of a haloalkane dehalogenase, DbjA, from Bradyrhizobium japonicum USDA110.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun,
63,
294-296.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Nikolausz,
I.Nijenhuis,
K.Ziller,
H.H.Richnow,
and
M.Kästner
(2006).
Stable carbon isotope fractionation during degradation of dichloromethane by methylotrophic bacteria.
|
| |
Environ Microbiol,
8,
156-164.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Petrek,
M.Otyepka,
P.Banás,
P.Kosinová,
J.Koca,
and
J.Damborský
(2006).
CAVER: a new tool to explore routes from protein clefts, pockets and cavities.
|
| |
BMC Bioinformatics,
7,
316.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
P.Banás,
M.Otyepka,
P.Jerábek,
M.Petrek,
and
J.Damborský
(2006).
Mechanism of enhanced conversion of 1,2,3-trichloropropane by mutant haloalkane dehalogenase revealed by molecular modeling.
|
| |
J Comput Aided Mol Des,
20,
375-383.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
Z.Hasan,
R.Renirie,
R.Kerkman,
H.J.Ruijssenaars,
A.F.Hartog,
and
R.Wever
(2006).
Laboratory-evolved vanadium chloroperoxidase exhibits 100-fold higher halogenating activity at alkaline pH: catalytic effects from first and second coordination sphere mutations.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
281,
9738-9744.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.Jesenská,
M.Pavlová,
M.Strouhal,
R.Chaloupková,
I.Tesínská,
M.Monincová,
Z.Prokop,
M.Bartos,
I.Pavlík,
I.Rychlík,
P.Möbius,
Y.Nagata,
and
J.Damborsky
(2005).
Cloning, biochemical properties, and distribution of mycobacterial haloalkane dehalogenases.
|
| |
Appl Environ Microbiol,
71,
6736-6745.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
C.Morisseau,
and
B.D.Hammock
(2005).
Epoxide hydrolases: mechanisms, inhibitor designs, and biological roles.
|
| |
Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol,
45,
311-333.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
D.B.Janssen,
I.J.Dinkla,
G.J.Poelarends,
and
P.Terpstra
(2005).
Bacterial degradation of xenobiotic compounds: evolution and distribution of novel enzyme activities.
|
| |
Environ Microbiol,
7,
1868-1882.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
E.Blée,
S.Summerer,
M.Flenet,
H.Rogniaux,
A.Van Dorsselaer,
and
F.Schuber
(2005).
Soybean epoxide hydrolase: identification of the catalytic residues and probing of the reaction mechanism with secondary kinetic isotope effects.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
280,
6479-6487.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
U.Frerichs-Deeken,
and
S.Fetzner
(2005).
Dioxygenases without requirement for cofactors: identification of amino acid residues involved in substrate binding and catalysis, and testing for rate-limiting steps in the reaction of 1H-3-hydroxy-4-oxoquinaldine 2,4-dioxygenase.
|
| |
Curr Microbiol,
51,
344-352.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
Y.Sato,
M.Monincová,
R.Chaloupková,
Z.Prokop,
Y.Ohtsubo,
K.Minamisawa,
M.Tsuda,
J.Damborsky,
and
Y.Nagata
(2005).
Two rhizobial strains, Mesorhizobium loti MAFF303099 and Bradyrhizobium japonicum USDA110, encode haloalkane dehalogenases with novel structures and substrate specificities.
|
| |
Appl Environ Microbiol,
71,
4372-4379.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
D.B.Janssen
(2004).
Evolving haloalkane dehalogenases.
|
| |
Curr Opin Chem Biol,
8,
150-159.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
L.Rui,
L.Cao,
W.Chen,
K.F.Reardon,
and
T.K.Wood
(2004).
Active site engineering of the epoxide hydrolase from Agrobacterium radiobacter AD1 to enhance aerobic mineralization of cis-1,2-dichloroethylene in cells expressing an evolved toluene ortho-monooxygenase.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
279,
46810-46817.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Garcia-Viloca,
J.Gao,
M.Karplus,
and
D.G.Truhlar
(2004).
How enzymes work: analysis by modern rate theory and computer simulations.
|
| |
Science,
303,
186-195.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
R.M.de Jong,
W.Brugman,
G.J.Poelarends,
C.P.Whitman,
and
B.W.Dijkstra
(2004).
The X-ray structure of trans-3-chloroacrylic acid dehalogenase reveals a novel hydration mechanism in the tautomerase superfamily.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
279,
11546-11552.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
R.Chaloupková,
J.Sýkorová,
Z.Prokop,
A.Jesenská,
M.Monincová,
M.Pavlová,
M.Tsuda,
Y.Nagata,
and
J.Damborský
(2003).
Modification of activity and specificity of haloalkane dehalogenase from Sphingomonas paucimobilis UT26 by engineering of its entrance tunnel.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
278,
52622-52628.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
R.M.de Jong,
and
B.W.Dijkstra
(2003).
Structure and mechanism of bacterial dehalogenases: different ways to cleave a carbon-halogen bond.
|
| |
Curr Opin Struct Biol,
13,
722-730.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
R.M.de Jong,
J.J.Tiesinga,
H.J.Rozeboom,
K.H.Kalk,
L.Tang,
D.B.Janssen,
and
B.W.Dijkstra
(2003).
Structure and mechanism of a bacterial haloalcohol dehalogenase: a new variation of the short-chain dehydrogenase/reductase fold without an NAD(P)H binding site.
|
| |
EMBO J,
22,
4933-4944.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
Y.Nagata,
Z.Prokop,
S.Marvanová,
J.Sýkorová,
M.Monincová,
M.Tsuda,
and
J.Damborský
(2003).
Reconstruction of mycobacterial dehalogenase Rv2579 by cumulative mutagenesis of haloalkane dehalogenase LinB.
|
| |
Appl Environ Microbiol,
69,
2349-2355.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
Z.Prokop,
M.Monincová,
R.Chaloupková,
M.Klvana,
Y.Nagata,
D.B.Janssen,
and
J.Damborský
(2003).
Catalytic mechanism of the maloalkane dehalogenase LinB from Sphingomonas paucimobilis UT26.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
278,
45094-45100.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.J.Oakley,
Z.Prokop,
M.Bohác,
J.Kmunícek,
T.Jedlicka,
M.Monincová,
I.Kutá-Smatanová,
Y.Nagata,
J.Damborský,
and
M.C.Wilce
(2002).
Exploring the structure and activity of haloalkane dehalogenase from Sphingomonas paucimobilis UT26: evidence for product- and water-mediated inhibition.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
41,
4847-4855.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
A.Jesenská,
M.Bartos,
V.Czerneková,
I.Rychlík,
I.Pavlík,
and
J.Damborský
(2002).
Cloning and expression of the haloalkane dehalogenase gene dhmA from Mycobacterium avium N85 and preliminary characterization of DhmA.
|
| |
Appl Environ Microbiol,
68,
3724-3730.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
T.Bosma,
J.Damborský,
G.Stucki,
and
D.B.Janssen
(2002).
Biodegradation of 1,2,3-trichloropropane through directed evolution and heterologous expression of a haloalkane dehalogenase gene.
|
| |
Appl Environ Microbiol,
68,
3582-3587.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
D.A.Whittington,
A.C.Rosenzweig,
C.A.Frederick,
and
S.J.Lippard
(2001).
Xenon and halogenated alkanes track putative substrate binding cavities in the soluble methane monooxygenase hydroxylase.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
40,
3476-3482.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
D.B.Janssen,
J.E.Oppentocht,
and
G.J.Poelarends
(2001).
Microbial dehalogenation.
|
| |
Curr Opin Biotechnol,
12,
254-258.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
G.J.Poelarends,
R.Saunier,
and
D.B.Janssen
(2001).
trans-3-Chloroacrylic acid dehalogenase from Pseudomonas pavonaceae 170 shares structural and mechanistic similarities with 4-oxalocrotonate tautomerase.
|
| |
J Bacteriol,
183,
4269-4277.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.Damborský,
E.Rorije,
A.Jesenská,
Y.Nagata,
G.Klopman,
and
W.J.Peijnenburg
(2001).
Structure-specificity relationships for haloalkane dehalogenases.
|
| |
Environ Toxicol Chem,
20,
2681-2689.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.E.van Hylckama Vlieg,
L.Tang,
J.H.Lutje Spelberg,
T.Smilda,
G.J.Poelarends,
T.Bosma,
A.E.van Merode,
M.W.Fraaije,
and
D.B.Janssen
(2001).
Halohydrin dehalogenases are structurally and mechanistically related to short-chain dehydrogenases/reductases.
|
| |
J Bacteriol,
183,
5058-5066.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.Hartleib,
and
H.Rüterjans
(2001).
Insights into the reaction mechanism of the diisopropyl fluorophosphatase from Loligo vulgaris by means of kinetic studies, chemical modification and site-directed mutagenesis.
|
| |
Biochim Biophys Acta,
1546,
312-324.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.S.Brody,
K.Vijay,
and
C.W.Price
(2001).
Catalytic function of an alpha/beta hydrolase is required for energy stress activation of the sigma(B) transcription factor in Bacillus subtilis.
|
| |
J Bacteriol,
183,
6422-6428.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
B.Golinelli-Pimpaneau,
O.Goncalves,
T.Dintinger,
D.Blanchard,
M.Knossow,
and
C.Tellier
(2000).
Structural evidence for a programmed general base in the active site of a catalytic antibody.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
97,
9892-9895.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
D.Hunkeler,
and
R.Aravena
(2000).
Evidence of substantial carbon isotope fractionation among substrate, inorganic carbon, and biomass during aerobic mineralization of 1, 2-dichloroethane by Xanthobacter autotrophicus.
|
| |
Appl Environ Microbiol,
66,
4870-4876.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
E.Y.Lau,
K.Kahn,
P.A.Bash,
and
T.C.Bruice
(2000).
The importance of reactant positioning in enzyme catalysis: a hybrid quantum mechanics/molecular mechanics study of a haloalkane dehalogenase.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
97,
9937-9942.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.Zou,
B.M.Hallberg,
T.Bergfors,
F.Oesch,
M.Arand,
S.L.Mowbray,
and
T.A.Jones
(2000).
Structure of Aspergillus niger epoxide hydrolase at 1.8 A resolution: implications for the structure and function of the mammalian microsomal class of epoxide hydrolases.
|
| |
Structure,
8,
111-122.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
C.Morisseau,
A.Archelas,
C.Guitton,
D.Faucher,
R.Furstoss,
and
J.C.Baratti
(1999).
Purification and characterization of a highly enantioselective epoxide hydrolase from Aspergillus niger.
|
| |
Eur J Biochem,
263,
386-395.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
C.Morisseau,
B.L.Ward,
D.G.Gilchrist,
and
B.D.Hammock
(1999).
Multiple epoxide hydrolases in Alternaria alternata f. sp. lycopersici and their relationship to medium composition and host-specific toxin production.
|
| |
Appl Environ Microbiol,
65,
2388-2395.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
F.Fischer,
S.Künne,
and
S.Fetzner
(1999).
Bacterial 2,4-dioxygenases: new members of the alpha/beta hydrolase-fold superfamily of enzymes functionally related to serine hydrolases.
|
| |
J Bacteriol,
181,
5725-5733.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
G.H.Krooshof,
R.Floris,
A.W.Tepper,
and
D.B.Janssen
(1999).
Thermodynamic analysis of halide binding to haloalkane dehalogenase suggests the occurrence of large conformational changes.
|
| |
Protein Sci,
8,
355-360.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
H.Naested,
M.Fennema,
L.Hao,
M.Andersen,
D.B.Janssen,
and
J.Mundy
(1999).
A bacterial haloalkane dehalogenase gene as a negative selectable marker in Arabidopsis.
|
| |
Plant J,
18,
571-576.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
I.S.Ridder,
H.J.Rozeboom,
and
B.W.Dijkstra
(1999).
Haloalkane dehalogenase from Xanthobacter autotrophicus GJ10 refined at 1.15 A resolution.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr,
55,
1273-1290.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
I.S.Ridder,
H.J.Rozeboom,
K.H.Kalk,
and
B.W.Dijkstra
(1999).
Crystal structures of intermediates in the dehalogenation of haloalkanoates by L-2-haloacid dehalogenase.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
274,
30672-30678.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
J.F.Schindler,
P.A.Naranjo,
D.A.Honaberger,
C.H.Chang,
J.R.Brainard,
L.A.Vanderberg,
and
C.J.Unkefer
(1999).
Haloalkane dehalogenases: steady-state kinetics and halide inhibition.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
38,
5772-5778.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.Newman,
T.S.Peat,
R.Richard,
L.Kan,
P.E.Swanson,
J.A.Affholter,
I.H.Holmes,
J.F.Schindler,
C.J.Unkefer,
and
T.C.Terwilliger
(1999).
Haloalkane dehalogenases: structure of a Rhodococcus enzyme.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
38,
16105-16114.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
K.E.Jaeger,
B.W.Dijkstra,
and
M.T.Reetz
(1999).
Bacterial biocatalysts: molecular biology, three-dimensional structures, and biotechnological applications of lipases.
|
| |
Annu Rev Microbiol,
53,
315-351.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.A.Argiriadi,
C.Morisseau,
B.D.Hammock,
and
D.W.Christianson
(1999).
Detoxification of environmental mutagens and carcinogens: structure, mechanism, and evolution of liver epoxide hydrolase.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
96,
10637-10642.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Nardini,
I.S.Ridder,
H.J.Rozeboom,
K.H.Kalk,
R.Rink,
D.B.Janssen,
and
B.W.Dijkstra
(1999).
The x-ray structure of epoxide hydrolase from Agrobacterium radiobacter AD1. An enzyme to detoxify harmful epoxides.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
274,
14579-14586.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
R.V.Orru,
and
K.Faber
(1999).
Stereoselectivities of microbial epoxide hydrolases.
|
| |
Curr Opin Chem Biol,
3,
16-21.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
V.Nardi-Dei,
T.Kurihara,
C.Park,
M.Miyagi,
S.Tsunasawa,
K.Soda,
and
N.Esaki
(1999).
DL-2-Haloacid dehalogenase from Pseudomonas sp. 113 is a new class of dehalogenase catalyzing hydrolytic dehalogenation not involving enzyme-substrate ester intermediate.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
274,
20977-20981.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
W.Chen,
F.Brühlmann,
R.D.Richins,
and
A.Mulchandani
(1999).
Engineering of improved microbes and enzymes for bioremediation.
|
| |
Curr Opin Biotechnol,
10,
137-141.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.Warshel,
and
J.Florián
(1998).
Computer simulations of enzyme catalysis: finding out what has been optimized by evolution.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
95,
5950-5955.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
D.J.Quirk,
C.Park,
J.E.Thompson,
and
R.T.Raines
(1998).
His...Asp catalytic dyad of ribonuclease A: conformational stability of the wild-type, D121N, D121A, and H119A enzymes.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
37,
17958-17964.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
E.Blée
(1998).
Phytooxylipins and plant defense reactions.
|
| |
Prog Lipid Res,
37,
33-72.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
G.H.Krooshof,
I.S.Ridder,
A.W.Tepper,
G.J.Vos,
H.J.Rozeboom,
K.H.Kalk,
B.W.Dijkstra,
and
D.B.Janssen
(1998).
Kinetic analysis and X-ray structure of haloalkane dehalogenase with a modified halide-binding site.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
37,
15013-15023.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
G.J.Davies,
L.Mackenzie,
A.Varrot,
M.Dauter,
A.M.Brzozowski,
M.Schülein,
and
S.G.Withers
(1998).
Snapshots along an enzymatic reaction coordinate: analysis of a retaining beta-glycoside hydrolase.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
37,
11707-11713.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
H.F.Tzeng,
L.T.Laughlin,
and
R.N.Armstrong
(1998).
Semifunctional site-specific mutants affecting the hydrolytic half-reaction of microsomal epoxide hydrolase.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
37,
2905-2911.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.Q.Liu,
T.Kurihara,
S.Ichiyama,
M.Miyagi,
S.Tsunasawa,
H.Kawasaki,
K.Soda,
and
N.Esaki
(1998).
Reaction mechanism of fluoroacetate dehalogenase from Moraxella sp. B.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
273,
30897-30902.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.U.Flanagan,
J.Rossjohn,
M.W.Parker,
P.G.Board,
and
G.Chelvanayagam
(1998).
A homology model for the human theta-class glutathione transferase T1-1.
|
| |
Proteins,
33,
444-454.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
L.T.Laughlin,
H.F.Tzeng,
S.Lin,
and
R.N.Armstrong
(1998).
Mechanism of microsomal epoxide hydrolase. Semifunctional site-specific mutants affecting the alkylation half-reaction.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
37,
2897-2904.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
L.W.Schultz,
D.J.Quirk,
and
R.T.Raines
(1998).
His...Asp catalytic dyad of ribonuclease A: structure and function of the wild-type, D121N, and D121A enzymes.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
37,
8886-8898.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
P.Holloway,
K.L.Knoke,
J.T.Trevors,
and
H.Lee
(1998).
Alteration of the substrate range of haloalkane dehalogenase by site-directed mutagenesis.
|
| |
Biotechnol Bioeng,
59,
520-523.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
R.Rink,
and
D.B.Janssen
(1998).
Kinetic mechanism of the enantioselective conversion of styrene oxide by epoxide hydrolase from Agrobacterium radiobacter AD1.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
37,
18119-18127.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.D.Copley
(1998).
Microbial dehalogenases: enzymes recruited to convert xenobiotic substrates.
|
| |
Curr Opin Chem Biol,
2,
613-617.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
Y.F.Li,
Y.Hata,
T.Fujii,
T.Hisano,
M.Nishihara,
T.Kurihara,
and
N.Esaki
(1998).
Crystal structures of reaction intermediates of L-2-haloacid dehalogenase and implications for the reaction mechanism.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
273,
15035-15044.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
A.C.Wallace,
N.Borkakoti,
and
J.M.Thornton
(1997).
TESS: a geometric hashing algorithm for deriving 3D coordinate templates for searching structural databases. Application to enzyme active sites.
|
| |
Protein Sci,
6,
2308-2323.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.H.Maulitz,
F.C.Lightstone,
Y.J.Zheng,
and
T.C.Bruice
(1997).
Nonenzymatic and enzymatic hydrolysis of alkyl halides: a theoretical study of the SN2 reactions of acetate and hydroxide ions with alkyl chlorides.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
94,
6591-6595.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.Marsh,
and
D.M.Ferguson
(1997).
Knowledge-based modeling of a bacterial dichloromethane dehalogenase.
|
| |
Proteins,
28,
217-226.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
F.C.Lightstone,
Y.J.Zheng,
A.H.Maulitz,
and
T.C.Bruice
(1997).
Non-enzymatic and enzymatic hydrolysis of alkyl halides: a haloalkane dehalogenation enzyme evolved to stabilize the gas-phase transition state of an SN2 displacement reaction.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
94,
8417-8420.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
F.Müller,
M.Arand,
H.Frank,
A.Seidel,
W.Hinz,
L.Winkler,
K.Hänel,
E.Blée,
J.K.Beetham,
B.D.Hammock,
and
F.Oesch
(1997).
Visualization of a covalent intermediate between microsomal epoxide hydrolase, but not cholesterol epoxide hydrolase, and their substrates.
|
| |
Eur J Biochem,
245,
490-496.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
G.H.Krooshof,
E.M.Kwant,
J.Damborský,
J.Koca,
and
D.B.Janssen
(1997).
Repositioning the catalytic triad aspartic acid of haloalkane dehalogenase: effects on stability, kinetics, and structure.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
36,
9571-9580.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
I.S.Ridder,
H.J.Rozeboom,
K.H.Kalk,
D.B.Janssen,
and
B.W.Dijkstra
(1997).
Three-dimensional structure of L-2-haloacid dehalogenase from Xanthobacter autotrophicus GJ10 complexed with the substrate-analogue formate.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
272,
33015-33022.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
J.E.Murphy,
B.Stec,
L.Ma,
and
E.R.Kantrowitz
(1997).
Trapping and visualization of a covalent enzyme-phosphate intermediate.
|
| |
Nat Struct Biol,
4,
618-622.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
J.Q.Liu,
T.Kurihara,
M.Miyagi,
S.Tsunasawa,
M.Nishihara,
N.Esaki,
and
K.Soda
(1997).
Paracatalytic inactivation of L-2-haloacid dehalogenase from Pseudomonas sp. YL by hydroxylamine. Evidence for the formation of an ester intermediate.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
272,
3363-3368.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
L.M.Watkins,
H.J.Mahoney,
J.K.McCulloch,
and
F.M.Raushel
(1997).
Augmented hydrolysis of diisopropyl fluorophosphate in engineered mutants of phosphotriesterase.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
272,
25596-25601.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.B.Andberg,
M.Hamberg,
and
J.Z.Haeggström
(1997).
Mutation of tyrosine 383 in leukotriene A4 hydrolase allows conversion of leukotriene A4 into 5S,6S-dihydroxy-7,9-trans-11,14-cis-eicosatetraenoic acid. Implications for the epoxide hydrolase mechanism.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
272,
23057-23063.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.P.Roach,
Y.P.Chen,
S.A.Woodin,
D.E.Lincoln,
C.R.Lovell,
and
J.H.Dawson
(1997).
Notomastus lobatus chloroperoxidase and Amphitrite ornata dehaloperoxidase both contain histidine as their proximal heme iron ligand.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
36,
2197-2202.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.D.Copley
(1997).
Diverse mechanistic approaches to difficult chemical transformations: microbial dehalogenation of chlorinated aromatic compounds.
|
| |
Chem Biol,
4,
169-174.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
Y.Nagata,
K.Miyauchi,
J.Damborsky,
K.Manova,
A.Ansorgova,
and
M.Takagi
(1997).
Purification and characterization of a haloalkane dehalogenase of a new substrate class from a gamma-hexachlorocyclohexane-degrading bacterium, Sphingomonas paucimobilis UT26.
|
| |
Appl Environ Microbiol,
63,
3707-3710.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
B.L.Stoddard,
A.Dean,
and
P.A.Bash
(1996).
Combining Laue diffraction and molecular dynamics to study enzyme intermediates.
|
| |
Nat Struct Biol,
3,
590-595.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
E.M.Jacoby,
I.Schlichting,
C.B.Lantwin,
W.Kabsch,
and
R.L.Krauth-Siegel
(1996).
Crystal structure of the Trypanosoma cruzi trypanothione reductase.mepacrine complex.
|
| |
Proteins,
24,
73-80.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
G.Yang,
R.Q.Liu,
K.L.Taylor,
H.Xiang,
J.Price,
and
D.Dunaway-Mariano
(1996).
Identification of active site residues essential to 4-chlorobenzoyl-coenzyme A dehalogenase catalysis by chemical modification and site directed mutagenesis.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
35,
10879-10885.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.I.Manchester,
and
R.L.Ornstein
(1996).
Rational approach to improving reductive catalysis by cytochrome P450cam.
|
| |
Biochimie,
78,
714-722.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.P.Schanstra,
and
D.B.Janssen
(1996).
Kinetics of halide release of haloalkane dehalogenase: evidence for a slow conformational change.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
35,
5624-5632.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.P.Schanstra,
I.S.Ridder,
G.J.Heimeriks,
R.Rink,
G.J.Poelarends,
K.H.Kalk,
B.W.Dijkstra,
and
D.B.Janssen
(1996).
Kinetic characterization and X-ray structure of a mutant of haloalkane dehalogenase with higher catalytic activity and modified substrate range.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
35,
13186-13195.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
J.P.Schanstra,
J.Kingma,
and
D.B.Janssen
(1996).
Specificity and kinetics of haloalkane dehalogenase.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
271,
14747-14753.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Arand,
H.Wagner,
and
F.Oesch
(1996).
Asp333, Asp495, and His523 form the catalytic triad of rat soluble epoxide hydrolase.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
271,
4223-4229.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
R.G.Eckenhoff
(1996).
Amino acid resolution of halothane binding sites in serum albumin.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
271,
15521-15526.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
T.Hisano,
Y.Hata,
T.Fujii,
J.Q.Liu,
T.Kurihara,
N.Esaki,
and
K.Soda
(1996).
Crystal structure of L-2-haloacid dehalogenase from Pseudomonas sp. YL. An alpha/beta hydrolase structure that is different from the alpha/beta hydrolase fold.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
271,
20322-20330.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
B.Borhan,
A.D.Jones,
F.Pinot,
D.F.Grant,
M.J.Kurth,
and
B.D.Hammock
(1995).
Mechanism of soluble epoxide hydrolase. Formation of an alpha-hydroxy ester-enzyme intermediate through Asp-333.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
270,
26923-26930.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
B.L.Stoddard,
and
G.K.Farber
(1995).
Direct measurement of reactivity in the protein crystal by steady-state kinetic studies.
|
| |
Structure,
3,
991-996.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
C.Kennes,
F.Pries,
G.H.Krooshof,
E.Bokma,
J.Kingma,
and
D.B.Janssen
(1995).
Replacement of tryptophan residues in haloalkane dehalogenase reduces halide binding and catalytic activity.
|
| |
Eur J Biochem,
228,
403-407.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
D.B.Janssen,
J.R.van der Ploeg,
and
F.Pries
(1995).
Genetic adaptation of bacteria to halogenated aliphatic compounds.
|
| |
Environ Health Perspect,
103,
29-32.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
E.Díaz,
and
K.N.Timmis
(1995).
Identification of functional residues in a 2-hydroxymuconic semialdehyde hydrolase. A new member of the alpha/beta hydrolase-fold family of enzymes which cleaves carbon-carbon bonds.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
270,
6403-6411.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
F.Löffler,
F.Lingens,
and
R.Müller
(1995).
Dehalogenation of 4-chlorobenzoate. Characterisation of 4-chlorobenzoyl-coenzyme A dehalogenase from Pseudomonas sp. CBS3.
|
| |
Biodegradation,
6,
203-212.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
F.Pinot,
D.F.Grant,
J.K.Beetham,
A.G.Parker,
B.Borhan,
S.Landt,
A.D.Jones,
and
B.D.Hammock
(1995).
Molecular and biochemical evidence for the involvement of the Asp-333-His-523 pair in the catalytic mechanism of soluble epoxide hydrolase.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
270,
7968-7974.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
F.Pinot,
D.F.Grant,
J.L.Spearow,
A.G.Parker,
and
B.D.Hammock
(1995).
Differential regulation of soluble epoxide hydrolase by clofibrate and sexual hormones in the liver and kidneys of mice.
|
| |
Biochem Pharmacol,
50,
501-508.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
F.Pries,
J.Kingma,
G.H.Krooshof,
C.M.Jeronimus-Stratingh,
A.P.Bruins,
and
D.B.Janssen
(1995).
Histidine 289 is essential for hydrolysis of the alkyl-enzyme intermediate of haloalkane dehalogenase.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
270,
10405-10411.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
I.S.Ridder,
H.J.Rozeboom,
J.Kingma,
D.B.Janssen,
and
B.W.Dijkstra
(1995).
Crystallization and preliminary X-ray analysis of L-2-haloacid dehalogenase from Xanthobacter autotrophicus GJ10.
|
| |
Protein Sci,
4,
2619-2620.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.K.Beetham,
D.Grant,
M.Arand,
J.Garbarino,
T.Kiyosue,
F.Pinot,
F.Oesch,
W.R.Belknap,
K.Shinozaki,
and
B.D.Hammock
(1995).
Gene evolution of epoxide hydrolases and recommended nomenclature.
|
| |
DNA Cell Biol,
14,
61-71.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.Q.Liu,
T.Kurihara,
V.Nardi-Dei,
T.Okamura,
N.Esaki,
and
K.Soda
(1995).
Overexpression and feasible purification of thermostable L-2-halo acid dehalogenase of Pseudomonas sp. YL.
|
| |
Biodegradation,
6,
223-227.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Kocabiyik,
B.Aslan,
and
R.Müller
(1995).
Cloning and expression of a haloacid dehalogenase from Pseudomonas sp. strain 19 S.
|
| |
Biodegradation,
6,
217-222.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
D.B.Janssen,
and
J.P.Schanstra
(1994).
Engineering proteins for environmental applications.
|
| |
Curr Opin Biotechnol,
5,
253-259.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
D.B.Janssen,
J.R.van der Ploeg,
and
F.Pries
(1994).
Genetics and biochemistry of 1,2-dichloroethane degradation.
|
| |
Biodegradation,
5,
249-257.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
F.Pries,
J.R.van der Ploeg,
J.Dolfing,
and
D.B.Janssen
(1994).
Degradation of halogenated aliphatic compounds: the role of adaptation.
|
| |
FEMS Microbiol Rev,
15,
279-295.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.Q.Liu,
T.Kurihara,
A.K.Hasan,
V.Nardi-Dei,
H.Koshikawa,
N.Esaki,
and
K.Soda
(1994).
Purification and characterization of thermostable and nonthermostable 2-haloacid dehalogenases with different stereospecificities from Pseudomonas sp. strain YL.
|
| |
Appl Environ Microbiol,
60,
2389-2393.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
L.P.Wackett
(1994).
Dehalogenation in environmental biotechnology.
|
| |
Curr Opin Biotechnol,
5,
260-265.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
O.Gursky,
E.Fontano,
B.Bhyravbhatla,
and
D.L.Caspar
(1994).
Stereospecific dihaloalkane binding in a pH-sensitive cavity in cubic insulin crystals.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
91,
12388-12392.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
R.C.Prince
(1994).
Haloalkane dehalogenase caught in the act.
|
| |
Trends Biochem Sci,
19,
3-4.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
V.Nardi-Dei,
T.Kurihara,
T.Okamura,
J.Q.Liu,
H.Koshikawa,
H.Ozaki,
Y.Terashima,
N.Esaki,
and
K.Soda
(1994).
Comparative studies of genes encoding thermostable L-2-halo acid dehalogenase from Pseudomonas sp. strain YL, other dehalogenases, and two related hypothetical proteins from Escherichia coli.
|
| |
Appl Environ Microbiol,
60,
3375-3380.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
codes are
shown on the right.
|
 |

