 |
PDBsum entry 2dap

|
|
|

|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |

|

|

|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
Oxidoreductase
|
PDB id
|
|

|

|
2dap
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.1.4.1.16
- diaminopimelate dehydrogenase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
meso-2,6-diaminopimelate + NADP+ + H2O = (S)-2-amino-6-oxoheptanedioate + NH4+ + NADPH + H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
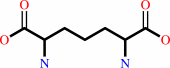 meso-2,6-diaminopimelate
meso-2,6-diaminopimelate
|
+
|
NADP(+)
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
corresponds exactly
|
+
|
H2O
|
=
|
(S)-2-amino-6-oxoheptanedioate
|
+
|
NH4(+)
|
+
|
 NADPH
NADPH
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Biochemistry
37:3278-3285
(1998)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Substrate and inhibitor binding sites in Corynebacterium glutamicum diaminopimelate dehydrogenase.
|
|
G.Scapin,
M.Cirilli,
S.G.Reddy,
Y.Gao,
J.C.Vederas,
J.S.Blanchard.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
The three-dimensional structures of Corynebacterium glutamicum diaminopimelate
dehydrogenase as a binary complex with the substrate meso-diaminopimelate
(meso-DAP) and a ternary complex with NADP+ and an isoxazoline inhibitor [Abbot,
S.D., Lane-Bell, P., Kanwar, P.S.S., and Vederas, J. C. (1994) J. Am. Chem. Soc.
116, 6513-6520] have been solved and refined against X-ray diffraction data to
2.2 A. Diaminopimelate dehydrogenase is a homodimer of approximately 35,000
molecular weight subunits and is the only dehydrogenase present in the bacterial
diaminopimelate/lysine biosynthetic pathway. Inhibitors of the enzymes of
L-lysine biosynthesis have been proposed as potential antibiotics or herbicides,
since mammals lack this metabolic pathway. Diaminopimelate dehydrogenase
catalyzes the unique, reversible, pyridine dinucleotide-dependent oxidative
deamination of the D-amino acid stereocenter of meso-diaminopimelate to generate
L-2-amino-6-oxopimelate. The enzyme is absolutely specific for the meso
stereoisomer of DAP and must distinguish between two opposite chiral amino acid
centers on the same symmetric substrate. The determination of the
three-dimensional structure of the enzyme--meso-diaminopimelate complex allows a
description of the molecular basis of this stereospecific discrimination. The
substrate is bound in an elongated cavity, in which the distribution of residues
that act as hydrogen bond donors or acceptors defines a single orientation in
which the substrate may bind in order to position the D-amino acid center of
meso-DAP near the oxidized nucleotide. The previously described isoxazoline
inhibitor binds at the same site as DAP but has its L-amino acid center
positioned where the D-amino acid center of meso-DAP would normally be located,
thereby generating a nonproductive inhibitor complex. The relative positions of
the N-terminal dinucleotide and C-terminal substrate-binding domains in the
diaminopimelate dehydrogenase--NADP+, diaminopimelate dehydrogenase--DAP, and
diaminopimelate dehydrogenase--NADP(+)--inhibitor complexes confirm our previous
observations that the enzyme undergoes significant conformational changes upon
binding of both dinucleotide and substrate.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
A.Ciulli,
D.Y.Chirgadze,
A.G.Smith,
T.L.Blundell,
and
C.Abell
(2007).
Crystal structure of Escherichia coli ketopantoate reductase in a ternary complex with NADP+ and pantoate bound: substrate recognition, conformational change, and cooperativity.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
282,
8487-8497.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
A.J.Stein,
and
J.H.Geiger
(2002).
The crystal structure and mechanism of 1-L-myo-inositol- 1-phosphate synthase.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
277,
9484-9491.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
R.A.Norman,
M.S.McAlister,
J.Murray-Rust,
F.Movahedzadeh,
N.G.Stoker,
and
N.Q.McDonald
(2002).
Crystal structure of inositol 1-phosphate synthase from Mycobacterium tuberculosis, a key enzyme in phosphatidylinositol synthesis.
|
| |
Structure,
10,
393-402.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
S.S.Ray,
J.B.Bonanno,
K.R.Rajashankar,
M.G.Pinho,
G.He,
H.De Lencastre,
A.Tomasz,
and
S.K.Burley
(2002).
Cocrystal structures of diaminopimelate decarboxylase: mechanism, evolution, and inhibition of an antibiotic resistance accessory factor.
|
| |
Structure,
10,
1499-1508.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Cirilli,
G.Scapin,
A.Sutherland,
J.C.Vederas,
and
J.S.Blanchard
(2000).
The three-dimensional structure of the ternary complex of Corynebacterium glutamicum diaminopimelate dehydrogenase-NADPH-L-2-amino-6-methylene-pimelate.
|
| |
Protein Sci,
9,
2034-2037.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
T.M.Fuchs,
B.Schneider,
K.Krumbach,
L.Eggeling,
and
R.Gross
(2000).
Characterization of a bordetella pertussis diaminopimelate (DAP) biosynthesis locus identifies dapC, a novel gene coding for an N-succinyl-L,L-DAP aminotransferase.
|
| |
J Bacteriol,
182,
3626-3631.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
T.L.Born,
and
J.S.Blanchard
(1999).
Structure/function studies on enzymes in the diaminopimelate pathway of bacterial cell wall biosynthesis.
|
| |
Curr Opin Chem Biol,
3,
607-613.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
code is
shown on the right.
|
 |

