 |
PDBsum entry 2d80

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.3.1.1.75
- poly(3-hydroxybutyrate) depolymerase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
|
1.
|
[(3R)-hydroxybutanoate](n) + H2O = [(3R)-hydroxybutanoate](n-1) + (R)-3-hydroxybutanoate + H+
|
|
2.
|
[(3R)-hydroxybutanoate](n) + H2O = [(3R)-hydroxybutanoate](n-2) + (3R)-hydroxybutanoate dimer + H+
|
|
3.
|
[(3R)-hydroxybutanoate](n) + H2O = [(3R)-hydroxybutanoate](n-3) + (3R)-hydroxybutanoate trimer + H+
|
|
4.
|
[(3R)-hydroxybutanoate](n) + H2O = [(3R)-hydroxybutanoate](n-4) + (3R)-hydroxybutanoate tetramer + H+
|
|
5.
|
[(3R)-hydroxybutanoate](n) + H2O = [(3R)-hydroxybutanoate](n-5) + (3R)-hydroxybutanoate pentamer + H+
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
[(3R)-hydroxybutanoate](n)
|
+
|
H2O
|
=
|
[(3R)-hydroxybutanoate](n-1)
|
+
|
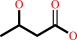 (R)-3-hydroxybutanoate
(R)-3-hydroxybutanoate
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
[(3R)-hydroxybutanoate](n)
|
+
|
H2O
|
=
|
[(3R)-hydroxybutanoate](n-2)
|
+
|
(3R)-hydroxybutanoate dimer
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
[(3R)-hydroxybutanoate](n)
|
+
|
H2O
|
=
|
[(3R)-hydroxybutanoate](n-3)
|
+
|
(3R)-hydroxybutanoate trimer
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
[(3R)-hydroxybutanoate](n)
|
+
|
H2O
|
=
|
[(3R)-hydroxybutanoate](n-4)
|
+
|
(3R)-hydroxybutanoate tetramer
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
[(3R)-hydroxybutanoate](n)
|
+
|
H2O
|
=
|
[(3R)-hydroxybutanoate](n-5)
|
+
|
(3R)-hydroxybutanoate pentamer
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
J Mol Biol
356:993
(2006)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
The Crystal Structure of Polyhydroxybutyrate Depolymerase from Penicillium funiculosum Provides Insights into the Recognition and Degradation of Biopolyesters.
|
|
T.Hisano,
K.Kasuya,
Y.Tezuka,
N.Ishii,
T.Kobayashi,
M.Shiraki,
E.Oroudjev,
H.Hansma,
T.Iwata,
Y.Doi,
T.Saito,
K.Miki.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Polyhydroxybutyrate is a microbial polyester that can be produced from renewable
resources, and is degraded by the enzyme polyhydroxybutyrate depolymerase. The
crystal structures of polyhydroxybutyrate depolymerase from Penicillium
funiculosum and its S39A mutant complexed with the methyl ester of a trimer
substrate of (R)-3-hydroxybutyrate have been determined at resolutions of 1.71A
and 1.66A, respectively. The enzyme is comprised of a single domain, which
represents a circularly permuted variant of the alpha/beta hydrolase fold. The
catalytic residues Ser39, Asp121, and His155 are located at topologically
conserved positions. The main chain amide groups of Ser40 and Cys250 form an
oxyanion hole. A crevice is formed on the surface of the enzyme, to which a
single polymer chain can be bound by predominantly hydrophobic interactions with
several hydrophobic residues. The structure of the S39A mutant-trimeric
substrate complex reveals that Trp307 is responsible for the recognition of the
ester group adjacent to the scissile group. It is also revealed that the
substrate-binding site includes at least three, and possibly four, subsites for
binding monomer units of polyester substrates. Thirteen hydrophobic residues,
which are exposed to solvent, are aligned around the mouth of the crevice,
forming a putative adsorption site for the polymer surface. These residues may
contribute to the sufficient binding affinity of the enzyme for PHB granules
without a distinct substrate-binding domain.

|

|
|
|

|
| |
Selected figure(s)
|
|

|
| |
 |
 |

|
 |

|
 |
Figure 4.
Figure 4. Simulated-annealing |mF[o] -DF[c]| electron
density map for H(R3HB)[3]M bound to the S39A mutant, calculated
from the model excluding H(R3HB)[3]M. Models of S39A and the
R3HB trimer (H(R3HB)[3]M lacking the methyl group) are also
shown as a line and a stick model, respectively. The map is
contoured at 3.5s. Figures were produced using the PyMOL program
(DeLano, W. L.; http://www.pymol.org/).
|
 |
Figure 5.
Figure 5. A close-up stereoview of the active site (the
S39A-H(R3HB)[3]M complex). Side-chains of catalytic residues and
residues forming the substrate-binding site in the crevice are
represented as ball-and-stick models. The amide nitrogen atoms
of Ser40, Cys250, and Asn302 are also shown. A model of the R3HB
trimer (designated as (R3HB)[3]) is also shown as a black
ball-and-stick model. A hydrogen bond between Nd1 atom of Trp307
and the carbonyl oxygen of an ester linkage adjacent to a
scissile linkage, and one between His155 and Asp121 are
indicated as green lines. The side-chain of Ser39 of the
wild-type protein (shown in red) is superimposed on Ala39 of the
mutant model, and a hydrogen bond between the Og atom of Ser39
and the amide group of Ser40 is tentatively indicated with a
green broken line.
|
 |
|
|

|
| |
The above figures are
reprinted
by permission from Elsevier:
J Mol Biol
(2006,
356,
993-0)
copyright 2006.
|
|
| |
Figures were
selected
by an automated process.
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
A.Sznajder,
and
D.Jendrossek
(2011).
Biochemical characterization of a new type of intracellular PHB depolymerase from Rhodospirillum rubrum with high hydrolytic activity on native PHB granules.
|
| |
Appl Microbiol Biotechnol,
89,
1487-1495.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
Y.Yu,
and
S.Lutz
(2011).
Circular permutation: a different way to engineer enzyme structure and function.
|
| |
Trends Biotechnol,
29,
18-25.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Knoll,
T.M.Hamm,
F.Wagner,
V.Martinez,
and
J.Pleiss
(2009).
The PHA Depolymerase Engineering Database: A systematic analysis tool for the diverse family of polyhydroxyalkanoate (PHA) depolymerases.
|
| |
BMC Bioinformatics,
10,
89.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
Z.Qian,
J.R.Horton,
X.Cheng,
and
S.Lutz
(2009).
Structural redesign of lipase B from Candida antarctica by circular permutation and incremental truncation.
|
| |
J Mol Biol,
393,
191-201.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
D.Jendrossek
(2007).
Peculiarities of PHA granules preparation and PHA depolymerase activity determination.
|
| |
Appl Microbiol Biotechnol,
74,
1186-1196.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Yamada,
K.Yamashita,
A.Wakuda,
K.Ichimura,
A.Maehara,
M.Maeda,
and
S.Taguchi
(2007).
Autoregulator protein PhaR for biosynthesis of polyhydroxybutyrate [P(3HB)] possibly has two separate domains that bind to the target DNA and P(3HB): Functional mapping of amino acid residues responsible for DNA binding.
|
| |
J Bacteriol,
189,
1118-1127.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
Z.Qian,
C.J.Fields,
and
S.Lutz
(2007).
Investigating the structural and functional consequences of circular permutation on lipase B from Candida antarctica.
|
| |
Chembiochem,
8,
1989-1996.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
B.Gebauer,
and
D.Jendrossek
(2006).
Assay of poly(3-hydroxybutyrate) depolymerase activity and product determination.
|
| |
Appl Environ Microbiol,
72,
6094-6100.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
T.Hiraishi,
Y.Hirahara,
Y.Doi,
M.Maeda,
and
S.Taguchi
(2006).
Effects of mutations in the substrate-binding domain of poly[(R)-3-hydroxybutyrate] (PHB) depolymerase from Ralstonia pickettii T1 on PHB degradation.
|
| |
Appl Environ Microbiol,
72,
7331-7338.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
codes are
shown on the right.
|
 |

