 |
PDBsum entry 2czi

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Hydrolase
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
Crystal structure of human myo-inositol monophosphatase 2 (impa2) with calcium and phosphate ions
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
Inositol monophosphatase 2. Chain: a. Synonym: impase 2, imp 2, inositol-1(or 4)-monophosphatase 2, myo- inositol monophosphatase a2. Engineered: yes
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Homo sapiens. Human. Organism_taxid: 9606. Gene: impa2. Expressed in: escherichia coli. Expression_system_taxid: 562.
|
|
Biol. unit:
|
 |
 Dimer (from PDB file)
Dimer (from PDB file)
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
3.00Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.250
|
R-free:
|
0.286
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
R.Arai,K.Ito,T.Ohnishi,H.Ohba,T.Yoshikawa,M.Shirouzu,S.Yokoyama,Riken Structural Genomics/proteomics Initiative (Rsgi)
|
Key ref:

|
 |
R.Arai
et al.
(2007).
Crystal structure of human myo-inositol monophosphatase 2, the product of the putative susceptibility gene for bipolar disorder, schizophrenia, and febrile seizures.
Proteins,
67,
732-742.
PubMed id:
DOI:

|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
13-Jul-05
|
Release date:
|
25-Jul-06
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
O14732
(IMPA2_HUMAN) -
Inositol monophosphatase 2 from Homo sapiens
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
288 a.a.
259 a.a.
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|
|
Key: |
 |
PfamA domain |
 |
 |
 |
Secondary structure |
 |
 |
CATH domain |
 |
|

|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.3.1.3.25
- inositol-phosphate phosphatase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

Pathway:
|
 |
myo-Inositol Biosynthesis
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
a myo-inositol phosphate + H2O = myo-inositol + phosphate
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
myo-inositol phosphate
|
+
|
H2O
|
=
|
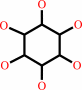 myo-inositol
myo-inositol
|
+
|
phosphate
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
corresponds exactly
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Proteins
67:732-742
(2007)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Crystal structure of human myo-inositol monophosphatase 2, the product of the putative susceptibility gene for bipolar disorder, schizophrenia, and febrile seizures.
|
|
R.Arai,
K.Ito,
T.Ohnishi,
H.Ohba,
R.Akasaka,
Y.Bessho,
K.Hanawa-Suetsugu,
T.Yoshikawa,
M.Shirouzu,
S.Yokoyama.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
The human IMPA2 gene, which encodes myo-inositol monophosphatase 2 (IMPA2), is
mapped onto 18p11.2, a susceptibility region for bipolar disorder. This
chromosomal region has also been proposed to include a susceptibility locus for
schizophrenia and febrile seizures. Here we report the crystal structures of
human IMPA2 and its complex with calcium and phosphate ions. Human IMPA2
comprises an alpha-beta protein with a five-layered sandwich of alpha-helices
and beta-sheets (alpha-beta-alpha-beta-alpha). The crystal structure and
analytical ultracentrifugation results indicated that IMPA2 exists as a dimer in
solution. The overall structure of IMPA2 is similar to that of IMPA1, except for
the loop regions. In IMPA1, the loop region (31-43) is located at the entrance
of the active site cavity. In the corresponding region (42-54) of IMPA2, the
residues are disordered and partially form an alpha-helix. The structural
difference in the opening of the active site cavity suggests that the substrate
specificity differs between IMPA1 and IMPA2. The widely opened cavity of IMPA2
implies that the physiological substrate may be a larger compound than inositol
monophosphate. The structure of IMPA2 complexed with Ca2+ revealed two metals
and one phosphate binding sites, which were the same sites as in IMPA1 complexed
with Mn2+ and phosphate, suggesting that the mechanism of the enzymatic reaction
is similar to that of IMPA1. The crystal structures of human IMPA2 are useful
for understanding the effect of nonsynonymous polymorphism reported in IMPA2,
and will contribute to further functional analyses of IMPA2 that potentially
predisposes to the vulnerabilities of bipolar disorder, schizophrenia, and
febrile seizures.

|

|
|
|

|
| |
Selected figure(s)
|
|

|
| |
 |
 |

|
 |

|
 |
Figure 4.
Figure 4. The structure of the active site region of human
IMPA2. (A) The structure of the active site region of IMPA2
Crystal 1 and the composite annealed omit electron density map
contoured at 1  (2.7
Å resolution) (stereoview). (B) The structure of the
active site region of IMPA2 Crystal 2. (C) The structure of the
active site region of IMPA2 Crystal 3. (D) The structure of the
active site region of IMPA2 Crystal 4 (stereoview). Two calcium
ions and one phosphate ion are superimposed with the F[o] - F[c]
electron density map contoured at 3 (2.7
Å resolution) (stereoview). (B) The structure of the
active site region of IMPA2 Crystal 2. (C) The structure of the
active site region of IMPA2 Crystal 3. (D) The structure of the
active site region of IMPA2 Crystal 4 (stereoview). Two calcium
ions and one phosphate ion are superimposed with the F[o] - F[c]
electron density map contoured at 3  (3.0
Å resolution). (3.0
Å resolution).
|
 |
Figure 6.
Figure 6. The sites of the three nonsynonymous polymorphisms
(His76Tyr, Arg148Gln, and Ala181Val) reported in IMPA2 on the
IMPA2 dimer (Crystal 1).
|
 |
|
|

|
| |
The above figures are
reprinted
by permission from John Wiley & Sons, Inc.:
Proteins
(2007,
67,
732-742)
copyright 2007.
|
|
| |
Figures were
selected
by an automated process.
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
J.Fu,
K.Peterson,
M.Guttieri,
E.Souza,
and
V.Raboy
(2008).
Barley (Hordeum vulgare L.) inositol monophosphatase: gene structure and enzyme characteristics.
|
| |
Plant Mol Biol,
67,
629-642.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.K.Brown,
G.Meng,
H.Ghadbane,
D.J.Scott,
L.G.Dover,
J.Nigou,
G.S.Besra,
and
K.Fütterer
(2007).
Dimerization of inositol monophosphatase Mycobacterium tuberculosis SuhB is not constitutive, but induced by binding of the activator Mg2+.
|
| |
BMC Struct Biol,
7,
55.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
code is
shown on the right.
|
 |

