 |
PDBsum entry 2cyh

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.5.2.1.8
- peptidylprolyl isomerase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
[protein]-peptidylproline (omega=180) = [protein]-peptidylproline (omega=0)
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
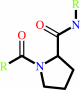 Peptidylproline (omega=180)
Peptidylproline (omega=180)
|
=
|
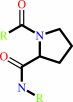 peptidylproline (omega=0)
peptidylproline (omega=0)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Biochemistry
35:7362-7368
(1996)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Mechanistic implication of crystal structures of the cyclophilin-dipeptide complexes.
|
|
Y.Zhao,
H.Ke.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
The structures of cyclophilin A complexed with dipeptides of Ser-Pro, His-Pro,
and Gly-Pro have been determined and refined at high resolution. Comparison of
these structures revealed that the dipeptide complexes have the same molecular
conformation and the same binding of the dipeptides. The side chains of the
N-terminal amino acid of the above dipeptides do not strongly interact with
cyclophilin, implying their minor contribution to the cis-trans isomerization
and thus accounting for the broad catalytic specificity of the enzyme. The
binding of the dipeptides is similar to that of the common substrate
succinyl-Ala-Ala-Pro-Phe-p-nitroanilide in terms of the N-terminal hydrogen
bonding and the hydrophobic interaction of the proline side chain. However,
substantial difference between these structures are observed in (1) hydrogen
bonding between the carboxyl terminus of the peptides and Arg55 and between
Arg55 and Gln63, (2) the side chain conformation of Arg55, and (3) water binding
at the active site. These differences imply either that dipeptides are not
substrates but competitive inhibitors of peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerases or
that dipeptides are subject to different catalytic mechanisms from tetrapeptides.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
C.J.Dunsmore,
K.J.Malone,
K.R.Bailey,
M.A.Wear,
H.Florance,
S.Shirran,
P.E.Barran,
A.P.Page,
M.D.Walkinshaw,
and
N.J.Turner
(2011).
Design and synthesis of conformationally constrained cyclophilin inhibitors showing a cyclosporin-A phenotype in C. elegans.
|
| |
Chembiochem,
12,
802-810.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
B.D.Janssen,
and
C.S.Hayes
(2009).
Kinetics of paused ribosome recycling in Escherichia coli.
|
| |
J Mol Biol,
394,
251-267.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.Schlegel,
G.S.Armstrong,
J.S.Redzic,
F.Zhang,
and
E.Z.Eisenmesser
(2009).
Characterizing and controlling the inherent dynamics of cyclophilin-A.
|
| |
Protein Sci,
18,
811-824.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.B.Moparthi,
P.Hammarström,
and
U.Carlsson
(2009).
A nonessential role for Arg 55 in cyclophilin18 for catalysis of proline isomerization during protein folding.
|
| |
Protein Sci,
18,
475-479.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
X.Hanoulle,
A.Badillo,
J.M.Wieruszeski,
D.Verdegem,
I.Landrieu,
R.Bartenschlager,
F.Penin,
and
G.Lippens
(2009).
Hepatitis C virus NS5A protein is a substrate for the peptidyl-prolyl cis/trans isomerase activity of cyclophilins A and B.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
284,
13589-13601.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
V.Thai,
P.Renesto,
C.A.Fowler,
D.J.Brown,
T.Davis,
W.Gu,
D.D.Pollock,
D.Kern,
D.Raoult,
and
E.Z.Eisenmesser
(2008).
Structural, biochemical, and in vivo characterization of the first virally encoded cyclophilin from the Mimivirus.
|
| |
J Mol Biol,
378,
71-86.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
P.Mark,
and
L.Nilsson
(2007).
A molecular dynamics study of Cyclophilin A free and in complex with the Ala-Pro dipeptide.
|
| |
Eur Biophys J,
36,
213-224.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
D.Trzesniak,
and
W.F.van Gunsteren
(2006).
Catalytic mechanism of cyclophilin as observed in molecular dynamics simulations: pathway prediction and reconciliation of X-ray crystallographic and NMR solution data.
|
| |
Protein Sci,
15,
2544-2551.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
P.K.Agarwal
(2006).
Enzymes: An integrated view of structure, dynamics and function.
|
| |
Microb Cell Fact,
5,
2.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
X.J.Wang,
and
F.A.Etzkorn
(2006).
Peptidyl-prolyl isomerase inhibitors.
|
| |
Biopolymers,
84,
125-146.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.Kallen,
R.Sedrani,
G.Zenke,
and
J.Wagner
(2005).
Structure of human cyclophilin A in complex with the novel immunosuppressant sanglifehrin A at 1.6 A resolution.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
280,
21965-21971.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
L.L.Huang,
X.M.Zhao,
C.Q.Huang,
L.Yu,
and
Z.X.Xia
(2005).
Structure of recombinant human cyclophilin J, a novel member of the cyclophilin family.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr,
61,
316-321.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
G.Kontopidis,
P.Taylor,
and
M.D.Walkinshaw
(2004).
Enzymatic and structural characterization of non-peptide ligand-cyclophilin complexes.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr,
60,
479-485.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
Q.Huai,
H.Wang,
W.Zhang,
R.W.Colman,
H.Robinson,
and
H.Ke
(2004).
Crystal structure of phosphodiesterase 9 shows orientation variation of inhibitor 3-isobutyl-1-methylxanthine binding.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
101,
9624-9629.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
B.R.Howard,
F.F.Vajdos,
S.Li,
W.I.Sundquist,
and
C.P.Hill
(2003).
Structural insights into the catalytic mechanism of cyclophilin A.
|
| |
Nat Struct Biol,
10,
475-481.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
E.Z.Eisenmesser,
D.A.Bosco,
M.Akke,
and
D.Kern
(2002).
Enzyme dynamics during catalysis.
|
| |
Science,
295,
1520-1523.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
Wu Sy,
J.Dornan,
G.Kontopidis,
P.Taylor,
and
M.D.Walkinshaw
(2001).
The First Direct Determination of a Ligand Binding Constant in Protein Crystals.
|
| |
Angew Chem Int Ed Engl,
40,
582-586.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
M.T.Ivery
(2000).
Immunophilins: switched on protein binding domains?
|
| |
Med Res Rev,
20,
452-484.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
L.Ma,
L.C.Hsieh-Wilson,
and
P.G.Schultz
(1998).
Antibody catalysis of peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerization in the folding of RNase T1.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
95,
7251-7256.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
Y.Zhao,
and
H.Ke
(1996).
Crystal structure implies that cyclophilin predominantly catalyzes the trans to cis isomerization.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
35,
7356-7361.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
code is
shown on the right.
|
 |

