 |
PDBsum entry 2cli

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Lyase
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
Tryptophan synthase in complex with n-(4'- trifluoromethoxybenzenesulfonyl)-2-amino-1-ethylphosphate (f9)
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
Tryptophan synthase alpha chain. Chain: a. Engineered: yes. Tryptophan synthase beta chain. Chain: b. Engineered: yes. Other_details: internal aldimine formed between b-k87 and c4 of pyridoxal-5'-phosphate
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Salmonella typhimurium. Organism_taxid: 602. Expressed in: escherichia coli. Expression_system_taxid: 562.
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
1.70Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.188
|
R-free:
|
0.206
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
H.Ngo,R.Harris,N.Kimmich,P.Casino,D.Niks,L.Blumenstein,T.R.Barends, V.Kulik,M.Weyand,I.Schlichting,M.F.Dunn
|
|
Key ref:
|
 |
H.Ngo
et al.
(2007).
Synthesis and characterization of allosteric probes of substrate channeling in the tryptophan synthase bienzyme complex.
Biochemistry,
46,
7713-7727.
PubMed id:
|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
27-Apr-06
|
Release date:
|
12-Jun-07
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
Chains A, B:
E.C.4.2.1.20
- tryptophan synthase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

Pathway:
|
 |
Tryptophan Biosynthesis
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
(1S,2R)-1-C-(indol-3-yl)glycerol 3-phosphate + L-serine = D-glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate + L-tryptophan + H2O
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
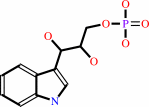 (1S,2R)-1-C-(indol-3-yl)glycerol 3-phosphate
(1S,2R)-1-C-(indol-3-yl)glycerol 3-phosphate
|
+
|
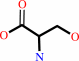 L-serine
L-serine
|
=
|
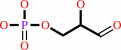 D-glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate
D-glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate
|
+
|
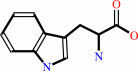 L-tryptophan
L-tryptophan
|
+
|
H2O
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Cofactor:
|
 |
Pyridoxal 5'-phosphate
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Pyridoxal 5'-phosphate
Bound ligand (Het Group name =
PLP)
matches with 93.75% similarity
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
Biochemistry
46:7713-7727
(2007)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Synthesis and characterization of allosteric probes of substrate channeling in the tryptophan synthase bienzyme complex.
|
|
H.Ngo,
R.Harris,
N.Kimmich,
P.Casino,
D.Niks,
L.Blumenstein,
T.R.Barends,
V.Kulik,
M.Weyand,
I.Schlichting,
M.F.Dunn.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Allosteric interactions regulate substrate channeling in Salmonella typhimurium
tryptophan synthase. The channeling of indole between the alpha- and beta-sites
via the interconnecting 25 A tunnel is regulated by allosteric signaling arising
from binding of ligand to the alpha-site, and covalent reaction of l-Ser at the
beta-site. This signaling switches the alpha- and beta-subunits between open
conformations of low activity and closed conformations of high activity. Our
objective is to synthesize and characterize new classes of alpha-site ligands
(ASLs) that mimic the binding of substrates, 3-indole-d-glycerol 3'-phosphate
(IGP) or d-glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate (G3P), for use in the investigation of
alpha-site-beta-site interactions. The new synthesized IGP analogues contain an
aryl group linked to an O-phosphoethanolamine moiety through amide, sulfonamide,
or thiourea groups. The G3P analogue, thiophosphoglycolohydroxamate, contains a
hydroxamic acid group linked to a thiophosphate moiety. Crystal structures of
the internal aldimine complexed with G3P and with three of the new ASLs are
presented. These structural and solution studies of the ASL complexes with the
internal aldimine form of the enzyme establish the following. (1) ASL binding
occurs with high specificity and relatively high affinities at the alpha-site.
(2) Binding of the new ASLs slows the entry of indole analogues into the
beta-site by blocking the tunnel opening at the alpha-site. (3) ASL binding
stabilizes the closed conformations of the beta-subunit for the
alpha-aminoacrylate and quinonoid forms of the enzyme. (4) The new ASLs exhibit
allosteric properties that parallel the behaviors of IGP and G3P.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
E.Tolonen,
B.Bueno,
S.Kulshreshta,
P.Cieplak,
M.Argáez,
L.Velázquez,
and
B.Stec
(2011).
Allosteric transition and binding of small molecule effectors causes curvature change in central β-sheets of selected enzymes.
|
| |
J Mol Model,
17,
899-911.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Q.Fatmi,
and
C.E.Chang
(2010).
The role of oligomerization and cooperative regulation in protein function: the case of tryptophan synthase.
|
| |
PLoS Comput Biol,
6,
e1000994.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
R.S.Phillips,
E.W.Miles,
P.McPhie,
S.Marchal,
R.Lange,
G.Holtermann,
and
R.S.Goody
(2010).
Effects of hydrostatic pressure on the conformational equilibrium of tryptophan synthase from Salmonella typhimurium.
|
| |
Ann N Y Acad Sci,
1189,
95.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Raboni,
S.Bettati,
and
A.Mozzarelli
(2009).
Tryptophan synthase: a mine for enzymologists.
|
| |
Cell Mol Life Sci,
66,
2391-2403.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.F.Dunn,
D.Niks,
H.Ngo,
T.R.Barends,
and
I.Schlichting
(2008).
Tryptophan synthase: the workings of a channeling nanomachine.
|
| |
Trends Biochem Sci,
33,
254-264.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
T.R.Barends,
M.F.Dunn,
and
I.Schlichting
(2008).
Tryptophan synthase, an allosteric molecular factory.
|
| |
Curr Opin Chem Biol,
12,
593-600.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
|
 |
|

