 |
PDBsum entry 2cfd

|
|
|

|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |

|

|

|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
Oxidoreductase
|
PDB id
|
|

|

|
2cfd
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Oxidoreductase
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
Agao in complex with wc4l3 (ru-wire inhibitor, 4-carbon linker, lambda enantiomer, data set 3)
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
Phenylethylamine oxidase. Chain: a, b. Fragment: agao holoenzyme, residues 3-638. Synonym: amine oxidase, copper amine oxidase. Engineered: yes. Other_details: residue a382 was an active site tyrosine residue, which was autocatalytically modified to become tpq
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Arthrobacter globiformis. Organism_taxid: 1665. Expressed in: escherichia coli. Expression_system_taxid: 469008.
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
1.60Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.195
|
R-free:
|
0.213
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
D.B.Langley,A.P.Duff,H.C.Freeman,J.M.Guss,G.A.Juda,D.M.Dooley, S.M.Contakes,N.W.Halpern-Manners,A.R.Dunn,H.B.Gray
|
|
Key ref:
|
 |
D.B.Langley
et al.
(2008).
Enantiomer-specific binding of ruthenium(II) molecular wires by the amine oxidase of Arthrobacter globiformis.
J Am Chem Soc,
130,
8069-8078.
PubMed id:
|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
20-Feb-06
|
Release date:
|
01-May-07
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
P46881
(PAOX_ARTGO) -
Phenylethylamine oxidase from Arthrobacter globiformis
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
638 a.a.
619 a.a.*
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|
|
Key: |
 |
 |
Secondary structure |
 |
 |
CATH domain |
 |
|
*
PDB and UniProt seqs differ
at 1 residue position (black
cross)
|
|

|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.1.4.3.21
- primary-amine oxidase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
a primary methyl amine + O2 + H2O = an aldehyde + H2O2 + NH4+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
primary methyl amine
|
+
|
 O2
O2
|
+
|
H2O
|
=
|
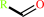 aldehyde
aldehyde
|
+
|
 H2O2
H2O2
|
+
|
NH4(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
J Am Chem Soc
130:8069-8078
(2008)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Enantiomer-specific binding of ruthenium(II) molecular wires by the amine oxidase of Arthrobacter globiformis.
|
|
D.B.Langley,
D.E.Brown,
L.E.Cheruzel,
S.M.Contakes,
A.P.Duff,
K.M.Hilmer,
D.M.Dooley,
H.B.Gray,
J.M.Guss,
H.C.Freeman.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
The copper amine oxidase from Arthrobacter globiformis (AGAO) is reversibly
inhibited by molecular wires comprising a Ru(II) complex head group and an
aromatic tail group joined by an alkane linker. The crystal structures of a
series of Ru(II)-wire-AGAO complexes differing with respect to the length of the
alkane linker have been determined. All wires lie in the AGAO active-site
channel, with their aromatic tail group in contact with the
trihydroxyphenylalanine quinone (TPQ) cofactor of the enzyme. The TPQ cofactor
is consistently in its active ("off-Cu") conformation, and the side chain of the
so-called "gate" residue Tyr296 is consistently in the "gate-open" conformation.
Among the wires tested, the most stable complex is produced when the wire has a
-(CH2)4- linker. In this complex, the Ru(II)(phen)(bpy)2 head group is level
with the protein molecular surface. Crystal structures of AGAO in complex with
optically pure forms of the C4 wire show that the linker and head group in the
two enantiomers occupy slightly different positions in the active-site channel.
Both the Lambda and Delta isomers are effective competitive inhibitors of amine
oxidation. Remarkably, inhibition by the C4 wire shows a high degree of
selectivity for AGAO in comparison with other copper-containing amine oxidases.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
A.P.McGrath,
K.M.Hilmer,
C.A.Collyer,
D.M.Dooley,
and
J.M.Guss
(2010).
A new crystal form of human diamine oxidase.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun,
66,
137-142.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
A.P.McGrath,
K.M.Hilmer,
C.A.Collyer,
E.M.Shepard,
B.O.Elmore,
D.E.Brown,
D.M.Dooley,
and
J.M.Guss
(2009).
Structure and inhibition of human diamine oxidase.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
48,
9810-9822.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
C.L.Davies,
E.L.Dux,
and
A.K.Duhme-Klair
(2009).
Supramolecular interactions between functional metal complexes and proteins.
|
| |
Dalton Trans,
(),
10141-10154.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
E.Meggers
(2009).
Targeting proteins with metal complexes.
|
| |
Chem Commun (Camb),
(),
1001-1010.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
C.A.Whited,
W.Belliston-Bittner,
A.R.Dunn,
J.R.Winkler,
and
H.B.Gray
(2008).
Probing the heme-thiolate oxygenase domain of inducible nitric oxide synthase with Ru(II) and Re(I) electron tunneling wires.
|
| |
J Porphyr Phthalocyanines,
12,
971-978.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
code is
shown on the right.
|
 |

