 |
PDBsum entry 2cab

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 2:
|
 |
E.C.4.2.1.1
- carbonic anhydrase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
hydrogencarbonate + H+ = CO2 + H2O
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 hydrogencarbonate
hydrogencarbonate
|
+
|
H(+)
|
=
|
 CO2
CO2
|
+
|
H2O
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Cofactor:
|
 |
Zn(2+)
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 3:
|
 |
E.C.4.2.1.69
- cyanamide hydratase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
urea = cyanamide + H2O
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
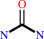 urea
urea
|
=
|
 cyanamide
cyanamide
|
+
|
H2O
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Note, where more than one E.C. class is given (as above), each may
correspond to a different protein domain or, in the case of polyprotein
precursors, to a different mature protein.
|
|
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
Ann N Y Acad Sci
429:49-60
(1984)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Structure, refinement, and function of carbonic anhydrase isozymes: refinement of human carbonic anhydrase I.
|
|
K.K.Kannan,
M.Ramanadham,
T.A.Jones.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
The structure of human erythrocyte carbonic anhydrase I has been refined to a
final R value of 19% to 2-A resolution by a combination of least squares
refinement and model fitting in a three-dimensional graphics display. About 300
solvent atoms have been located bound to the protein molecule. An interesting
hydrogen bond network involving Zn2+, the liganded solvent, side chain groups of
Thr-199, Glu-106, Thr-7, and His-64 through two solvent molecules have been
found that may be important for the catalytic mechanism of the carbonic
anhydrase.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
V.Alterio,
S.M.Monti,
E.Truppo,
C.Pedone,
C.T.Supuran,
and
G.De Simone
(2010).
The first example of a significant active site conformational rearrangement in a carbonic anhydrase-inhibitor adduct: the carbonic anhydrase I-topiramate complex.
|
| |
Org Biomol Chem,
8,
3528-3533.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
C.M.Maupin,
R.McKenna,
D.N.Silverman,
and
G.A.Voth
(2009).
Elucidation of the proton transport mechanism in human carbonic anhydrase II.
|
| |
J Am Chem Soc,
131,
7598-7608.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
D.J.Sindhikara,
A.E.Roitberg,
and
K.M.Merz
(2009).
Apo and nickel-bound forms of the Pyrococcus horikoshii species of the metalloregulatory protein: NikR characterized by molecular dynamics simulations.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
48,
12024-12033.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.M.Chambers,
P.A.Hill,
J.A.Aaron,
Z.Han,
D.W.Christianson,
N.N.Kuzma,
and
I.J.Dmochowski
(2009).
Cryptophane xenon-129 nuclear magnetic resonance biosensors targeting human carbonic anhydrase.
|
| |
J Am Chem Soc,
131,
563-569.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
V.Alterio,
M.Hilvo,
A.Di Fiore,
C.T.Supuran,
P.Pan,
S.Parkkila,
A.Scaloni,
J.Pastorek,
S.Pastorekova,
C.Pedone,
A.Scozzafava,
S.M.Monti,
and
G.De Simone
(2009).
Crystal structure of the catalytic domain of the tumor-associated human carbonic anhydrase IX.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
106,
16233-16238.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
J.Jeyakanthan,
S.Rangarajan,
P.Mridula,
S.P.Kanaujia,
Y.Shiro,
S.Kuramitsu,
S.Yokoyama,
and
K.Sekar
(2008).
Observation of a calcium-binding site in the gamma-class carbonic anhydrase from Pyrococcus horikoshii.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr,
64,
1012-1019.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
V.M.Krishnamurthy,
G.K.Kaufman,
A.R.Urbach,
I.Gitlin,
K.L.Gudiksen,
D.B.Weibel,
and
G.M.Whitesides
(2008).
Carbonic anhydrase as a model for biophysical and physical-organic studies of proteins and protein-ligand binding.
|
| |
Chem Rev,
108,
946.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
C.M.Maupin,
and
G.A.Voth
(2007).
Preferred orientations of His64 in human carbonic anhydrase II.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
46,
2938-2947.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
D.K.Srivastava,
K.M.Jude,
A.L.Banerjee,
M.Haldar,
S.Manokaran,
J.Kooren,
S.Mallik,
and
D.W.Christianson
(2007).
Structural analysis of charge discrimination in the binding of inhibitors to human carbonic anhydrases I and II.
|
| |
J Am Chem Soc,
129,
5528-5537.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
J.M.Swanson,
C.M.Maupin,
H.Chen,
M.K.Petersen,
J.Xu,
Y.Wu,
and
G.A.Voth
(2007).
Proton solvation and transport in aqueous and biomolecular systems: insights from computer simulations.
|
| |
J Phys Chem B,
111,
4300-4314.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Ferraroni,
S.Tilli,
F.Briganti,
W.R.Chegwidden,
C.T.Supuran,
K.E.Wiebauer,
R.E.Tashian,
and
A.Scozzafava
(2002).
Crystal structure of a zinc-activated variant of human carbonic anhydrase I, CA I Michigan 1: evidence for a second zinc binding site involving arginine coordination.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
41,
6237-6244.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
D.A.Whittington,
A.Waheed,
B.Ulmasov,
G.N.Shah,
J.H.Grubb,
W.S.Sly,
and
D.W.Christianson
(2001).
Crystal structure of the dimeric extracellular domain of human carbonic anhydrase XII, a bitopic membrane protein overexpressed in certain cancer tumor cells.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
98,
9545-9550.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
T.M.Iverson,
B.E.Alber,
C.Kisker,
J.G.Ferry,
and
D.C.Rees
(2000).
A closer look at the active site of gamma-class carbonic anhydrases: high-resolution crystallographic studies of the carbonic anhydrase from Methanosarcina thermophila.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
39,
9222-9231.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
B.E.Alber,
and
J.G.Ferry
(1996).
Characterization of heterologously produced carbonic anhydrase from Methanosarcina thermophila.
|
| |
J Bacteriol,
178,
3270-3274.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
T.Stams,
S.K.Nair,
T.Okuyama,
A.Waheed,
W.S.Sly,
and
D.W.Christianson
(1996).
Crystal structure of the secretory form of membrane-associated human carbonic anhydrase IV at 2.8-A resolution.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
93,
13589-13594.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
C.L.Borders,
J.A.Broadwater,
P.A.Bekeny,
J.E.Salmon,
A.S.Lee,
A.M.Eldridge,
and
V.B.Pett
(1994).
A structural role for arginine in proteins: multiple hydrogen bonds to backbone carbonyl oxygens.
|
| |
Protein Sci,
3,
541-548.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
I.M.Johansson,
and
C.Forsman
(1994).
Solvent hydrogen isotope effects and anion inhibition of CO2 hydration catalysed by carbonic anhydrase from Pisum sativum.
|
| |
Eur J Biochem,
224,
901-907.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
W.R.Chegwidden,
L.E.Wagner,
P.J.Venta,
N.C.Bergenhem,
Y.S.Yu,
and
R.E.Tashian
(1994).
Marked zinc activation of ester hydrolysis by a mutation, 67-His (CAT) to Arg (CGT), in the active site of human carbonic anhydrase I.
|
| |
Hum Mutat,
4,
294-296.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
I.M.Johansson,
and
C.Forsman
(1993).
Kinetic studies of pea carbonic anhydrase.
|
| |
Eur J Biochem,
218,
439-446.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.E.Karpen,
P.L.de Haseth,
and
K.E.Neet
(1992).
Differences in the amino acid distributions of 3(10)-helices and alpha-helices.
|
| |
Protein Sci,
1,
1333-1342.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
H.T.Wright
(1991).
Nonenzymatic deamidation of asparaginyl and glutaminyl residues in proteins.
|
| |
Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol,
26,
1.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Nilges,
G.M.Clore,
and
A.M.Gronenborn
(1990).
1H-NMR stereospecific assignments by conformational data-base searches.
|
| |
Biopolymers,
29,
813-822.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.E.Eriksson,
T.A.Jones,
and
A.Liljas
(1988).
Refined structure of human carbonic anhydrase II at 2.0 A resolution.
|
| |
Proteins,
4,
274-282.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
D.Hewett-Emmett,
P.J.Hopkins,
R.E.Tashian,
and
J.Czelusniak
(1984).
Origins and molecular evolution of the carbonic anhydrase isozymes.
|
| |
Ann N Y Acad Sci,
429,
338-358.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
code is
shown on the right.
|
 |

