 |
PDBsum entry 2c7z

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Transferase
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
Plant enzyme crystal form ii
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
3-ketoacyl-coa thiolase 2. Chain: a. Fragment: residues 38-441. Synonym: beta-ketothiolase 2, acetyl-coa acyltransferase 2, peroxisomal 3-oxoacyl-coa thiolase 2, peroxisome defective protein 1. Engineered: yes
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Arabidopsis thaliana. Mouse-ear cress. Organism_taxid: 3702. Expressed in: escherichia coli. Expression_system_taxid: 469008.
|
|
Biol. unit:
|
 |
 Dimer (from PDB file)
Dimer (from PDB file)
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
2.37Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.202
|
R-free:
|
0.276
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
R.Sundaramoorthy,E.Micossi,M.S.Alphey,G.A.Leonard,W.N.Hunter
|
Key ref:

|
 |
R.Sundaramoorthy
et al.
(2006).
The crystal structure of a plant 3-ketoacyl-CoA thiolase reveals the potential for redox control of peroxisomal fatty acid beta-oxidation.
J Mol Biol,
359,
347-357.
PubMed id:
DOI:

|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
30-Nov-05
|
Release date:
|
17-May-06
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
Q56WD9
(THIK2_ARATH) -
3-ketoacyl-CoA thiolase 2, peroxisomal from Arabidopsis thaliana
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
462 a.a.
396 a.a.
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|
|
Key: |
 |
PfamA domain |
 |
 |
 |
Secondary structure |
 |
 |
CATH domain |
 |
|

|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.2.3.1.16
- acetyl-CoA C-acyltransferase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
an acyl-CoA + acetyl-CoA = a 3-oxoacyl-CoA + CoA
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
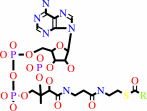 acyl-CoA
acyl-CoA
|
+
|
 acetyl-CoA
acetyl-CoA
|
=
|
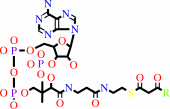 3-oxoacyl-CoA
3-oxoacyl-CoA
|
+
|
 CoA
CoA
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
J Mol Biol
359:347-357
(2006)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
The crystal structure of a plant 3-ketoacyl-CoA thiolase reveals the potential for redox control of peroxisomal fatty acid beta-oxidation.
|
|
R.Sundaramoorthy,
E.Micossi,
M.S.Alphey,
V.Germain,
J.H.Bryce,
S.M.Smith,
G.A.Leonard,
W.N.Hunter.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Crystal structures of peroxisomal Arabidopsis thaliana 3-ketoacyl-CoA thiolase
(AtKAT), an enzyme of fatty acid beta-oxidation, are reported. The subunit, a
typical thiolase, is a combination of two similar alpha/beta domains capped with
a loop domain. The comparison of AtKAT with the Saccharomyces cerevisiae
homologue (ScKAT) structure reveals a different placement of subunits within the
functional dimers and that a polypeptide segment forming an extended loop around
the open catalytic pocket of ScKAT converts to alpha-helix in AtKAT, and
occludes the active site. A disulfide is formed between Cys192, on this helix,
and Cys138, a catalytic residue. Access to Cys138 is determined by the structure
of this polypeptide segment. AtKAT represents an oxidized, previously unknown
inactive form, whilst ScKAT is the reduced and active enzyme. A high level of
sequence conservation is observed, including Cys192, in eukaryotic peroxisomal,
but not mitochondrial or prokaryotic KAT sequences, for this labile loop/helix
segment. This indicates that KAT activity in peroxisomes is influenced by a
disulfide/dithiol change linking fatty acid beta-oxidation with redox regulation.

|

|
|
|

|
| |
Selected figure(s)
|
|

|
| |
 |
 |

|
 |

|
 |
Figure 3.
Figure 3. Structural overlay of AtKAT (red) and ScKAT (grey)
dimers based on the least-squares fit of a single subunit A.
Helices are depicted as cylinders, β-strands as arrows.
Figure 3. Structural overlay of AtKAT (red) and ScKAT (grey)
dimers based on the least-squares fit of a single subunit A.
Helices are depicted as cylinders, β-strands as arrows.
|
 |
Figure 4.
Figure 4. Active site details. AtKAT sections are shown in
stick-mode with atomic positions, C colored grey, N blue, O red
and S orange, with hydrogen bonding interactions (distances <3.4
Å) as blue broken lines. (a) Hydrogen bonding associated
with a buried water molecule, a blue sphere, which binds Cys425.
(b) The environment of His393. Helix α4 is depicted as a
yellow ribbon. Figure 4. Active site details. AtKAT sections
are shown in stick-mode with atomic positions, C colored grey, N
blue, O red and S orange, with hydrogen bonding interactions
(distances <3.4 Å) as blue broken lines. (a) Hydrogen
bonding associated with a buried water molecule, a blue sphere,
which binds Cys425. (b) The environment of His393. Helix α4 is
depicted as a yellow ribbon.
|
 |
|
|

|
| |
The above figures are
reprinted
by permission from Elsevier:
J Mol Biol
(2006,
359,
347-357)
copyright 2006.
|
|
| |
Figures were
selected
by the author.
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
A.A.Wiszniewski,
W.Zhou,
S.M.Smith,
and
J.D.Bussell
(2009).
Identification of two Arabidopsis genes encoding a peroxisomal oxidoreductase-like protein and an acyl-CoA synthetase-like protein that are required for responses to pro-auxins.
|
| |
Plant Mol Biol,
69,
503-515.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.H.Dyer,
A.Maina,
I.D.Gomez,
M.Cadet,
S.Oeljeklaus,
and
A.C.Schiedel
(2009).
Cloning, expression and purification of an acetoacetyl CoA thiolase from sunflower cotyledon.
|
| |
Int J Biol Sci,
5,
736-744.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
I.A.Graham
(2008).
Seed storage oil mobilization.
|
| |
Annu Rev Plant Biol,
59,
115-142.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
G.Feron,
G.Mauvais,
J.Lherminier,
J.Michel,
X.D.Wang,
C.Viel,
and
R.Cachon
(2007).
Metabolism of fatty acid in yeast: addition of reducing agents to the reaction medium influences beta-oxidation activities, gamma-decalactone production, and cell ultrastructure in Sporidiobolus ruinenii cultivated on ricinoleic acid methyl ester.
|
| |
Can J Microbiol,
53,
738-749.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
|
 |

