 |
PDBsum entry 2bjs

|
|
|

|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |

|

|

|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
Oxidoreductase
|
PDB id
|
|

|

|
2bjs
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.1.21.3.1
- isopenicillin-N synthase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

Pathway:
|
 |
Penicillin N and Deacetoxycephalosporin C Biosynthesis
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
N-[(5S)-5-amino-5-carboxypentanoyl]-L-cysteinyl-D-valine + O2 = isopenicillin N + 2 H2O
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
N-[(5S)-5-amino-5-carboxypentanoyl]-L-cysteinyl-D-valine
|
+
|
 O2
O2
|
=
|
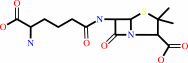 isopenicillin N
isopenicillin N
|
+
|
2
×
H2O
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
corresponds exactly
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
Chemistry
23:12815-12824
(2017)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Terminally Truncated Isopenicillin N Synthase Generates a Dithioester Product: Evidence for a Thioaldehyde Intermediate during Catalysis and a New Mode of Reaction for Non-Heme Iron Oxidases.
|
|
L.A.McNeill,
T.J.N.Brown,
M.Sami,
I.J.Clifton,
N.I.Burzlaff,
T.D.W.Claridge,
R.M.Adlington,
J.E.Baldwin,
P.J.Rutledge,
C.J.Schofield.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Isopenicillin N synthase (IPNS) catalyses the four-electron oxidation of a
tripeptide, l-δ-(α-aminoadipoyl)-l-cysteinyl-d-valine (ACV), to give
isopenicillin N (IPN), the first-formed β-lactam in penicillin and
cephalosporin biosynthesis. IPNS catalysis is dependent upon an iron(II)
cofactor and oxygen as a co-substrate. In the absence of substrate, the carbonyl
oxygen of the side-chain amide of the penultimate residue, Gln330, co-ordinates
to the active-site metal iron. Substrate binding ablates the interaction between
Gln330 and the metal, triggering rearrangement of seven C-terminal residues,
which move to take up a conformation that extends the final α-helix and
encloses ACV in the active site. Mutagenesis studies are reported, which probe
the role of the C-terminal and other aspects of the substrate binding pocket in
IPNS. The hydrophobic nature of amino acid side-chains around the ACV binding
pocket is important in catalysis. Deletion of seven C-terminal residues exposes
the active site and leads to formation of a new type of thiol oxidation product.
The isolated product is shown by LC-MS and NMR analyses to be the ene-thiol
tautomer of a dithioester, made up from two molecules of ACV linked between the
thiol sulfur of one tripeptide and the oxidised cysteinyl β-carbon of the
other. A mechanism for its formation is proposed, supported by an X-ray crystal
structure, which shows the substrate ACV bound at the active site, its cysteinyl
β-carbon exposed to attack by a second molecule of substrate, adjacent.
Formation of this product constitutes a new mode of reaction for IPNS and
non-heme iron oxidases in general.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

