
|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Transferase
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
Crystal structure of an archaeal pentameric riboflavin synthase
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
Riboflavin synthase. Chain: a, b, c, d, e. Engineered: yes
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Methanocaldococcus jannaschii. Organism_taxid: 2190. Gene: ribc. Expressed in: escherichia coli. Expression_system_taxid: 562.
|
|
Biol. unit:
|
 |
Pentamer (from
)
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
2.30Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.211
|
R-free:
|
0.276
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
A.Ramsperger,M.Augustin,A.K.Schott,S.Gerhardt,T.Krojer,W.Eisenreich, B.Illarionov,M.Cushman,A.Bacher,R.Huber,M.Fischer
|
Key ref:

|
 |
A.Ramsperger
et al.
(2006).
Crystal structure of an archaeal pentameric riboflavin synthase in complex with a substrate analog inhibitor: stereochemical implications.
J Biol Chem,
281,
1224-1232.
PubMed id:
DOI:

|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
11-Oct-05
|
Release date:
|
08-Nov-05
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
Chains A, B, C, D, E:
E.C.2.5.1.9
- riboflavin synthase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
2 6,7-dimethyl-8-(1-D-ribityl)lumazine + H+ = 5-amino-6- (D-ribitylamino)uracil + riboflavin
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
2
×
6,7-dimethyl-8-(1-D-ribityl)lumazine
|
+
|
H(+)
|
=
|
 5-amino-6- (D-ribitylamino)uracil
5-amino-6- (D-ribitylamino)uracil
|
+
|
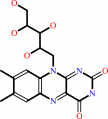 riboflavin
riboflavin
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
J Biol Chem
281:1224-1232
(2006)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Crystal structure of an archaeal pentameric riboflavin synthase in complex with a substrate analog inhibitor: stereochemical implications.
|
|
A.Ramsperger,
M.Augustin,
A.K.Schott,
S.Gerhardt,
T.Krojer,
W.Eisenreich,
B.Illarionov,
M.Cushman,
A.Bacher,
R.Huber,
M.Fischer.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Whereas eubacterial and eukaryotic riboflavin synthases form homotrimers,
archaeal riboflavin synthases from Methanocaldococcus jannaschii and
Methanothermobacter thermoautrophicus are homopentamers with sequence similarity
to the 6,7-dimethyl-8-ribityllumazine synthase catalyzing the penultimate step
in riboflavin biosynthesis. Recently it could be shown that the complex
dismutation reaction catalyzed by the pentameric M. jannaschii riboflavin
synthase generates riboflavin with the same regiochemistry as observed for
trimeric riboflavin synthases. Here we present crystal structures of the
pentameric riboflavin synthase from M. jannaschii and its complex with the
substrate analog inhibitor, 6,7-dioxo-8-ribityllumazine. The complex structure
shows five active sites located between adjacent monomers of the pentamer. Each
active site can accommodate two substrate analog molecules in anti-parallel
orientation. The topology of the two bound ligands at the active site is well in
line with the known stereochemistry of a pentacyclic adduct of
6,7-dimethyl-8-ribityllumazine that has been shown to serve as a kinetically
competent intermediate. The pentacyclic intermediates of trimeric and pentameric
riboflavin synthases are diastereomers.

|

|
|
|

|
| |
Selected figure(s)
|
|

|
| |
 |
 |

|
 |

|
 |
Figure 1.
Terminal reactions of the pathway of riboflavin biosynthesis.
1, 5-amino-6-ribitylamino-2,4(1H,3H)-pyrimidinedione; 2,
3,4-dihydroxy-2-butanone 4-phosphate; 3,
6,7-dimethyl-8-ribityllumazine; 4, riboflavin.
|
 |
Figure 2.
A, ribbon presentation of a M. jannaschii riboflavin synthase
monomer. B, structural alignment of a M. jannaschii riboflavin
synthase monomer (red) with S. pombe lumazine synthase (green;
Protein Data Bank entry code 1KYZ (38)). C, stereo ribbon
presentation of the M. jannaschii riboflavin synthase pentamer
in complex with 6,7-dioxo-8-ribityllumazine (red) viewed along
the 5-fold non-crystallographic symmetry axis. Individual
subunits are shown in different colors.
|
 |
|
|

|
| |
The above figures are
reprinted
by permission from the ASBMB:
J Biol Chem
(2006,
281,
1224-1232)
copyright 2006.
|
|
| |
Figures were
selected
by an automated process.
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
M.Fischer,
and
A.Bacher
(2011).
Biosynthesis of vitamin B2: a unique way to assemble a xylene ring.
|
| |
Chembiochem,
12,
670-680.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
D.E.Scott,
A.Ciulli,
and
C.Abell
(2007).
Coenzyme biosynthesis: enzyme mechanism, structure and inhibition.
|
| |
Nat Prod Rep,
24,
1009-1026.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
D.Gotz,
S.Paytubi,
S.Munro,
M.Ludgren,
R.Bernander,
and
M.F.White
(2007).
Responses of hyperthermophilic crenarchaea to UV irradiation.
|
| |
Genome Biol,
8,
R220.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
Y.Zhang,
B.Illarionov,
A.Bacher,
M.Fischer,
G.I.Georg,
Q.Z.Ye,
D.Vander Velde,
P.E.Fanwick,
Y.Song,
and
M.Cushman
(2007).
A novel lumazine synthase inhibitor derived from oxidation of 1,3,6,8-tetrahydroxy-2,7-naphthyridine to a tetraazaperylenehexaone derivative.
|
| |
J Org Chem,
72,
2769-2776.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
L.De Colibus,
and
A.Mattevi
(2006).
New frontiers in structural flavoenzymology.
|
| |
Curr Opin Struct Biol,
16,
722-728.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
V.Zylberman,
S.Klinke,
I.Haase,
A.Bacher,
M.Fischer,
and
F.A.Goldbaum
(2006).
Evolution of vitamin B2 biosynthesis: 6,7-dimethyl-8-ribityllumazine synthases of Brucella.
|
| |
J Bacteriol,
188,
6135-6142.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
|
 |

