
|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Transferase (carbamoyl-p,aspartate)
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
Crystal and molecular structures of native and ctp-liganded aspartate carbamoyltransferase from escherichia coli
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
Aspartate carbamoyltransferase, catalytic chain. Chain: a. Engineered: yes. Aspartate carbamoyltransferase, regulatory chain. Chain: b. Engineered: yes
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Escherichia coli. Organism_taxid: 562. Organism_taxid: 562
|
|
Biol. unit:
|
 |
 Dodecamer (from
)
Dodecamer (from
)
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
R.B.Honzatko,J.L.Crawford,H.L.Monaco,J.E.Ladner,B.F.P.Edwards, D.R.Evans,S.G.Warren,D.C.Wiley,R.C.Ladner,W.N.Lipscomb
|
Key ref:

|
 |
R.B.Honzatko
et al.
(1982).
Crystal and molecular structures of native and CTP-liganded aspartate carbamoyltransferase from Escherichia coli.
J Mol Biol,
160,
219-263.
PubMed id:
DOI:

|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
24-Mar-82
|
Release date:
|
07-Dec-82
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
Chain A:
E.C.2.1.3.2
- aspartate carbamoyltransferase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

Pathway:
|
 |
Pyrimidine Biosynthesis
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
carbamoyl phosphate + L-aspartate = N-carbamoyl-L-aspartate + phosphate + H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
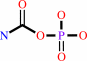 carbamoyl phosphate
carbamoyl phosphate
|
+
|
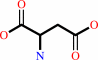 L-aspartate
L-aspartate
|
=
|
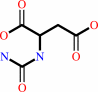 N-carbamoyl-L-aspartate
N-carbamoyl-L-aspartate
|
+
|
 phosphate
phosphate
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
J Mol Biol
160:219-263
(1982)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Crystal and molecular structures of native and CTP-liganded aspartate carbamoyltransferase from Escherichia coli.
|
|
R.B.Honzatko,
J.L.Crawford,
H.L.Monaco,
J.E.Ladner,
B.F.Ewards,
D.R.Evans,
S.G.Warren,
D.C.Wiley,
R.C.Ladner,
W.N.Lipscomb.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |
|
|

|
| |
Selected figure(s)
|
|

|
| |
 |
 |

|
 |

|
 |
Figure 3.
FIG:. . Variation ofthtl crystallographic -factor with wsolution fi)r the 1132 (0) and 1'311 (m) rystal
forms. )ata ww grouped ccording o resolution in 20 hells venly spaced in limits of sine theta. The
solid inw rcpresrnt he t~hrorrtical variaton of th factor at he, sprcified co-ordiate error r.m.s.).
|
 |
Figure 10.
FIN: 10. Intrrfam betw-een catalytic chair) Cl (unbroken inrs) and rrgulatory and catalytic: chains H4
and 4 broken lines). Cl cont.rihutes Clu238 o a polar link ith Tyrl65 of C4. and thr tmrklwnr of
Ala237 and ys236 f Cl ink to Asp111 f R4.
|
 |
|
|

|
| |
The above figures are
reprinted
by permission from Elsevier:
J Mol Biol
(1982,
160,
219-263)
copyright 1982.
|
|
| |
Figures were
selected
by an automated process.
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
B.Stec,
M.K.Williams,
K.A.Stieglitz,
and
E.R.Kantrowitz
(2007).
Comparison of two T-state structures of regulatory-chain mutants of Escherichia coli aspartate transcarbamoylase suggests that His20 and Asp19 modulate the response to heterotropic effectors.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr,
63,
1243-1253.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
J.M.West,
H.Tsuruta,
and
E.R.Kantrowitz
(2004).
A fluorescent probe-labeled Escherichia coli aspartate transcarbamoylase that monitors the allosteric conformational state.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
279,
945-951.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Elstner,
Q.Cui,
P.Munih,
E.Kaxiras,
T.Frauenheim,
and
M.Karplus
(2003).
Modeling zinc in biomolecules with the self consistent charge-density functional tight binding (SCC-DFTB) method: applications to structural and energetic analysis.
|
| |
J Comput Chem,
24,
565-581.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.F.Vickrey,
G.Herve,
and
D.R.Evans
(2002).
Pseudomonas aeruginosa aspartate transcarbamoylase. Characterization of its catalytic and regulatory properties.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
277,
24490-24498.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
U.Ermler,
C.H.Hagemeier,
A.Roth,
U.Demmer,
W.Grabarse,
E.Warkentin,
and
J.A.Vorholt
(2002).
Structure of methylene-tetrahydromethanopterin dehydrogenase from methylobacterium extorquens AM1.
|
| |
Structure,
10,
1127-1137.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
L.Jin,
B.Stec,
W.N.Lipscomb,
and
E.R.Kantrowitz
(1999).
Insights into the mechanisms of catalysis and heterotropic regulation of Escherichia coli aspartate transcarbamoylase based upon a structure of the enzyme complexed with the bisubstrate analogue N-phosphonacetyl-L-aspartate at 2.1 A.
|
| |
Proteins,
37,
729-742.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Flamand,
F.Megret,
M.Mathieu,
J.Lepault,
F.A.Rey,
and
V.Deubel
(1999).
Dengue virus type 1 nonstructural glycoprotein NS1 is secreted from mammalian cells as a soluble hexamer in a glycosylation-dependent fashion.
|
| |
J Virol,
73,
6104-6110.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
V.J.LiCata,
D.S.Burz,
N.J.Moerke,
and
N.M.Allewell
(1998).
The magnitude of the allosteric conformational transition of aspartate transcarbamylase is altered by mutations.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
37,
17381-17385.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Van de Casteele,
P.Chen,
M.Roovers,
C.Legrain,
and
N.Glansdorff
(1997).
Structure and expression of a pyrimidine gene cluster from the extreme thermophile Thermus strain ZO5.
|
| |
J Bacteriol,
179,
3470-3481.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
Y.Ha,
M.T.McCann,
M.Tuchman,
and
N.M.Allewell
(1997).
Substrate-induced conformational change in a trimeric ornithine transcarbamoylase.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
94,
9550-9555.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
G.Rimbach,
A.Markant,
J.Pallauf,
and
K.Krämer
(1996).
[Zinc--update of an essential trace element]
|
| |
Z Ernahrungswiss,
35,
123-142.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
L.B.Murata,
and
H.K.Schachman
(1996).
Structural similarity between ornithine and aspartate transcarbamoylases of Escherichia coli: characterization of the active site and evidence for an interdomain carboxy-terminal helix in ornithine transcarbamoylase.
|
| |
Protein Sci,
5,
709-718.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
L.B.Murata,
and
H.K.Schachman
(1996).
Structural similarity between ornithine and aspartate transcarbamoylases of Escherichia coli: implications for domain switching.
|
| |
Protein Sci,
5,
719-728.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
D.P.Baker,
L.Fetler,
R.T.Keiser,
P.Vachette,
and
E.R.Kantrowitz
(1995).
Weakening of the interface between adjacent catalytic chains promotes domain closure in Escherichia coli aspartate transcarbamoylase.
|
| |
Protein Sci,
4,
258-267.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
K.C.Chou,
and
C.T.Zhang
(1995).
Prediction of protein structural classes.
|
| |
Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol,
30,
275-349.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
R.H.Stote,
and
M.Karplus
(1995).
Zinc binding in proteins and solution: a simple but accurate nonbonded representation.
|
| |
Proteins,
23,
12-31.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
C.B.Peterson,
B.B.Zhou,
D.Hsieh,
A.N.Creager,
and
H.K.Schachman
(1994).
Association of the catalytic subunit of aspartate transcarbamoylase with a zinc-containing polypeptide fragment of the regulatory chain leads to increases in thermal stability.
|
| |
Protein Sci,
3,
960-966.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
E.Cheah,
P.D.Carr,
P.M.Suffolk,
S.G.Vasudevan,
N.E.Dixon,
and
D.L.Ollis
(1994).
Structure of the Escherichia coli signal transducing protein PII.
|
| |
Structure,
2,
981-990.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
J.Jeloková,
C.Karlsson,
M.Estonius,
H.Jörnvall,
and
J.O.Höög
(1994).
Features of structural zinc in mammalian alcohol dehydrogenase. Site-directed mutagenesis of the zinc ligands.
|
| |
Eur J Biochem,
225,
1015-1019.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
N.V.Grishin,
and
M.A.Phillips
(1994).
The subunit interfaces of oligomeric enzymes are conserved to a similar extent to the overall protein sequences.
|
| |
Protein Sci,
3,
2455-2458.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
P.England,
C.Leconte,
P.Tauc,
and
G.Hervé
(1994).
Apparent cooperativity for carbamoylphosphate in Escherichia coli aspartate transcarbamoylase only reflects cooperativity for aspartate.
|
| |
Eur J Biochem,
222,
775-780.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
B.Chatton,
J.L.Bocco,
M.Gaire,
C.Hauss,
B.Reimund,
J.Goetz,
and
C.Kedinger
(1993).
Transcriptional activation by the adenovirus larger E1a product is mediated by members of the cellular transcription factor ATF family which can directly associate with E1a.
|
| |
Mol Cell Biol,
13,
561-570.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
B.L.Vallee,
and
D.S.Auld
(1993).
Cocatalytic zinc motifs in enzyme catalysis.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
90,
2715-2718.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.J.Tanner,
P.E.Smith,
and
K.L.Krause
(1993).
Molecular dynamics simulations and rigid body (TLS) analysis of aspartate carbamoyltransferase: evidence for an uncoupled R state.
|
| |
Protein Sci,
2,
927-935.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
R.P.Kosman,
J.E.Gouaux,
and
W.N.Lipscomb
(1993).
Crystal structure of CTP-ligated T state aspartate transcarbamoylase at 2.5 A resolution: implications for ATCase mutants and the mechanism of negative cooperativity.
|
| |
Proteins,
15,
147-176.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
S.T.Bergh,
and
D.R.Evans
(1993).
Subunit structure of a class A aspartate transcarbamoylase from Pseudomonas fluorescens.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
90,
9818-9822.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
Y.R.Yang,
and
H.K.Schachman
(1993).
Aspartate transcarbamoylase containing circularly permuted catalytic polypeptide chains.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
90,
11980-11984.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
C.B.Peterson,
and
H.K.Schachman
(1991).
Role of a carboxyl-terminal helix in the assembly, interchain interactions, and stability of aspartate transcarbamoylase.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
88,
458-462.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
F.Van Vliet,
X.G.Xi,
C.De Staercke,
B.de Wannemaeker,
A.Jacobs,
J.Cherfils,
M.M.Ladjimi,
G.Hervé,
and
R.Cunin
(1991).
Heterotropic interactions in aspartate transcarbamoylase: turning allosteric ATP activation into inhibition as a consequence of a single tyrosine to phenylalanine mutation.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
88,
9180-9183.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.L.Scully,
and
D.R.Evans
(1991).
Comparative modeling of mammalian aspartate transcarbamylase.
|
| |
Proteins,
9,
191-206.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
B.L.Vallee,
and
D.S.Auld
(1990).
Active-site zinc ligands and activated H2O of zinc enzymes.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
87,
220-224.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
C.J.Newton,
and
E.R.Kantrowitz
(1990).
The regulatory subunit of Escherichia coli aspartate carbamoyltransferase may influence homotropic cooperativity and heterotropic interactions by a direct interaction with the loop containing residues 230-245 of the catalytic chain.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
87,
2309-2313.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
E.B.Springman,
E.L.Angleton,
H.Birkedal-Hansen,
and
H.E.Van Wart
(1990).
Multiple modes of activation of latent human fibroblast collagenase: evidence for the role of a Cys73 active-site zinc complex in latency and a "cysteine switch" mechanism for activation.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
87,
364-368.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
E.R.Kantrowitz,
and
W.N.Lipscomb
(1990).
Escherichia coli aspartate transcarbamoylase: the molecular basis for a concerted allosteric transition.
|
| |
Trends Biochem Sci,
15,
53-59.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.N.Davidson,
G.N.Rao,
L.Niswander,
C.Andreano,
C.Tamer,
and
K.C.Chen
(1990).
Organization and nucleotide sequence of the 3' end of the human CAD gene.
|
| |
DNA Cell Biol,
9,
667-676.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
T.A.Hoover,
and
J.C.Williams
(1990).
Characterization of Coxiella burnetii pyrB.
|
| |
Ann N Y Acad Sci,
590,
485-490.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
E.Eisenstein,
D.W.Markby,
and
H.K.Schachman
(1989).
Changes in stability and allosteric properties of aspartate transcarbamoylase resulting from amino acid substitutions in the zinc-binding domain of the regulatory chains.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
86,
3094-3098.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.G.Major,
M.E.Wales,
J.E.Houghton,
J.A.Maley,
J.N.Davidson,
and
J.R.Wild
(1989).
Molecular evolution of enzyme structure: construction of a hybrid hamster/Escherichia coli aspartate transcarbamoylase.
|
| |
J Mol Evol,
28,
442-450.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.M.Berg
(1989).
DNA binding specificity of steroid receptors.
|
| |
Cell,
57,
1065-1068.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
L.M.Green,
and
J.M.Berg
(1989).
A retroviral Cys-Xaa2-Cys-Xaa4-His-Xaa4-Cys peptide binds metal ions: spectroscopic studies and a proposed three-dimensional structure.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
86,
4047-4051.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.F.Perutz
(1989).
Mechanisms of cooperativity and allosteric regulation in proteins.
|
| |
Q Rev Biophys,
22,
139-237.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Faure,
J.H.Camonis,
and
M.Jacquet
(1989).
Molecular characterization of a Dictyostelium discoideum gene encoding a multifunctional enzyme of the pyrimidine pathway.
|
| |
Eur J Biochem,
179,
345-358.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.P.Glackin,
M.P.McCarthy,
D.Mallikarachchi,
J.B.Matthew,
and
N.M.Allewell
(1989).
Electrostatic interactions in the assembly of Escherichia coli aspartate transcarbamylase.
|
| |
Proteins,
5,
66-77.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
P.E.Hodges,
and
L.E.Rosenberg
(1989).
The spfash mouse: a missense mutation in the ornithine transcarbamylase gene also causes aberrant mRNA splicing.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
86,
4142-4146.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.M.Berg
(1988).
Proposed structure for the zinc-binding domains from transcription factor IIIA and related proteins.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
85,
99.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Wittekind,
J.Dodd,
L.Vu,
J.M.Kolb,
J.M.Buhler,
A.Sentenac,
and
M.Nomura
(1988).
Isolation and characterization of temperature-sensitive mutations in RPA190, the gene encoding the largest subunit of RNA polymerase I from Saccharomyces cerevisiae.
|
| |
Mol Cell Biol,
8,
3997-4008.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
T.Kikuchi,
G.Némethy,
and
H.A.Scheraga
(1988).
Prediction of the packing arrangement of strands in beta-sheets of globular proteins.
|
| |
J Protein Chem,
7,
473-490.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.Cherfils,
P.Vachette,
P.Tauc,
and
J.Janin
(1987).
The pAR5 mutation and the allosteric mechanism of Escherichia coli aspartate carbamoyltransferase.
|
| |
EMBO J,
6,
2843-2847.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
N.N.Sandal,
K.Bojsen,
and
K.A.Marcker
(1987).
A small family of nodule specific genes from soybean.
|
| |
Nucleic Acids Res,
15,
1507-1519.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
D.S.Burz,
and
N.M.Allewell
(1986).
Mapping Structural Perturbations in Escherichia Coli Aspartate Transcarbamylase by Medium Resolution Hydrogen Exchange.
|
| |
Biophys J,
49,
70-72.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
K.F.Foltermann,
D.A.Beck,
and
J.R.Wild
(1986).
In vivo formation of hybrid aspartate transcarbamoylases from native subunits of divergent members of the family Enterobacteriaceae.
|
| |
J Bacteriol,
167,
285-290.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.A.Middleton,
and
E.R.Kantrowitz
(1986).
Importance of the loop at residues 230-245 in the allosteric interactions of Escherichia coli aspartate carbamoyltransferase.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
83,
5866-5870.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
D.Peters,
and
J.Peters
(1985).
A simple and novel interpretation of the three-dimensional structure of globular proteins based on quantum-mechanical computations on small model molecules. I.
|
| |
Biopolymers,
24,
491-508.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
E.A.Robey,
and
H.K.Schachman
(1985).
Regeneration of active enzyme by formation of hybrids from inactive derivatives: implications for active sites shared between polypeptide chains of aspartate transcarbamoylase.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
82,
361-365.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
I.M.Klotz
(1985).
Ligand--receptor interactions: facts and fantasies.
|
| |
Q Rev Biophys,
18,
227-259.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
K.L.Krause,
K.W.Volz,
and
W.N.Lipscomb
(1985).
Structure at 2.9-A resolution of aspartate carbamoyltransferase complexed with the bisubstrate analogue N-(phosphonacetyl)-L-aspartate.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
82,
1643-1647.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
P.McIntyre,
L.Graf,
J.F.Mercer,
S.A.Wake,
P.Hudson,
and
N.Hoogenraad
(1985).
The primary structure of the imported mitochondrial protein, ornithine transcarbamylase from rat liver: mRNA levels during ontogeny.
|
| |
DNA,
4,
147-156.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
H.K.Schachman,
C.D.Pauza,
M.Navre,
M.J.Karels,
L.Wu,
and
Y.R.Yang
(1984).
Location of amino acid alterations in mutants of aspartate transcarbamoylase: Structural aspects of interallelic complementation.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
81,
115-119.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
H.M.Ke,
R.B.Honzatko,
and
W.N.Lipscomb
(1984).
Structure of unligated aspartate carbamoyltransferase of Escherichia coli at 2.6-A resolution.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
81,
4037-4040.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
J.E.Houghton,
D.A.Bencini,
G.A.O'Donovan,
and
J.R.Wild
(1984).
Protein differentiation: a comparison of aspartate transcarbamoylase and ornithine transcarbamoylase from Escherichia coli K-12.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
81,
4864-4868.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
K.F.Foltermann,
M.S.Shanley,
and
J.R.Wild
(1984).
Assembly of the aspartate transcarbamoylase holoenzyme from transcriptionally independent catalytic and regulatory cistrons.
|
| |
J Bacteriol,
157,
891-898.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
D.A.Bencini,
J.E.Houghton,
T.A.Hoover,
K.F.Foltermann,
J.R.Wild,
and
G.A.O'Donovan
(1983).
The DNA sequence of argI from Escherichia coli K12.
|
| |
Nucleic Acids Res,
11,
8509-8518.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.P.McCarthy,
and
N.M.Allewell
(1983).
Thermodynamics of assembly of Escherichia coli aspartate transcarbamoylase.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
80,
6824-6828.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
R.Hensel,
U.Mayr,
and
C.Y.Yang
(1983).
The complete primary structure of the allosteric L-lactate dehydrogenase from Lactobacillus casei.
|
| |
Eur J Biochem,
134,
503-511.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
T.A.Hoover,
W.D.Roof,
K.F.Foltermann,
G.A.O'Donovan,
D.A.Bencini,
and
J.R.Wild
(1983).
Nucleotide sequence of the structural gene (pyrB) that encodes the catalytic polypeptide of aspartate transcarbamoylase of Escherichia coli.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
80,
2462-2466.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
W.H.Konigsberg,
and
L.Henderson
(1983).
Amino acid sequence of the catalytic subunit of aspartate transcarbamoylase from Escherichia coli.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
80,
2467-2471.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
R.B.Honzatko,
and
W.N.Lipscomb
(1982).
Interactions of metal-nucleotide complexes with aspartate carbamoyltransferase in the crystalline state.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
79,
7171-7174.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
codes are
shown on the right.
|
 |

