 |
PDBsum entry 2akc

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.3.1.3.2
- acid phosphatase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
a phosphate monoester + H2O = an alcohol + phosphate
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
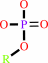 phosphate monoester
phosphate monoester
|
+
|
H2O
|
=
|
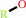 alcohol
alcohol
|
+
|
 phosphate
phosphate
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Biochemistry
46:2079-2090
(2007)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Structure and mutational analysis of the PhoN protein of Salmonella typhimurium provide insight into mechanistic details.
|
|
R.D.Makde,
S.K.Mahajan,
V.Kumar.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
The Salmonella typhimurium PhoN protein is a nonspecific acid phosphatase and
belongs to the phosphatidic acid phosphatase type 2 (PAP2) superfamily. We
report here the crystal structures of phosphate-bound PhoN, the PhoN-tungstate
complex, and the T159D mutant of PhoN along with functional characterization of
three mutants: L39T, T159D, and D201N. Invariant active site residues, Lys-123,
Arg-130, Ser-156, Gly-157, His-158, and Arg-191, interact with phosphate and
tungstate oxyanions. Ser-156 also accepts a hydrogen bond from Thr-159. The
T159D mutation, surprisingly, severely diminishes phosphatase activity,
apparently by disturbing the active site scaffold: Arg-191 is swung out of the
active site resulting in conformational changes in His-158 and His-197 residues.
Our results reveal a hitherto unknown functional role of Arg-191, namely,
restricting the active conformation of catalytic His-158 and His-197 residues.
Consistent with the conserved nature of Asp-201 in the PAP2 superfamily, the
D201N mutation completely abolished phosphatase activity. On the basis of this
observation and in silico analysis we suggest that the crucial mechanistic role
of Asp-201 is to stabilize the positive charge on the phosphohistidine
intermediate generated by the transfer of phosphoryl to the nucleophile,
His-197, located within hydrogen bond distance to the invariant Asp-201. This is
in contrast to earlier suggestions that Asp-201 stabilizes His-197 and the
His197-Asp201 dyad facilitates formation of the phosphoenzyme intermediate
through a charge-relay system. Finally, the L39T mutation in the conserved
polyproline motif (39LPPPP43) of dimeric PhoN leads to a marginal reduction in
activity, in contrast to the nearly 50-fold reduction observed for monomeric
Prevotella intermedia acid phosphatase, suggesting that the varying quaternary
structure of PhoN orthologues may have functional significance.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
F.Manabe,
H.Shoun,
and
T.Wakagi
(2011).
Conserved residues in membrane-bound acid pyrophosphatase from Sulfolobus tokodaii, a thermoacidophilic archaeon.
|
| |
Extremophiles,
15,
359-364.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
Z.Lu,
D.Dunaway-Mariano,
and
K.N.Allen
(2008).
The catalytic scaffold of the haloalkanoic acid dehalogenase enzyme superfamily acts as a mold for the trigonal bipyramidal transition state.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
105,
5687-5692.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
codes are
shown on the right.
|
 |

