 |
PDBsum entry 2a89

|
|
|

|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |

|

|

|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
Oxidoreductase
|
PDB id
|
|

|

|
2a89
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.1.5.3.1
- sarcosine oxidasee (formaldehyde-forming).
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
sarcosine + O2 + H2O = formaldehyde + glycine + H2O2
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
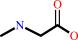 sarcosine
sarcosine
|
+
|
 O2
O2
|
+
|
H2O
|
=
|
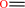 formaldehyde
formaldehyde
|
+
|
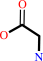 glycine
glycine
|
+
|
 H2O2
H2O2
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Cofactor:
|
 |
FAD
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
FAD
Bound ligand (Het Group name =
FCG)
matches with 92.98% similarity
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Biochemistry
44:15444-15450
(2005)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Structure of the sodium borohydride-reduced N-(cyclopropyl)glycine adduct of the flavoenzyme monomeric sarcosine oxidase.
|
|
Z.W.Chen,
G.Zhao,
S.Martinovic,
M.S.Jorns,
F.S.Mathews.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Monomeric sarcosine oxidase (MSOX) is a flavoprotein that contains covalently
bound FAD [8a-(S-cysteinyl)FAD] and catalyzes the oxidation of sarcosine
(N-methylglycine) and other secondary amino acids, such as l-proline. Our
previous studies showed that N-(cyclopropyl)glycine (CPG) acts as a
mechanism-based inactivator of MSOX [Zhao, G., et al. (2000) Biochemistry 39,
14341-14347]. The reaction results in the formation of a modified reduced flavin
that can be further reduced and stabilized by treatment with sodium borohydride.
The borohydride-reduced CPG-modified enzyme exhibits a mass increase of 63 +/- 2
Da as compared with native MSOX. The crystal structure of the modified enzyme,
solved at 1.85 A resolution, shows that FAD is the only site of modification.
The modified FAD contains a fused five-membered ring, linking the C(4a) and N(5)
atoms of the flavin ring, with an additional oxygen atom bound to the carbon
atom attached to N(5) and a tetrahedral carbon atom at flavin C(4) with a
hydroxyl group attached to C(4). On the basis of the crystal structure of the
borohydride-stabilized adduct, we conclude that the labile CPG-modified flavin
is a 4a,5-dihydroflavin derivative with a substituent derived from the cleavage
of the cyclopropyl ring in CPG. The results are consistent with CPG-mediated
inactivation in a reaction initiated by single electron transfer from the amine
function in CPG to FAD in MSOX, followed by collapse of the radical pair to
yield a covalently modified 4a,5-dihydroflavin.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
P.F.Fitzpatrick
(2010).
Oxidation of amines by flavoproteins.
|
| |
Arch Biochem Biophys,
493,
13-25.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
H.Gaweska,
M.Henderson Pozzi,
D.M.Schmidt,
D.G.McCafferty,
and
P.F.Fitzpatrick
(2009).
Use of pH and kinetic isotope effects to establish chemistry as rate-limiting in oxidation of a peptide substrate by LSD1.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
48,
5440-5445.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
E.C.Ralph,
J.S.Hirschi,
M.A.Anderson,
W.W.Cleland,
D.A.Singleton,
and
P.F.Fitzpatrick
(2007).
Insights into the mechanism of flavoprotein-catalyzed amine oxidation from nitrogen isotope effects on the reaction of N-methyltryptophan oxidase.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
46,
7655-7664.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
P.F.Fitzpatrick
(2007).
Insights into the mechanisms of flavoprotein oxidases from kinetic isotope effects.
|
| |
J Labelled Comp Radiopharm,
50,
1016-1025.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
G.Zhao,
and
M.S.Jorns
(2006).
Spectral and kinetic characterization of the michaelis charge transfer complex in monomeric sarcosine oxidase.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
45,
5985-5992.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
|
 |

