 |
PDBsum entry 2zut

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Transferase
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
Crystal structure of galacto-n-biose/lacto-n-biose i phosphorylase in complex with galnac
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
Lacto-n-biose phosphorylase. Chain: a, b, c, d. Synonym: galacto-n-biose/lacto-n-biose i phosphorylase. Engineered: yes
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Bifidobacterium longum. Organism_taxid: 216816. Strain: jcm1217. Gene: lnpa. Expressed in: escherichia coli. Expression_system_taxid: 562.
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
1.90Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.163
|
R-free:
|
0.204
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
M.Hidaka,M.Nishimoto,M.Kitaoka,T.Wakagi,H.Shoun,S.Fushinobu
|
Key ref:

|
 |
M.Hidaka
et al.
(2009).
The crystal structure of galacto-N-biose/lacto-N-biose I phosphorylase: a large deformation of a TIM barrel scaffold.
J Biol Chem,
284,
7273-7283.
PubMed id:
DOI:

|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
28-Oct-08
|
Release date:
|
30-Dec-08
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
E8MF13
(LNPA_BIFL2) -
1,3-beta-galactosyl-N-acetylhexosamine phosphorylase from Bifidobacterium longum subsp. longum (strain ATCC 15707 / DSM 20219 / JCM 1217 / NCTC 11818 / E194b)
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
751 a.a.
744 a.a.
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|
|
Key: |
 |
PfamA domain |
 |
 |
 |
Secondary structure |
 |
 |
CATH domain |
 |
|

|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.2.4.1.211
- 1,3-beta-galactosyl-N-acetylhexosamine phosphorylase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
beta-D-galactosyl-(1->3)-N-acetyl-D-glucosamine + phosphate = alpha-D- galactose 1-phosphate + N-acetyl-D-glucosamine
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
beta-D-galactosyl-(1->3)-N-acetyl-D-glucosamine
|
+
|
 phosphate
phosphate
|
=
|
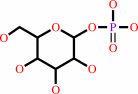 alpha-D- galactose 1-phosphate
alpha-D- galactose 1-phosphate
|
+
|
N-acetyl-D-glucosamine
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
corresponds exactly
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
J Biol Chem
284:7273-7283
(2009)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
The crystal structure of galacto-N-biose/lacto-N-biose I phosphorylase: a large deformation of a TIM barrel scaffold.
|
|
M.Hidaka,
M.Nishimoto,
M.Kitaoka,
T.Wakagi,
H.Shoun,
S.Fushinobu.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Galacto-N-biose/lacto-N-biose I phosphorylase (GLNBP) from Bifidobacterium
longum, a key enzyme for intestinal growth, phosphorolyses galacto-N-biose and
lacto-N-biose I with anomeric inversion. GLNBP homologues are often found in
human pathogenic and commensal bacteria, and their substrate specificities
potentially define the nutritional acquisition ability of these microbes in
their habitat. We report the crystal structures of GLNBP in five different
ligand-binding forms. This is the first three-dimensional structure of glycoside
hydrolase (GH) family 112. The GlcNAc- and GalNAc-bound forms provide structural
insights into distinct substrate preferences of GLNBP and its homologues from
pathogens. The catalytic domain consists of a partially broken TIM barrel fold
that is structurally similar to a thermophilic beta-galactosidase, strongly
supporting the current classification of GLNBP homologues as one of the GH
families. Anion binding induces a large conformational change by rotating a
half-unit of the barrel. This is an unusual example of molecular adaptation of a
TIM barrel scaffold to substrates.

|

|
|
|

|
| |
Selected figure(s)
|
|

|
| |
 |
 |

|
 |

|
 |
Figure 1.
Schematic representation of the reaction catalyzed by
GalHexNAcP.
|
 |
Figure 2.
Overall structure of GLNBP. The TIM barrel fold domain
(blue), Ig-like fold domain (green), α/β fold domain (yellow),
and C-terminal domain (red) are shown. A, dimeric structure of
GlcNAc-NO[3]-EG crystal form. Subunits in the closed and
semiclosed states are shown in a ribbon model. The semiclosed
state subunit is shown with a different color code (TIM barrel
domain in light blue, Ig-like domain in light green, α/β
domain in brown, and C-terminal domain in pink). The ligand-free
form in the open state (subunit A) (B) and GlcNAc-NO[3]-EG in
the closed state (subunit A) (C) are shown from the same view as
A. Ligands in the active site (GlcNAc, ethylene glycol, and  )
are shown as a space-filling model. Asp-313 and Trp-233 are
shown as a stick model (cyan), and the Cα atom of Gly-371 is
shown as a red sphere. )
are shown as a space-filling model. Asp-313 and Trp-233 are
shown as a stick model (cyan), and the Cα atom of Gly-371 is
shown as a red sphere.
|
 |
|
|

|
| |
The above figures are
reprinted
by permission from the ASBMB:
J Biol Chem
(2009,
284,
7273-7283)
copyright 2009.
|
|
| |
Figures were
selected
by an automated process.
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
C.Luley-Goedl,
and
B.Nidetzky
(2010).
Carbohydrate synthesis by disaccharide phosphorylases: reactions, catalytic mechanisms and application in the glycosciences.
|
| |
Biotechnol J,
5,
1324-1338.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
H.Ashida,
H.Ozawa,
K.Fujita,
S.Suzuki,
and
K.Yamamoto
(2010).
Syntheses of mucin-type O-glycopeptides and oligosaccharides using transglycosylation and reverse-hydrolysis activities of Bifidobacterium endo-alpha-N-acetylgalactosaminidase.
|
| |
Glycoconj J,
27,
125-132.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
H.Yu,
V.Thon,
K.Lau,
L.Cai,
Y.Chen,
S.Mu,
Y.Li,
P.G.Wang,
and
X.Chen
(2010).
Highly efficient chemoenzymatic synthesis of β1-3-linked galactosides.
|
| |
Chem Commun (Camb),
46,
7507-7509.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Miwa,
T.Horimoto,
M.Kiyohara,
T.Katayama,
M.Kitaoka,
H.Ashida,
and
K.Yamamoto
(2010).
Cooperation of β-galactosidase and β-N-acetylhexosaminidase from bifidobacteria in assimilation of human milk oligosaccharides with type 2 structure.
|
| |
Glycobiology,
20,
1402-1409.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Fushinobu
(2010).
Unique sugar metabolic pathways of bifidobacteria.
|
| |
Biosci Biotechnol Biochem,
74,
2374-2384.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
H.Ashida,
A.Miyake,
M.Kiyohara,
J.Wada,
E.Yoshida,
H.Kumagai,
T.Katayama,
and
K.Yamamoto
(2009).
Two distinct alpha-L-fucosidases from Bifidobacterium bifidum are essential for the utilization of fucosylated milk oligosaccharides and glycoconjugates.
|
| |
Glycobiology,
19,
1010-1017.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Nakajima,
M.Nishimoto,
and
M.Kitaoka
(2009).
Characterization of three beta-galactoside phosphorylases from Clostridium phytofermentans: discovery of d-galactosyl-beta1->4-l-rhamnose phosphorylase.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
284,
19220-19227.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
|
 |

