 |
PDBsum entry 2zoa

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.3.1.4.46
- glycerophosphodiester phosphodiesterase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
a sn-glycero-3-phosphodiester + H2O = an alcohol + sn-glycerol 3-phosphate + H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
sn-glycero-3-phosphodiester
|
+
|
H2O
|
=
|
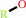 alcohol
alcohol
|
+
|
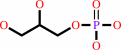 sn-glycerol 3-phosphate
sn-glycerol 3-phosphate
|
+
|
H(+)
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 41.67% similarity
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
Acta Crystallogr Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun
64:681-685
(2008)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Malonate-bound structure of the glycerophosphodiesterase from Enterobacter aerogenes (GpdQ) and characterization of the native Fe2+ metal-ion preference.
|
|
C.J.Jackson,
K.S.Hadler,
P.D.Carr,
A.J.Oakley,
S.Yip,
G.Schenk,
D.L.Ollis.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
The structure of a malonate-bound form of the glycerophosphodiesterase from
Enterobacter aerogenes, GpdQ, has been refined at a resolution of 2.2 A to a
final R factor of 17.1%. The structure was originally solved to 2.9 A resolution
using SAD phases from Zn2+ metal ions introduced into the active site of the
apoenzyme [Jackson et al. (2007), J. Mol. Biol. 367, 1047-1062]. However, the
2.9 A resolution was insufficient to discern significant details of the
architecture of the binuclear metal centre that constitutes the active site.
Furthermore, kinetic analysis revealed that the enzyme lost a significant amount
of activity in the presence of Zn2+, suggesting that it is unlikely to be a
catalytically relevant metal ion. In this communication, a higher resolution
structure of GpdQ is presented in which malonate is visibly coordinated in the
active site and analysis of the native metal-ion preference is presented using
atomic absorption spectroscopy and anomalous scattering. Catalytic implications
of the structure and its Fe2+ metal-ion preference are discussed.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

