 |
PDBsum entry 2zma

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.3.5.1.46
- 6-aminohexanoate-oligomer exohydrolase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
|
1.
|
[N-(6-aminohexanoyl)](n) + H2O = [N-(6-aminohexanoyl)](n-1) + 6-aminohexanoate
|
|
2.
|
N-(6-aminohexanoyl)-6-aminohexanoate + H2O = 2 6-aminohexanoate
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
[N-(6-aminohexanoyl)](n)
|
+
|
H2O
|
=
|
[N-(6-aminohexanoyl)](n-1)
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
corresponds exactly
|
+
|
 6-aminohexanoate
6-aminohexanoate
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
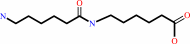 N-(6-aminohexanoyl)-6-aminohexanoate
N-(6-aminohexanoyl)-6-aminohexanoate
|
+
|
H2O
|
=
|
2
×
6-aminohexanoate
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
corresponds exactly
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
Febs J
276:2547-2556
(2009)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Molecular design of a nylon-6 byproduct-degrading enzyme from a carboxylesterase with a beta-lactamase fold.
|
|
Y.Kawashima,
T.Ohki,
N.Shibata,
Y.Higuchi,
Y.Wakitani,
Y.Matsuura,
Y.Nakata,
M.Takeo,
D.Kato,
S.Negoro.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
A carboxylesterase with a beta-lactamase fold from Arthrobacter possesses a low
level of hydrolytic activity (0.023 mumol.min(-1).mg(-1)) when acting on a
6-aminohexanoate linear dimer byproduct of the nylon-6 industry (Ald).
G181D/H266N/D370Y triple mutations in the parental esterase increased the
Ald-hydrolytic activity 160-fold. Kinetic studies showed that the triple mutant
possesses higher affinity for the substrate Ald (K(m) = 2.0 mm) than the
wild-type Ald hydrolase from Arthrobacter (K(m) = 21 mm). In addition, the
k(cat)/K(m) of the mutant (1.58 s(-1).mm(-1)) was superior to that of the
wild-type enzyme (0.43 s(-1).mm(-1)), demonstrating that the mutant efficiently
converts the unnatural amide compounds even at low substrate concentrations, and
potentially possesses an advantage for biotechnological applications. X-ray
crystallographic analyses of the G181D/H266N/D370Y enzyme and the inactive
S112A-mutant-Ald complex revealed that Ald binding induces rotation of
Tyr370/His375, movement of the loop region (N167-V177), and flip-flop of Tyr170,
resulting in the transition from open to closed forms. From the comparison of
the three-dimensional structures of various mutant enzymes and site-directed
mutagenesis at positions 266 and 370, we now conclude that Asn266 makes suitable
contacts with Ald and improves the electrostatic environment at the N-terminal
region of Ald cooperatively with Asp181, and that Tyr370 stabilizes Ald binding
by hydrogen-bonding/hydrophobic interactions at the C-terminal region of Ald.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
F.Kawai
(2010).
The biochemistry and molecular biology of xenobiotic polymer degradation by microorganisms.
|
| |
Biosci Biotechnol Biochem,
74,
1743-1759.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
K.Yasuhira,
N.Shibata,
G.Mongami,
Y.Uedo,
Y.Atsumi,
Y.Kawashima,
A.Hibino,
Y.Tanaka,
Y.H.Lee,
D.Kato,
M.Takeo,
Y.Higuchi,
and
S.Negoro
(2010).
X-ray crystallographic analysis of the 6-aminohexanoate cyclic dimer hydrolase: catalytic mechanism and evolution of an enzyme responsible for nylon-6 byproduct degradation.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
285,
1239-1248.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
P.Limphong,
G.Nimako,
P.W.Thomas,
W.Fast,
C.A.Makaroff,
and
M.W.Crowder
(2009).
Arabidopsis thaliana mitochondrial glyoxalase 2-1 exhibits beta-lactamase activity.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
48,
8491-8493.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
T.Ohki,
N.Shibata,
Y.Higuchi,
Y.Kawashima,
M.Takeo,
D.Kato,
and
S.Negoro
(2009).
Two alternative modes for optimizing nylon-6 byproduct hydrolytic activity from a carboxylesterase with a beta-lactamase fold: X-ray crystallographic analysis of directly evolved 6-aminohexanoate-dimer hydrolase.
|
| |
Protein Sci,
18,
1662-1673.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
codes are
shown on the right.
|
 |
|

