 |
PDBsum entry 2z7k

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.2.4.2.29
- tRNA-guanosine(34) preQ1 transglycosylase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
7-aminomethyl-7-carbaguanine + guanosine34 in tRNA = 7-aminomethyl-7- carbaguanosine34 in tRNA + guanine
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
7-aminomethyl-7-carbaguanine
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 70.59% similarity
|
+
|
guanosine(34) in tRNA
|
=
|
7-aminomethyl-7- carbaguanosine(34) in tRNA
|
+
|
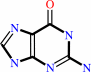 guanine
guanine
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
Chembiochem
10:716-727
(2009)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Crystal structure analysis and in silico pKa calculations suggest strong pKa shifts of ligands as driving force for high-affinity binding to TGT.
|
|
T.Ritschel,
S.Hoertner,
A.Heine,
F.Diederich,
G.Klebe.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
A novel ligand series is presented to inhibit tRNA-guanine transglycosylase
(TGT), a protein with a significant role in the pathogenicity mechanism of
Shigella flexneri, the causative agent of Shigellosis. The enzyme exchanges
guanine in the wobble position of tRNA(Asn,Asp,His,Tyr) against a modified base.
To prevent the base-exchange reaction, several series of inhibitors have already
been designed, synthesized, and tested. One aim of previous studies was to
address a hydrophobic pocket with different side chains attached to the parent
skeletons. Disappointingly, no significant increase in binding affinity could be
observed that could be explained by the disruption of a conserved water cluster.
The ligand series examined in this study are based on the known scaffold
lin-benzoguanine. Different side chains were introduced leading to
2-amino-lin-benzoguanines, which address a different pocket of the protein and
avoid disruption of the water cluster. With the introduction of an amino group
in the 2-position, a dramatic increase in binding affinity can be experienced.
To explain this significant gain in binding affinity, Poisson-Boltzmann
calculations were performed to explore pK(a) changes of ligand functional groups
upon protein binding, they can differ significantly on going from aqueous
solution to protein environment. For all complexes, a permanent protonation of
the newly designed ligands is suggested, leading to a charge-assisted hydrogen
bond in the protein-ligand complex. This increased strength in hydrogen bonding
takes beneficial effect on binding affinity of the ligands, resulting in
low-nanomolar binders. Crystal structures and docking emphasize the importance
of the newly created charge-assisted hydrogen bond. A detailed analysis of the
crystal structures in complex with substituted 2-amino-lin-benzoguanines
indicate pronounced disorder of the attached side chains addressing the ribose
33 binding pocket. Docking suggests multiple orientations of these side chains.
Obviously, an entropic advantage of the residual mobility experienced by these
ligands in the bound state is beneficial and reveals an overall improved protein
binding.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
P.C.Kohler,
T.Ritschel,
W.B.Schweizer,
G.Klebe,
and
F.Diederich
(2009).
High-affinity inhibitors of tRNA-guanine transglycosylase replacing the function of a structural water cluster.
|
| |
Chemistry,
15,
10809-10817.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
T.Ritschel,
P.C.Kohler,
G.Neudert,
A.Heine,
F.Diederich,
and
G.Klebe
(2009).
How to Replace the Residual Solvation Shell of Polar Active Site Residues to Achieve Nanomolar Inhibition of tRNA-Guanine Transglycosylase.
|
| |
ChemMedChem,
4,
2012-2023.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
codes are
shown on the right.
|
 |

