 |
PDBsum entry 2z6w

|
|
|

|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |

|

|

|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
Isomerase/immunosuppressant
|
PDB id
|
|

|

|
2z6w
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Isomerase/immunosuppressant
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
Crystal structure of human cyclophilin d in complex with cyclosporin a
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
Peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase. Chain: a, b. Fragment: residues 2-165. Synonym: ppiase, rotamase, cyclophilin d. Engineered: yes. Mutation: yes. Cyclosporin a. Chain: m, n. Synonym: ciclosporin, ciclosporine.
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Homo sapiens. Human. Organism_taxid: 9606. Gene: ppif, cyp3. Expressed in: escherichia coli bl21(de3). Expression_system_taxid: 469008. Synthetic: yes. Tolypocladium inflatum. Organism_taxid: 29910
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
0.96Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.130
|
R-free:
|
0.153
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
K.Kajitani,M.Fujihashi,Y.Kobayashi,S.Shimizu,Y.Tsujimoto,K.Miki
|
Key ref:

|
 |
K.Kajitani
et al.
(2008).
Crystal structure of human cyclophilin D in complex with its inhibitor, cyclosporin A at 0.96-A resolution.
Proteins,
70,
1635-1639.
PubMed id:
DOI:

|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
09-Aug-07
|
Release date:
|
29-Apr-08
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
Chains A, B:
E.C.5.2.1.8
- peptidylprolyl isomerase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
[protein]-peptidylproline (omega=180) = [protein]-peptidylproline (omega=0)
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
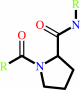 Peptidylproline (omega=180)
Peptidylproline (omega=180)
|
=
|
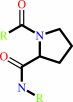 peptidylproline (omega=0)
peptidylproline (omega=0)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Proteins
70:1635-1639
(2008)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Crystal structure of human cyclophilin D in complex with its inhibitor, cyclosporin A at 0.96-A resolution.
|
|
K.Kajitani,
M.Fujihashi,
Y.Kobayashi,
S.Shimizu,
Y.Tsujimoto,
K.Miki.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |
|
|

|
| |
Selected figure(s)
|
|

|
| |
 |
 |

|
 |
Figure 1.
Figure 1. (A) Overall structure of CypD in complex with CsA.
CypD and CsA are shown as ribbon- and stick-models,
respectively. Panels A, B, and D were drawn with PyMOL
(http://www.pymol.org). (B) Close-up view of CsA superimposed on
its Fo-Fc omit electron density map (blue mesh) contoured at 6.0
 .
(C) Binding geometry of CsA on CypD. Green circles mark the CsA
atoms involved in the hydrophobic contact with CypD. The CypD
residues in green ellipsoids are involved in the hydrophobic
interactions with CsA. The red dotted lines represent hydrogen
bonding. This panel was prepared based on a scheme drawn with
LIGPLOT.[21] Abbreviations of CsA residues: Bmt,
(4R)-4[(E)-2-butenyl]-4,N-dimethyl-L-threonine; Aba: L- .
(C) Binding geometry of CsA on CypD. Green circles mark the CsA
atoms involved in the hydrophobic contact with CypD. The CypD
residues in green ellipsoids are involved in the hydrophobic
interactions with CsA. The red dotted lines represent hydrogen
bonding. This panel was prepared based on a scheme drawn with
LIGPLOT.[21] Abbreviations of CsA residues: Bmt,
(4R)-4[(E)-2-butenyl]-4,N-dimethyl-L-threonine; Aba: L-  -aminobutyric
acid, Sar: sarcosine, Mle, N-methyl leucine; Dal, D-alanine;
Mva, N-methyl valine. (D) Distribution of the conserved residues
among human cyclophilins represented on the surface of the
present CypD-CsA structure. Residues conserved in all five known
human cyclophilins (CypA, CypB, CypC, CypD, and CypE) are shown
in red. CypD residues conserved in 3 of 4, 2 of 4, and 1 of 4
other cyclophilins are shown in orange, yellow, and green,
respectively, and the unconserved CypD residues in the other
four cyclophilins are shown in blue. CsA is shown as a stick
model. -aminobutyric
acid, Sar: sarcosine, Mle, N-methyl leucine; Dal, D-alanine;
Mva, N-methyl valine. (D) Distribution of the conserved residues
among human cyclophilins represented on the surface of the
present CypD-CsA structure. Residues conserved in all five known
human cyclophilins (CypA, CypB, CypC, CypD, and CypE) are shown
in red. CypD residues conserved in 3 of 4, 2 of 4, and 1 of 4
other cyclophilins are shown in orange, yellow, and green,
respectively, and the unconserved CypD residues in the other
four cyclophilins are shown in blue. CsA is shown as a stick
model.
|
 |
|
|

|
| |
The above figure is
reprinted
by permission from John Wiley & Sons, Inc.:
Proteins
(2008,
70,
1635-1639)
copyright 2008.
|
|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
K.E.Muirhead,
E.Borger,
L.Aitken,
S.J.Conway,
and
F.J.Gunn-Moore
(2010).
The consequences of mitochondrial amyloid beta-peptide in Alzheimer's disease.
|
| |
Biochem J,
426,
255-270.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Malouitre,
H.Dube,
D.Selwood,
and
M.Crompton
(2010).
Mitochondrial targeting of cyclosporin A enables selective inhibition of cyclophilin-D and enhanced cytoprotection after glucose and oxygen deprivation.
|
| |
Biochem J,
425,
137-148.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
T.L.Davis,
J.R.Walker,
V.Campagna-Slater,
P.J.Finerty,
R.Paramanathan,
G.Bernstein,
F.MacKenzie,
W.Tempel,
H.Ouyang,
W.H.Lee,
E.Z.Eisenmesser,
and
S.Dhe-Paganon
(2010).
Structural and biochemical characterization of the human cyclophilin family of peptidyl-prolyl isomerases.
|
| |
PLoS Biol,
8,
e1000439.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.Czogalla
(2009).
Oral cyclosporine A--the current picture of its liposomal and other delivery systems.
|
| |
Cell Mol Biol Lett,
14,
139-152.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
|
 |
|

